In Python, the packages throw an exception when an error or fault seems within the code throughout execution. An exception is mainly an object that represents an error in Python. Every time the exception seems in this system, we have to deal with it utilizing completely different strategies. There are a number of methods to deal with or catch-all exceptions in Python.
This write-up gives an in-depth information on catching all exceptions in Python utilizing quite a few examples.
The right way to Catch All Exceptions in Python?
To catch all exceptions, numerous strategies are utilized in Python. A few of the strategies are proven beneath:
Technique 1: Catch All Exceptions Utilizing “attempt” and “besides” Assertion
The “attempt” and “besides” statements are employed to fetch/catch-all Python exceptions. The “attempt” assertion is used to execute this system code and lift an exception, and the “besides” assertion handles the exception that’s raised by the “attempt” assertion. Let’s perceive it by way of the beneath code:
list1 = [43, 32, 43, 53]
attempt:
print(list1[1])
print(list1[6])
besides:
print(“Error Occurred Whereas Accessing Checklist Aspect”)
Within the above code:
- The “attempt” block executes the code and accesses the checklist aspect positioned at index “1” and “6” utilizing the sq. bracket notion.
- The “besides” assertion executes the code when the exception is raised by the “attempt” assertion whereas accessing the checklist aspect at index “6” (that doesn’t exist within the checklist).
Output
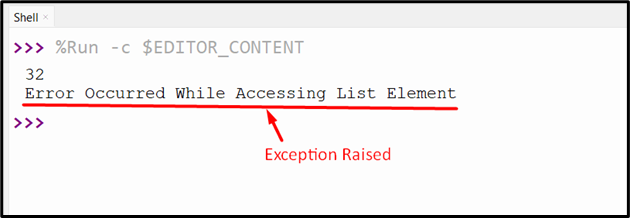
The exception has been caught efficiently.
Now, we are able to make the most of the “try-except” assertion to catch particular exceptions equivalent to ValueError, KeyError, and others. Right here is an instance code:
tuple1 = (45, 55, 65, 78)
attempt:
print(tuple1[0])
print(tuple1[4])
besides IndexError:
print(‘tuple index out of vary’)
On this code:
- The “besides” assertion catches the desired “IndexError” which is raised by accessing the out-of-range aspect worth “4” from the enter tuple.
- The “besides” assertion returns the exception message when the index error is raised.
Output
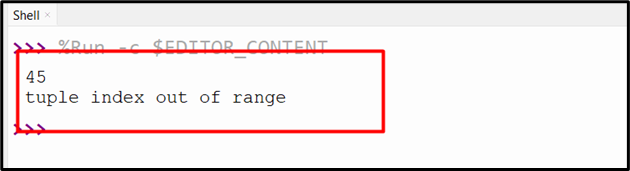
The desired exception has been caught efficiently.
Technique 2: Catch All Exceptions Utilizing “increase” Exception
The “increase” exception may also be utilized to catch all of the exceptions and show them to output. Right here is an instance code:
list1 = [1, 4, 5, 6]
list2 = [4, 5, 6, 7, 9]
if len(list1) == len(list2):
print(‘True’)
else:
increase Exception(‘Checklist Size is Not Equal’)
Within the above code:
- The “list1” and “list2” are initialized in this system.
- The “if” assertion is used to examine whether or not the given two lists are equal or not.
- If the checklist is equal, the “print()” assertion exhibits the desired message.
- The “increase Exception” is used contained in the “else” block to return the exception.
Output
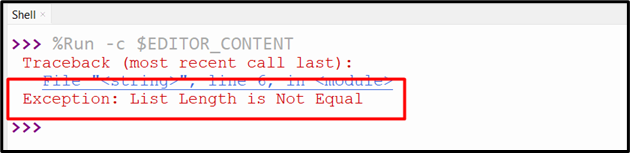
The exception has been caught efficiently.
Technique 3: Catch All Exceptions Utilizing “logger.exception”
The “logger.exception” technique of the “logging” module logs an error, together with the whole traceback data. This technique can be utilized together with the “try-except” assertion to catch all exceptions in Python. Right here is an instance code:
import logging
logger=logging.getLogger()
attempt:
num1 = 12
num2 = 0
print(num1/num2)
besides Exception as z:
logger.exception(“Exception Occurred: “ + str(z))
Within the above code:
- The “logging” module is imported.
- The “logger” object is created and used to write down the log’s message to the file or consoles and others.
- Within the “attempt” block, the “exception” is raised when the desired quantity is split by the “zero”.
- Whereas within the “besides” block, the “exception” is caught by the “logger.exception()” technique. This technique creates a log error message, together with traceback data.
Output

Conclusion
The “attempt” and “besides” assertion, the “increase” exception, and the “logger.exception” technique are utilized to fetch/catch all exceptions in Python. The “try-except” assertion is utilized to fetch/catch all of the exceptions and specified exceptions. The “increase Exception” and “logger.exception” technique can simply fetch or catch the exception in Python. This write-up delivered a complete tutorial on catching all exceptions in Python utilizing quite a few examples.