A “Histogram” is a sort of plot that reveals the frequency or rely of values that fall into discrete bins or intervals. It’s helpful for summarizing the form and unfold of a variable, in addition to figuring out outliers, gaps, or modes. The “seaborn.histplot()” perform of the “seaborn” library is used to create histograms for each univariate and bivariate information.
This write-up will clarify an entire information on Python “seaborn.histplot()” technique utilizing the beneath content material:
What’s the “seaborn.histplot()” Methodology in Python?
In Python, the “seaborn.histplot()” technique is utilized to visualise the distribution of a number of variables in a dataset. It may be utilized to create both univariate or bivariate histograms. As a basic visualization software, a histogram shows a variable’s distribution by counting the num/variety of values falling inside discrete “bins”.
Syntax
seaborn.histplot(information, x, y, hue, stat, bins, binwidth, discrete, kde, log_scale)
Parameters
Within the above syntax:
- The “information” parameter specifies the given/enter information as a NumPy array or dataframe.
- The “x” and “y” parameters decide the information key on the “x” and “y” axes.
- The “hue” parameter determines the colour of plot components by mapping a semantic information key.
- The “stat” parameter signifies the rely, density, frequency, or chance.
Word: The opposite elective parameters are used to carry out particular operations in Python. Examine this documentation for an in depth understanding of the seaborn “histplot()” technique syntax and its parameters.
Return Worth
The “seaborn.histplot()” technique retrieves matplotlib axes with the plot drawn on them.
Instance 1: Plotting Histogram Utilizing the “seaborn.histplot()” Methodology
Within the following code, the “seaborn.histplot()” technique plots the histogram:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
information=seaborn.load_dataset(“suggestions”)
seaborn.histplot(information=information, x=“total_bill”, hue=“time”)
plt.present()
Within the above code:
- The “seaborn” and “matplotlib” modules are imported.
- The “seaborn.load_dataset()” technique is used to load the seaborn predefined information set named “suggestions”.
- The “seaborn.histplot()” technique takes the dataset, together with the “x” parameter and “hue” parameter values, to plot the histogram.
Output
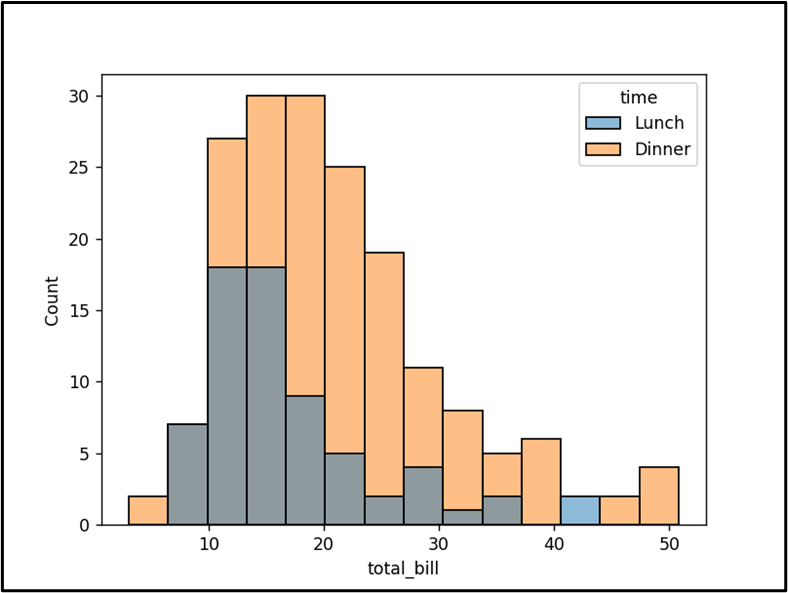
This snippet concludes that the histogram has been plotted efficiently.
Instance 2: Plotting Histogram by Including a (KDE) Utilizing the “seaborn.histplot()” Methodology
The beneath code plots the histogram by including the kernel density estimate “(KDE)” utilizing the “seaborn.histplot()” technique:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
information=seaborn.load_dataset(“suggestions”)
seaborn.histplot(information=information, x=“total_bill”, hue=“time”, kde=True)
plt.present()
Within the above code strains, the “seaborn.histplot()” technique takes the “dataset”, “x”, and “hue” parameters together with the “kde” parameter, respectively, so as to add the kernel density estimate on the highest of the histogram.
Output
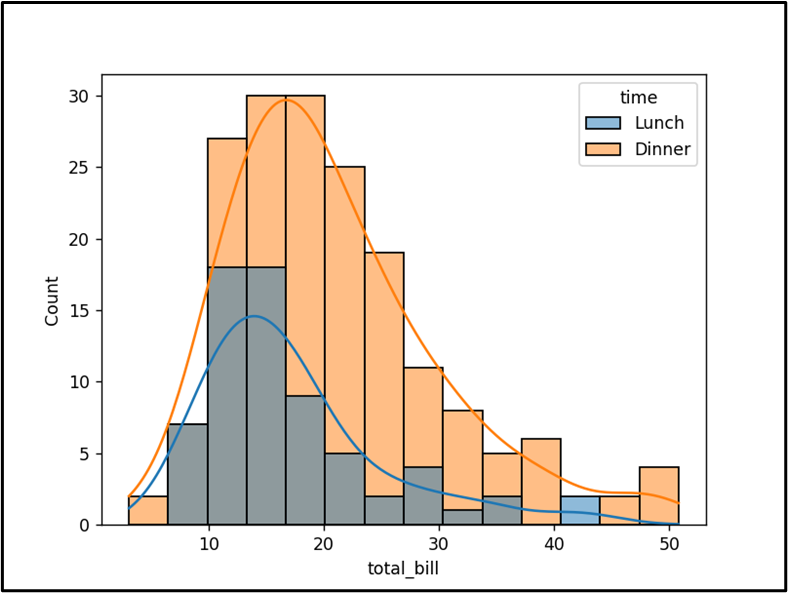
The “KDE” on the highest of the histogram has been created appropriately.
Instance 3: Altering the Sort of Graph to be Plotted Utilizing the “seaborn.histplot()” Methodology
The “factor” parameter is used to vary the kind of the graph, resembling bar, poly, and step to be plotted.
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
information=seaborn.load_dataset(“suggestions”)
seaborn.histplot(information=information, x=“total_bill”, hue=“time”, kde=True,factor=“poly”)
plt.present()
On this code, the “seaborn.histplot()” technique takes all the required parameters together with the “factor” parameter that specifies the kind of graph that must be plotted.
Output
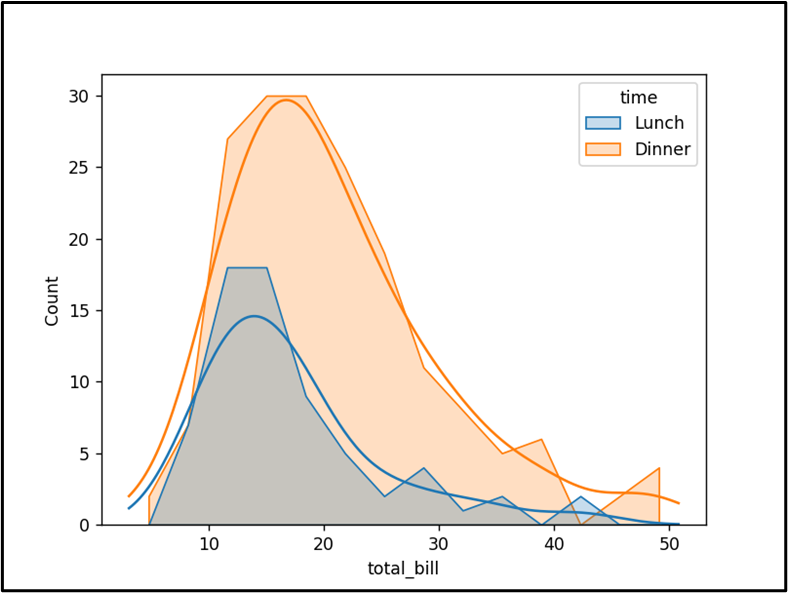
The histogram with the “poly” kind graph has been displayed efficiently.
Instance 4: Plotting Histogram With Controlling “bins” Numbers Utilizing the “seaborn.histplot()” Methodology
The histogram will also be plotted with a managed variety of “bins” utilizing the mentioned technique with the “bins” parameter:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
information=seaborn.load_dataset(“suggestions”)
seaborn.histplot(information=information, x=“total_bill”, hue=“time”, bins=50)
plt.present()
Within the above code, the “seaborn.histplot()” technique takes the “information”, “x”, “y”, “hue”, and “bins” parameters as its arguments, respectively, to plot the histogram based mostly on the worth of the bin. The “bins” right here divide the vary values into intervals.
Output
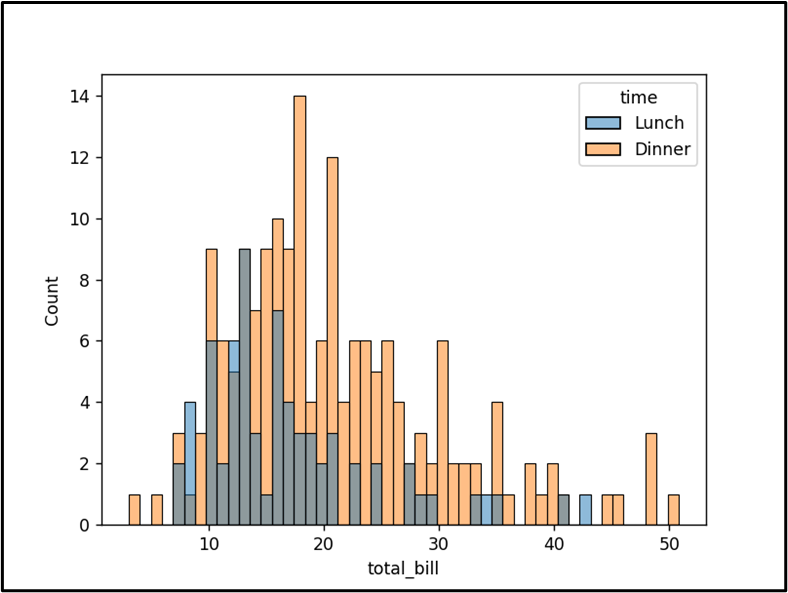
The histogram based mostly on the worth of the bin has been plotted efficiently.
Conclusion
The “seaborn.histplot()” technique is used to plot the univariate or bivariate histogram based mostly on the required “bins” worth. This technique takes a number of parameters resembling “bins”, “KDE” and “factor”, and so forth. to switch the bins worth interval, the kernel density estimation, and the kind of the graph to plot the histogram. This Python write-up introduced an in depth information on the “seaborn.histplot()” technique utilizing the examples.