The cp command is likely one of the important Linux instructions you most likely can be utilizing regularly.
Because the identify signifies, cp stands for copy and it’s used for copying information and directories.
It is one of many less complicated instructions with just a few choices however that does not imply you can’t know extra about it.
Earlier than you see some sensible examples of the cp command, I counsel getting acquainted with the idea of absolute and relative path since you’ll want to make use of them whereas copying information from one place to a different.
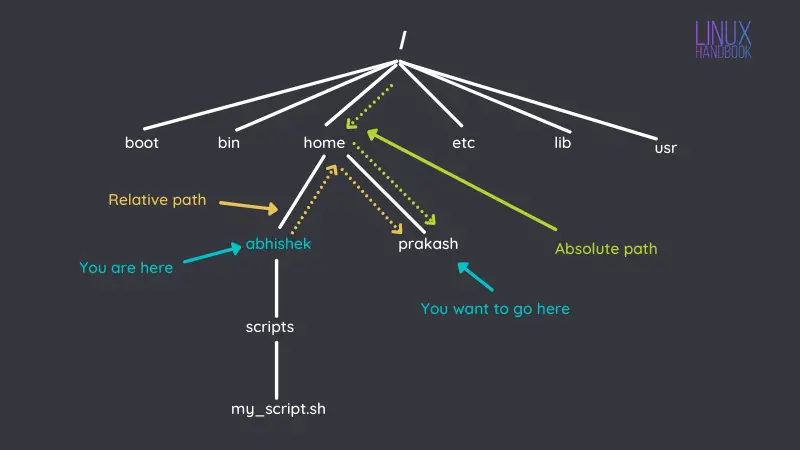
Absolute vs Relative Path in Linux: What’s the Distinction?
On this important Linux studying chapter, know concerning the relative and absolute paths in Linux. What’s the distinction between them and which one must you use.
Copy a file
The only and commonest use of the cp command is for copying information. For that, you simply should specify the supply file and the vacation spot the place you need to ‘paste’ the file.
cp source_file destination_directoryRename the file whereas copying it
You can even rename the file whereas copying it to a different location. That is like these ‘save as’ choices you see in textual content editors.
For this, you have to point out the brand new file identify together with the trail.
cp source_file destination_directory/new_filenameCopy a number of information
You can even copy a number of information to a different location.
cp file1 file2 file3 destination_directoryYou can not rename information on this case.
In fact, you should use wildcard growth and replica information of sure kind to a different location:
cp *.txt destination_directoryKeep away from overwriting whereas copying information
If you’re copying file1.txt to a listing the place there already exists a file named file1.txt, it is going to be overwritten with the file you’re copying.
You might not all the time need that. For this reason the cp command supplies a number of choices to take care of overwriting.
The firstmost is the interactive mode with possibility -i. Within the interactive mode, it would ask you to substantiate or deny the overwriting of the vacation spot file.
cp -i source_file destination_directory
cp: overwrite 'destination_directory/source_file'?Press Y to overwrite and N to skip copying the file.
The choice -n negates overwriting utterly. Vacation spot information will not be overwritten with this selection.
cp -n source_file destination_directory
There may be additionally possibility -b for robotically making a backup if the vacation spot file goes to be overwritten. B stands for backup, I presume.
cp -b source_file destination_directory
And lastly, there’s the ‘replace’ possibility -u which is able to overwrite the vacation spot file whether it is older than the supply file or if it vacation spot file doesn’t exist.
cp -u source_file destination_directoryCopy directories (folders)
The cp command can also be used for copy directories within the Linux command line.
It’s essential use the recursive possibility -r for copying directories.
cp -r source_dir destination_dirYou can even copy a number of directories to a different location:
cp -r dir1 dir2 dir3 target_directoryProtect attributes whereas copying
Whenever you copy a file to a different location, its timestamp, file permission and even possession will get modified.
That is the traditional habits. However in some circumstances, it’s possible you’ll need to protect the unique attribute even if you find yourself copying the file.
To protect the attributes, use the choice -p:
cp -p source_file destination_directory🏋️ Train time
Wish to observe the cp command slightly? Listed below are some easy workout routines for you.
- Open a terminal and create a listing named
practice_cp - Now, copy the /and so on/companies file on this newly created listing.
- Make some minor adjustments to the copied companies file in observe listing.
- Now, copy /and so on/companies file once more however in replace mode. Does it change something? Observe.
- Look into /var/log listing and replica the log information that begin with mail into your observe listing
- Now, return to your private home listing and create a brand new listing named new_dir (properly, I could not consider any higher)
- Copy the practice_cp listing to new_dir
That ought to be ok train for you. Get pleasure from studying Linux instructions with It is FOSS.
