A abstract() is a built-in MATLAB perform used for displaying the abstract of every variable within the desk or timetable. This perform additionally prints the abstract of every class mendacity within the categorical array. The abstract of the desk or timetable contains the min, max, and median values of every variable of the required desk or timetable. When utilized to a categorical array, the abstract() perform shows the incidence rely for every class inside the array. This perform is helpful for rapidly acquiring an outline of the information and understanding its traits.
On this article, we’ll discover ways to print the abstract of the desk, timetable, or categorical array in MATLAB.
Article Association
This information will encompass:
1: The way to Use abstract() Operate in MATLAB?
The abstract() is a built-in MATLAB perform that enables us to print the abstract of the given desk, timetable, or, categorical array. This perform takes the desk, timetable, or categorical array as enter and returns their abstract as output. This perform follows a easy syntax that’s given under:
abstract(T)
s = abstract(T)
abstract(A)
abstract(A,dim)
Right here:
abstract(T) yields to print the abstract of a timetable or a desk.
-
- If T represents a desk, then abstract(T) prints the outline of the desk variables utilizing T.Properties.Description.
- If T represents a timetable, then abstract(T) prints the outline of the row occasions and the timetable variables utilizing T.Properties.Description.
s = abstract(T) returns a construction s with a abstract of the offered desk or timetable. Every area in s is a construction by itself that represents a abstract of the information within the related variable in T. The construction moreover has a area that lists the row timings of T if T is a timetable.
abstract(A) shows the specific array abstract.
-
- The abstract(A) outputs the class names and the whole variety of gadgets in every class (the class counts) if A represents a vector. Moreover, it exhibits what number of parts are undefined.
- If A is a matrix, the abstract() perform considers its columns as vectors and outputs class counts for every of A’s columns.
- If A represents a multidirectional array, the abstract() perform solely applies to the primary dimension whose measurement is just not equal to 1.
abstract(A,dim) shows the general variety of parts in every class (the class counts) alongside the dim dimension.
2: The way to Print the Abstract of the Desk in MATLAB?
We use the abstract() perform that prints the abstract of every variable of the given desk in MATLAB. For instance:
Orange = [9;3;12;5;20;24];
Banana = [27;8;4;19;20;22];
Watermelon = [19;36;74;27;19; 7];
Strawberry = [6; 36; 18; 30; 29; 32];
Outlets = [ ‘A’; ‘B’; ‘C’; ‘D’; ‘E’; ‘F’];
T = desk(Outlets, Orange, Banana, Watermelon, Strawberry);
abstract(T)
Within the above instance, first, we create a desk having information of the six fruit outlets. Then we use the abstract() perform that prints the abstract of the variables of the required desk. This abstract contains every variable’s minimal, median, and most values.


2.1: The way to Print the Desk Abstract as a Construction in MATLAB?
We use the abstract() perform by specifying the output argument to print the abstract of the given desk as a construction in MATLAB. For instance:
Orange = [9;3;12;5;20;24];
Banana = [27;8;4;19;20;22];
Watermelon = [19;36;74;27;19; 7];
Strawbery = [6; 36; 18; 30; 29; 32];
Outlets = [ ‘A’; ‘B’; ‘C’; ‘D’; ‘E’; ‘F’];
T = desk(Outlets, Orange, Banana, Watermelon, Strawberry);
s = abstract(T)
The given instance is the beforehand mentioned instance however now it implements the abstract perform by specifying the output arguments and prints the abstract of the given desk as a construction.

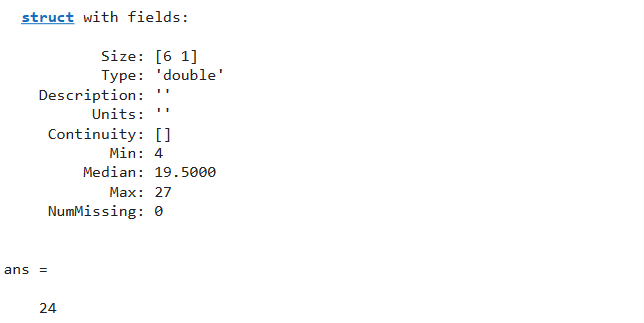
Now we are able to use the output argument s to show any variable info within the specified desk T utilizing the dot operator. For instance:
Orange = [9;3;12;5;20;24];
Banana = [27;8;4;19;20;22];
Watermelon = [19;36;74;27;19;7];
Strawberry = [6; 36; 18; 30; 29; 32];
Outlets = [ ‘A’; ‘B’; ‘C’; ‘D’; ‘E’; ‘F’];
T = desk(Outlets, Orange, Banana, Watermelon, Strawberry);
s= abstract(T);
s.Banana
s.Orange.Max
Within the given instance, we use the construction s to show the abstract of the variable Banana and to print the utmost worth of the variable Orange specified within the given desk T.
3: The way to Print the Abstract of the Timetable in MATLAB?
The abstract() perform will also be used to print the abstract of the given timetable in MATLAB. For instance:
Time = [hours(8:15)]‘;
time_table = timetable(Time,{‘CF‘;’NS‘;’NSM‘;’ISSM‘;’MA‘;’DF‘;’CSICS‘;’MSS‘},…
‘VariableNames‘,{‘Subjects_Name‘});
abstract(time_table)
Within the above instance, first, we create a timetable for a category. Then we use the abstract() perform that prints the abstract of the row occasions and the variables of the required timetable. This abstract contains every variable’s minimal, median, and most values.

3.1: The way to Print the Timetable Abstract as a Construction in MATLAB?
We use the abstract() perform by specifying the output argument to print the abstract of the given timetable as a construction in MATLAB. For instance:
Time = [hours(8:15)]‘;
time_table = timetable(Time,{‘CF‘;’NS‘;’NSM‘;’ISSM‘;’MA‘;’DF‘;’CSICS‘;’MSS‘},…
‘VariableNames‘,{‘Subjects_Name‘});
s=abstract(time_table)
s.Time
Within the given instance, we use the construction s to show the abstract of the variable Time specified within the given timetable T.

4: The way to Print the Abstract of the Categorical Array in MATLAB?
We will additionally use the abstract() perform to print the abstract of the given categorical array in MATLAB. For instance:
A = categorical({‘A’; ‘B’; ‘C’; ‘D’; ‘C’; ‘B’});
abstract(A)
Within the above instance, first, we create a categorical having 4 classes A, B, C, and, D. Then we use the abstract() perform that prints what number of occurrences of every class there are.

4.1: The way to Print the Abstract of the Categorical Array Alongside Dimension in MATLAB?
The MATLAB abstract() perform can print the abstract of the given categorical array alongside the dimension. For instance:
A = categorical({‘A’; ‘B’; ‘C’; ‘D’; ‘C’; ‘B’});
abstract(A,2)
Within the above instance, first, we create a categorical array having 4 classes A, B, C, and, D. Then we use the abstract() perform alongside dimension 2 that prints the index of occurrences of every class within the matrix type.

Conclusion
The MATLAB abstract() perform shows the abstract of the given desk, timetable, or categorical array in line with their properties. This perform takes an argument that could possibly be a desk, timetable, or, categorical array and returns the abstract of the required argument. This tutorial defined other ways of utilizing the MATLAB abstract() perform with easy examples.