This information demonstrates the right way to set up and use SQLite in Fedora Linux.
Conditions:
To carry out the steps which are demonstrated on this information, you want the next elements:
SQLite on Fedora Linux
SQLite is an open-source C library that implements a light-weight, high-performance, self-contained, and dependable SQL database engine. It helps all the fashionable SQL options. Every database is a single file that’s steady, cross-platform, and backward appropriate.
For essentially the most half, varied apps use the SQLite library to handle the databases relatively than utilizing the opposite heavyweight choices like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and such.
Moreover the code library, there are additionally SQLite binaries which are accessible for all the most important platforms together with Fedora Linux. It’s a command-line instrument that we will use to create and handle the SQLite databases.
On the time of writing, SQLite 3 is the newest main launch.
Putting in SQLite on Fedora Linux
SQLite is offered from the official package deal repos of Fedora Linux. Moreover the official SQLite package deal, you can too get hold of the prebuilt SQLite binaries from the official SQLite obtain web page.
Putting in from the Official Repo
First, replace the package deal database of DNF:
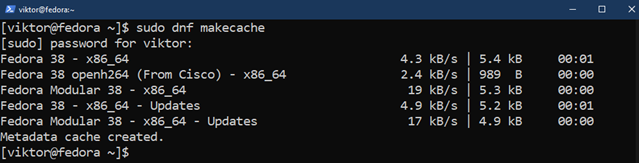
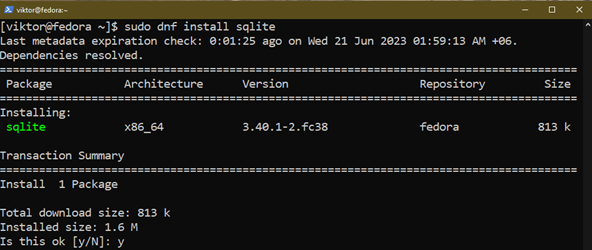
Now, set up SQLite utilizing the next command:
$ sudo dnf set up sqlite
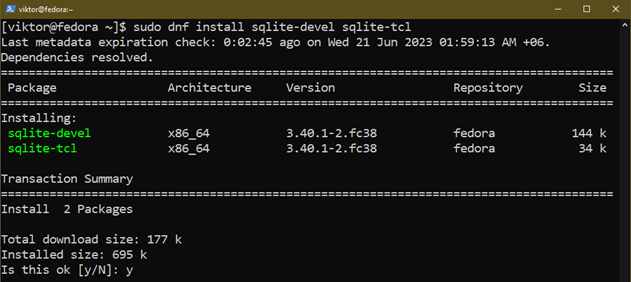
To make use of SQLite with varied programming languages, you even have to put in the next further packages:
$ sudo dnf set up sqlite-devel sqlite-tcl
Putting in from Binaries
We obtain and configure the SQLite prebuilt binaries from the official web site. Be aware that for higher system integration, we additionally must tinker with the PATH variable to incorporate the SQLite binaries.
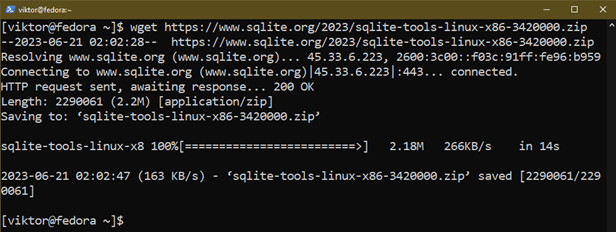
First, obtain the SQLite prebuilt binaries:
$ wget https://www.sqlite.org/2023/sqlite-tools-linux-x86-3420000.zip
Extract the archive to an acceptable location:
$ unzip sqlite-tools-linux-x86-3420000.zip -d /tmp/sqlite-bin
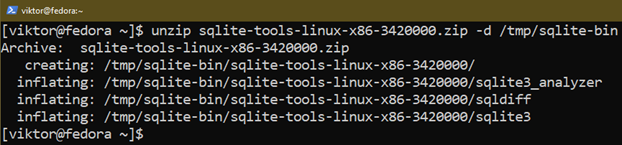
For demonstration functions, we extract the archive to /tmp/sqlite-bin. The listing is cleaned subsequent time the system restarts, so select a distinct location if you would like a persistent entry.
Subsequent, we add it to the PATH variable:
$ export PATH=/tmp/sqlite-bin:$PATH
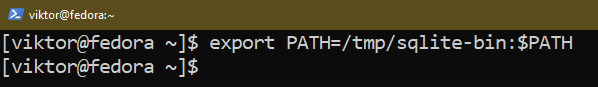
The command quickly updates the worth of the PATH setting variable. If you wish to make everlasting adjustments, try this information on including a listing to the $PATH in Linux.
We are able to confirm if the method is profitable:
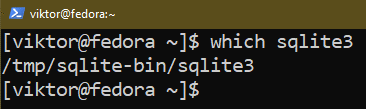
Putting in from the Supply
We are able to additionally obtain and compile SQLite from the supply code. It requires an acceptable C/C++ compiler and a few further packages. For basic customers, this methodology ought to be ignored.
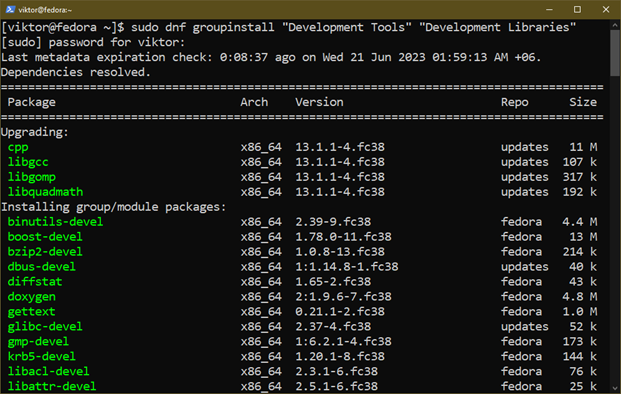
First, set up the required elements:
$ sudo dnf groupinstall “Growth Instruments” “Growth Libraries”
Now, obtain the SQLite supply code that incorporates a configure script:
$ wget https://www.sqlite.org/2023/sqlite-autoconf-3420000.tar.gz
Extract the archive:
$ tar -xvf sqlite-autoconf-3420000.tar.gz
Run the configure script from throughout the new listing:
$ ./configure –prefix=/usr
Subsequent, compile the supply code utilizing “make”:
As soon as the compilation is completed, we will set up it utilizing the next command:
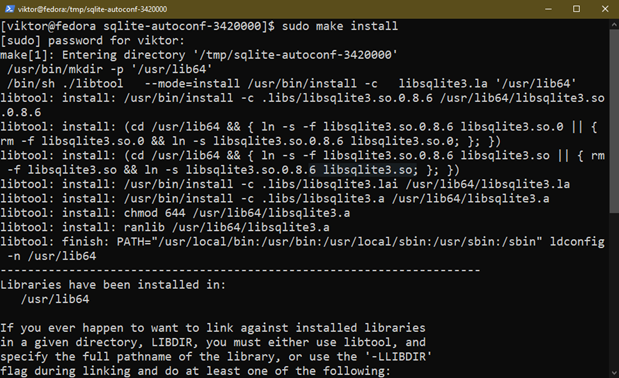
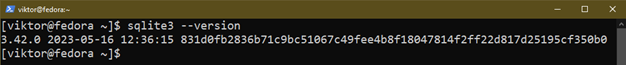
If the set up is profitable, SQLite ought to be accessible from the console:
Utilizing SQLite
In contrast to different database engines like MySQL or PostgreSQL, SQLite doesn’t require any further configuration. As soon as put in, it’s prepared for use. This part demonstrates some widespread usages of SQLite.
These procedures can even function a option to confirm the SQLite set up.
Making a New Database
Any SQLite database is a standalone DB file. Typically, the file identify serves because the identify of the database.
To create a brand new database, run the next command:
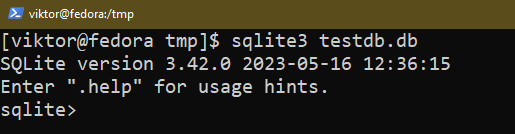
If you have already got a database file with the required identify, SQLite opens the database as an alternative. Then, SQLite launches an interactive shell the place you’ll be able to run the assorted instructions and queries to work together with the database.
Making a Desk
SQLite is a relational database engine that shops the info within the tables. Every column is given with a label and every row incorporates the info factors.
The next SQL question creates a desk named “take a look at”:
$ CREATE TABLE take a look at (id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, identify TEXT);
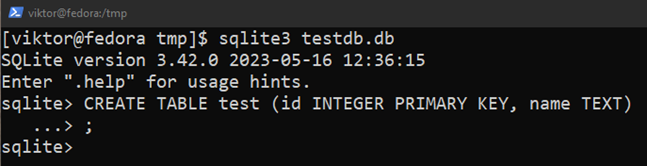
Right here:
-
- The desk take a look at incorporates two columns: “id” and “identify”.
- The “id” column shops the integer values. It’s additionally the first key.
- The “identify” column shops the strings.
The first secret’s necessary to narrate the info to different tables/databases. There could be just one major key per desk.
Inserting the Information into the Desk
To insert worth within the desk, use the next question:
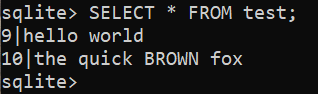
$ INSERT INTO take a look at (id, identify) VALUES (9, ‘whats up world’);
$ INSERT INTO take a look at (id, identify) VALUES (10, ‘the short BROWN fox’);

To view the outcome, run the next question:
Updating the Current Row
To replace the content material of an current row, use the next question:
$ UPDATE <table_name> SET <column> = <new_value> WHERE <search_condition>;
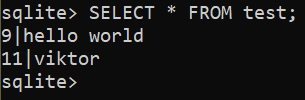
For instance, the next question updates the content material of row 2 of the “take a look at” desk:
$ UPDATE take a look at SET id = 11, identify = ‘viktor’ WHERE id = 10;
![]()
Verify the up to date outcome:
Deleting the Current Row
Just like updating the row values, we will delete an current row from a desk utilizing the DELETE assertion:
$ DELETE FROM <table_name> WHERE <search_condition>;
For instance, the next question removes “1” from the “take a look at” desk:
$ DELETE FROM take a look at WHERE id = 9;
![]()
Itemizing the Tables
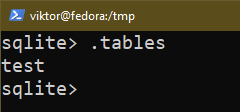
The next question prints all of the tables within the present database:
Desk Construction
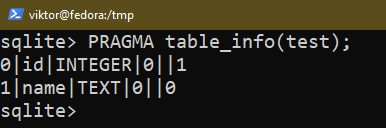
There are a few methods to verify the construction of an current desk. Use any of the next queries:
$ PRAGMA table_info(<table_name>);
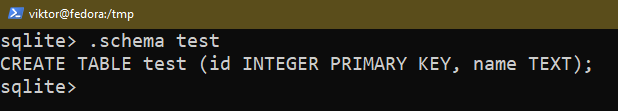
Altering the Columns in Desk
Utilizing the ALTER TABLE command, we will change the columns of a desk in SQLite. It may be used so as to add, take away, and rename the columns.
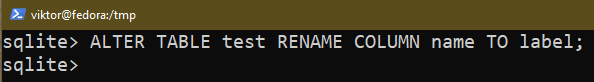
The next question renames the column identify to “label”:
$ ALTER TABLE <table_name> RENAME COLUMN identify TO label;
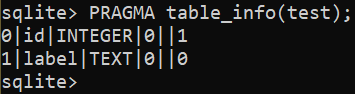
So as to add a brand new column to a desk, use the next question:
$ ALTER TABLE <table_name> ADD COLUMN test_column INTEGER;

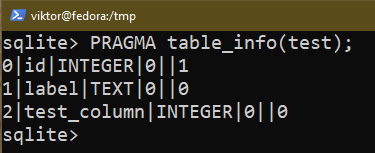
To take away an current column, use the next question:
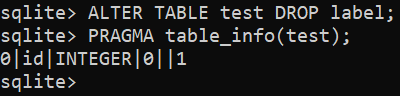
$ ALTER TABLE <table_name> DROP COLUMN <column_name>;
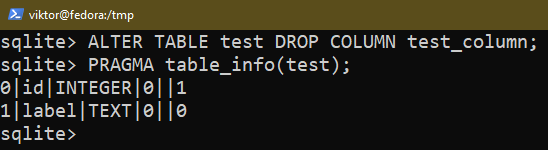
$ ALTER TABLE <table_name> DROP <column_name>;
Information Question
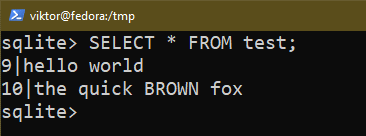
Utilizing the SELECT assertion, we will question the info from a database.
The next command lists all of the entries from a desk:
$ SELECT * FROM <table_name>;
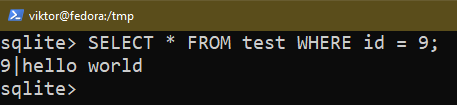
If you wish to apply sure circumstances, use the WHERE command:
$ SELECT * FROM <table_name> WHERE <situation>;
Exiting the SQLite Shell
To exit the SQLite shell, use the next command:
Conclusion
On this information, we demonstrated the assorted methods of putting in SQLite on Fedora Linux. We additionally demonstrated some widespread utilization of SQLite: making a database, managing the tables and rows, querying the info, and many others.
Enthusiastic about studying extra about SQLite? Take a look at the SQLite sub-category that incorporates lots of of guides on varied features of SQLite.
Glad computing!