Question Syntax:
Let’s have a look at the generic syntax:
from iterator in Data_Source
choose iterator;
Right here:
- The Data_Source will be the listing that holds the info.
- The iterator is used to fetch the weather from the Data_Source.
Knowledge Supply
On this whole information, we’ll use the next listing of data as a knowledge supply and all of the queries are utilized on this information supply solely. Just remember to run this code in your setting and modify the question statements with the next examples one after the other which we’re going to focus on:
utilizing System.Collections.Generic;
utilizing System.Linq;
utilizing System.Collections;
public class Calculations
{
public static void Fundamental()
{
// Listing creation
Listing country_prices = new Listing(){
// Add 5 data into Listing
new Costs() { merchandise = “Fruits”,location = “USA”, amount = 100, value = 345.78},
new Costs() { merchandise = “Nuts”,location = “India”, amount = 200, value = 3645.78},
new Costs() { merchandise = “Others”,location = “UK”, amount = 500, value = 90.68},
new Costs() { merchandise = “oil”,location = “USA”, amount = 100, value = 345.78},
new Costs() { merchandise = “Chillies”,location = “USA”, amount = 10, value = 67.89},
};
foreach(var i in country_prices)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
}
}
public class Costs {
public string merchandise {get;set;}
public string location {get;set;}
public int amount {get;set;}
public double value {get;set;}
}
Information:

Rationalization:
1. Create the costs with the next attributes: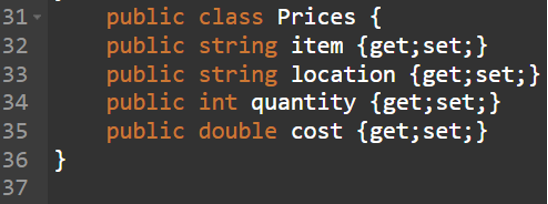
2. Create one other class which is “Calculations” with essential technique and create the country_prices listing with 5 data.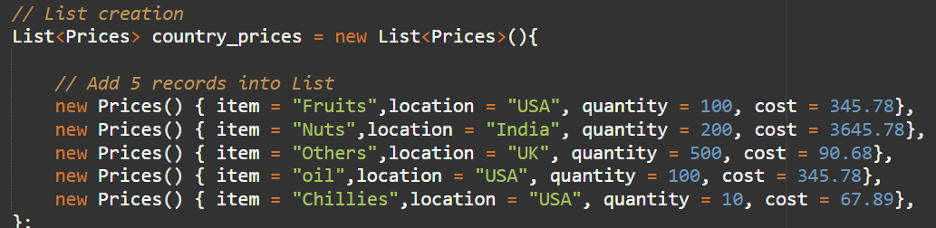
Choose
Mainly, “choose” is a projection operator which selects the attributes from the desired information supply. The question begins with “from”. Then, we specify the iterator that iterates over the info supply. Then, the “choose” operator is specified.
Syntax:
All Attributes: from iterator in Data_Source choose iterator;
Particular Attribute: from iterator in Data_Source choose iterator.attribute;
Instance 1:
Let’s write a question to pick all of the data from the listing.
utilizing System.Collections.Generic;
utilizing System.Linq;
utilizing System.Collections;
public class Calculations
{
public static void Fundamental()
{
// Listing creation
Listing country_prices = new Listing(){
// Add 5 data into Listing
new Costs() { merchandise = “Fruits”,location = “USA”, amount = 100, value = 345.78},
new Costs() { merchandise = “Nuts”,location = “India”, amount = 200, value = 3645.78},
new Costs() { merchandise = “Others”,location = “UK”, amount = 500, value = 90.68},
new Costs() { merchandise = “oil”,location = “USA”, amount = 100, value = 345.78},
new Costs() { merchandise = “Chillies”,location = “USA”, amount = 10, value = 67.89},
};
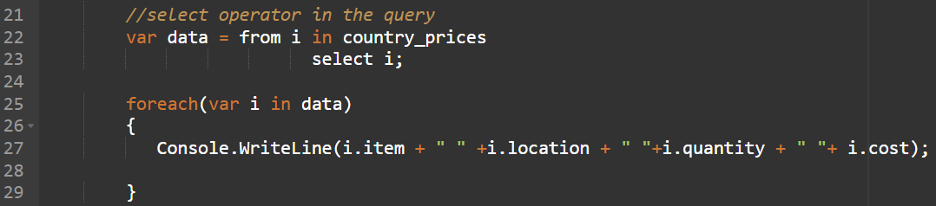
//choose operator within the question
var information = from i in country_prices
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
}
}
public class Costs {
public string merchandise {get;set;}
public string location {get;set;}
public int amount {get;set;}
public double value {get;set;}
}
Output:
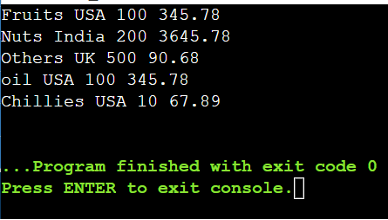
Right here, we didn’t specify any attribute within the “choose” question. We fetched all of the attributes from the question (information) contained in the “foreach” loop utilizing the iterator.
Instance 2:
Now, get the gadgets by specifying the merchandise attribute inside the “choose” operator. The question is “from i in country_prices choose i.merchandise”.
var information = from i in country_prices
choose i.merchandise;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Output:
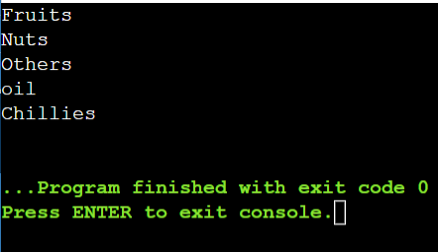
Line # 21 – Line # 29:
2. The place
If you wish to filter the info based mostly on some situations/s, you should use the “the place” operator within the question together with the “choose” clause. However the “the place” operator is used first after which the choose operator is specified.
Syntax:
Let’s see how one can use the “the place” operator contained in the LINQ question.
from iterator in Data_Source
the place situation/s
choose iterator.attribute;
Instance 1: Single Situation
Let’s filter the data based mostly on the merchandise attribute. Use the equal to (==) operator within the “the place” operator as a situation and evaluate the iterator with “Chillies”. So, the data which are associated to “Chillies” are chosen.
The question is “from i in country_prices
the place i.merchandise == “Chillies”
choose i”
var information = from i in country_prices
the place i.merchandise == “Chillies”
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
Output:
There is just one document with the “Chillies” merchandise.
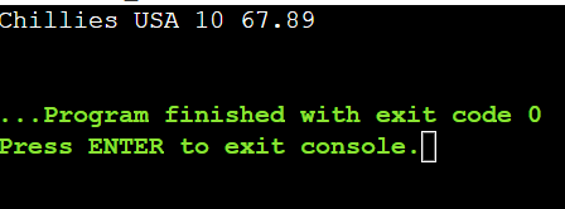
Line # 21 – Line # 30:
Instance 2: A number of Situations
Let’s filter the data based mostly on the situation and amount attributes. The amount must be higher than 50 and fewer than 300. The situation must be “USA”.
The question is “from i in country_prices
the place i.amount > 50
the place i.amount < 300
the place i.location == “USA”
choose i”
var information = from i in country_prices
the place i.amount > 50
the place i.amount < 300
the place i.location == “USA”
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
Output:
There are two data that matched the earlier situations.
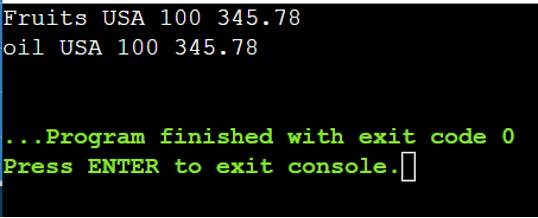
Line # 21 – Line # 32:
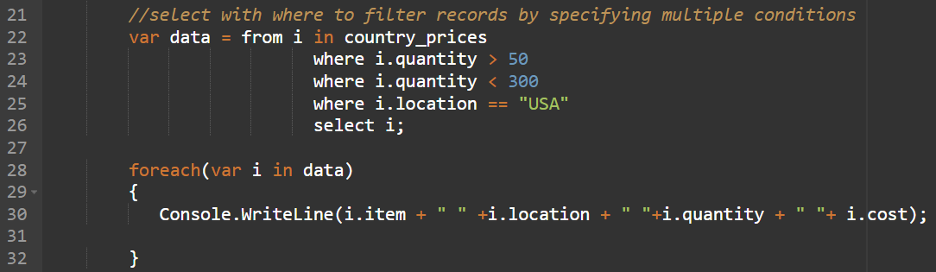
Instance 3: And (&&) Operator
We will specify the “and (&&)” operator to specify a number of situations at a time. If all of the situations are true, the data that fulfill all of the situations are returned by the question.
On this instance, we choose the data if the amount is larger than 20 and the fee is 67.89.
The question is “from i in country_prices
the place i.amount < 20 && i.value == 67.89
choose i”
the place i.amount < 20 && i.value == 67.89
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
Output:
There is just one document with the amount that’s lower than 20 and a price of 67.89
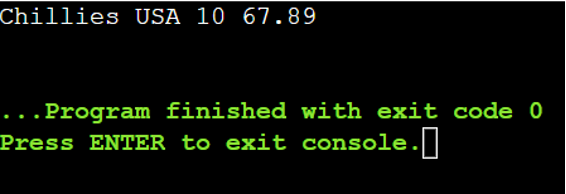
Line # 21 – Line # 29:
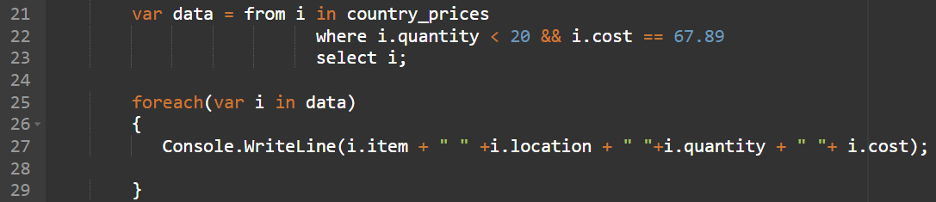
Instance 4: Or (||) Operator
The “or (||)” operator can be used to specify a number of situations at a time. If not less than one situation is true, the data that fulfill that situation are returned.
On this instance, we choose the data if the amount is larger than 300 or the situation is “Tokyo”.
The question is “from i in country_prices
the place i.amount > 300 || i.location == “Tokyo”
choose i”
the place i.amount > 300 || i.location == “Tokyo”
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
Output:
There is just one document with a amount that’s higher than 300 (the primary situation is matched).
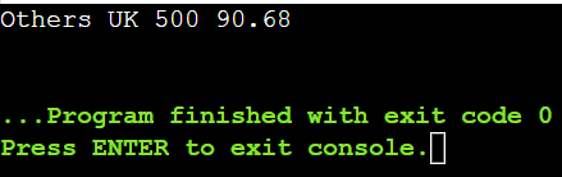
Line # 21 – Line # 29:
3. Order By
If you wish to prepare the data which are returned by the LINQ question in ascending or descending order based mostly on values in any of the attributes, you should use the “order by” operator within the question. You could specify this operator earlier than the “choose” operator.
Syntax:
Let’s see how one can use the “order by” operator contained in the LINQ question.
Ascending Order:
from iterator in Data_Source
order by iterator.attribute ascending
choose iterator;
Descending Order:
from iterator in Data_Source
order by iterator.attribute descending
choose iterator;
Instance 1: Ascending Order
Choose all of the attributes from the info supply (listing) and return them in ascending order based mostly on the values within the amount attribute.
The question is “from i in country_prices
orderby i.amount ascending
choose i”
orderby i.amount ascending
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
Output:
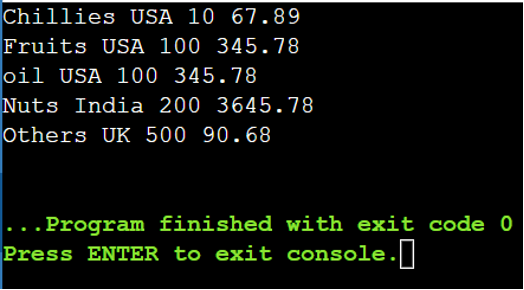
Line # 21 – Line # 29:
Instance 2: Descending Order
Choose all of the attributes from the info supply (listing) and return them in descending order based mostly on the values in the fee attribute.
The question is “from i in country_prices
orderby i.value descending
choose i”
orderby i.value descending
choose i;
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
Output:
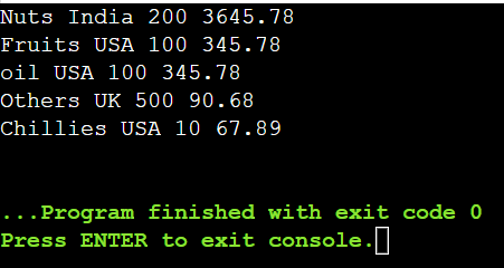
Line # 21 – Line # 29:
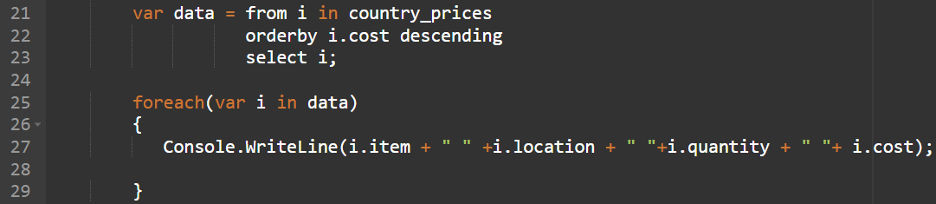
4. Restrict
Restrict in SQL limits the data which are returned by the question. It returns the highest data which are returned by the question. In LINQ, we will obtain this by using the Skip() with the Take() operator. Take() will get the desired variety of data. Skip() is used to specify the beginning document quantity. On this approach, we will obtain the “restrict” performance in LINQ.
Syntax:
(from iterator in Data_Source
choose iterator).Skip(n).Take(n);
- Skip() is used to skip the data and return the remaining data. It takes an integer which specifies the variety of components to be skipped. In our case, it’s 0.
- Take() is used to take “n” variety of data from the primary document.
Instance:
Choose the primary three data out of 5 data which are returned by the question.
The question is “(from i in country_prices
choose i).Skip(0).Take(3)”
choose i).Skip(0).Take(3);
foreach(var i in information)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.merchandise + ” “ +i.location + ” “+i.amount + ” “+ i.value);
}
}
Output:
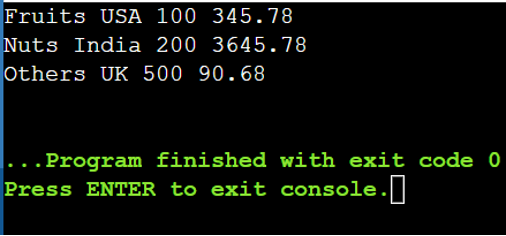
Line # 21 – Line # 28:
Conclusion
We realized how one can write the queries in C# LINQ which is much like SQL. As a part of this tutorial, we mentioned how one can use the “choose” operator to pick the data from the info supply. To filter the data which are returned by the question, we used the “the place” operator by specifying the situations. Then, we realized how one can kind the data which are returned by the question with the “order by” operator. Lastly, to restrict the data, we utilized the Skip() and Take() operators.