The “Heatmap” is a chart kind that makes use of varied shades of colours for instance information values. Python helps completely different libraries, equivalent to Matplotlib or Seaborn, to cope with information visualization and create varied varieties of plots. The “seaborn.heatmap()” of the “Seaborn” module is used to create a heatmap and plots the information as a coloured matrix.
This tutorial presents an in-depth information on the “seaborn.heatmap()” perform utilizing the below-provided content material:
What’s the “seaborn.heatmap()” in Python?
The “seaborn.heatmap()” perform is utilized in Python to plot/create rectangular information within the color-coded matrix type. The “seaborn.heatmap()” perform is proven under:
seaborn.heatmap(information, *, vmin=None, vmax=None, cmap=None, middle=None,cbar=True, cbar_kws=None, cbar_ax=None, sq.=False, sturdy=False, annot=None, fmt=‘.2g’, annot_kws=None, linewidths=0,yticklabels=‘auto’, masks=None, ax=None, linecolor=‘white’, xticklabels=‘auto’, **kwargs)
Within the above syntax:
- The “information” parameter is obligatory and should be a 2-dimensional array or DataFrame.
- The “vmin” and “vmax” parameters specify the minimal and most information values. If this isn’t specified, the “Seaborn” module will robotically decide these values.
- The “cmap” parameter specifies the “colormap” to make use of. If not specified, then the default colormap is used.
- The “middle” parameter specifies the middle worth of the colormap. If not specified, the imply of the information is used.
- The opposite parameters are non-compulsory and likewise carry out sure operations.
Let’s perceive this methodology through the under examples:
Instance 1: Implementing a Sequential Colormap on a Seaborn Heatmap
Let’s overview the given under code instance:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot
import numpy
numpy.random.seed(0)
information = numpy.random.rand(8, 8)
colormap = seaborn.color_palette(“Blues”)
seaborn.heatmap(information, cmap=colormap)
matplotlib.pyplot.present()
Within the above code:
- The “seaborn”, “matplotlib” and “numpy” module is imported.
- The “numpy.random.seed()” is used to set the random seed to “0”. It ensures that the identical/similar random numbers are created every time this system code is executed.
- The “numpy.random.rand()” perform is used to create a 2D array of random numbers with dimensions “8” x “8”.
- The “seaborn.color_palette()” is used to create the colormap utilizing the “Blues” palette from the “Seaborn”.
- Lastly, the “seaborn.heatmap()” takes the information and “cmap” as arguments to create the heatmap.
Output
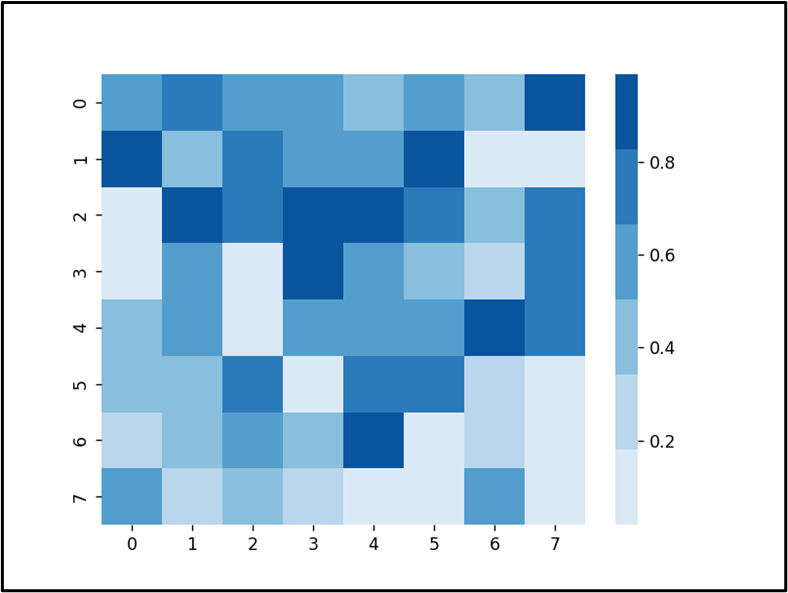
The heatmap of the random quantity with colours based mostly on the “Blues” colormap has been created.
Instance 2: Implementing a Sequential Colormap on a Seaborn HeatMap Utilizing cmap Parameter
We will use the “cmap” argument to move the inbuilt Seaborn colormap on to the “seaborn.heatmap()” perform. For example, take a look at the next code:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot
import numpy
numpy.random.seed(0)
information = numpy.random.rand(8, 8)
seaborn.heatmap(information, cmap=“Blues”)
matplotlib.pyplot.present()
Within the above code:
- The “cmap= Blues” is handed on to the “seaborn.heatmap()” perform to use a sequential colormap on a heatmap.
Output
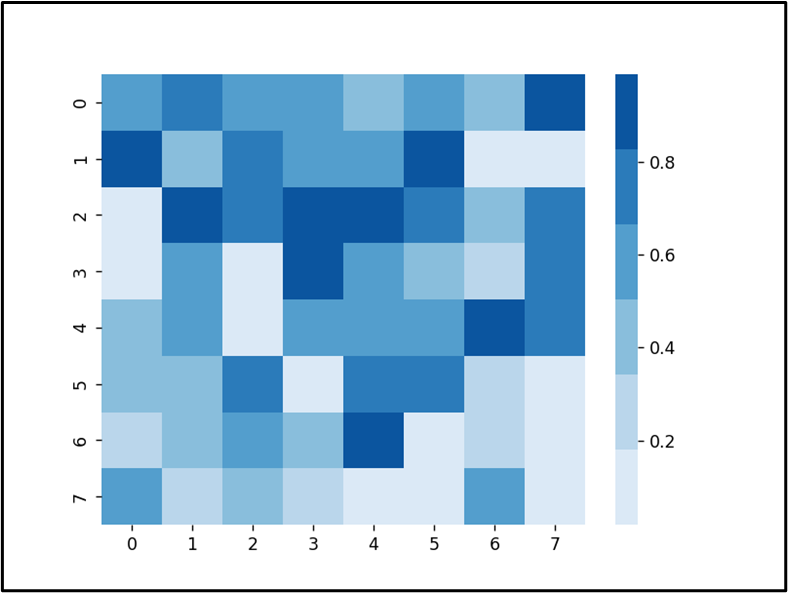
A random quantity heatmap in Blues “colormap” has been created efficiently.
Instance 3: Setting Colorbar Max and Min for Seaborn heatmap
The under code is used to set the max and min worth of the colour bar on a Seaborn heatmap:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot
import numpy
numpy.random.seed(0)
information = numpy.random.rand(8, 8)
seaborn.heatmap(information, cmap=“Blues”, vmin=0.2, vmax=0.5)
matplotlib.pyplot.present()
Right here on this code:
- The “vmin” and the “vmax” parameter is used to set the utmost and minimal worth for the colour bar on a Seaborn heatmap.
- These parameter values are handed to the “seaborn.heatmap()” perform to create a heatmap with colormap.
Output
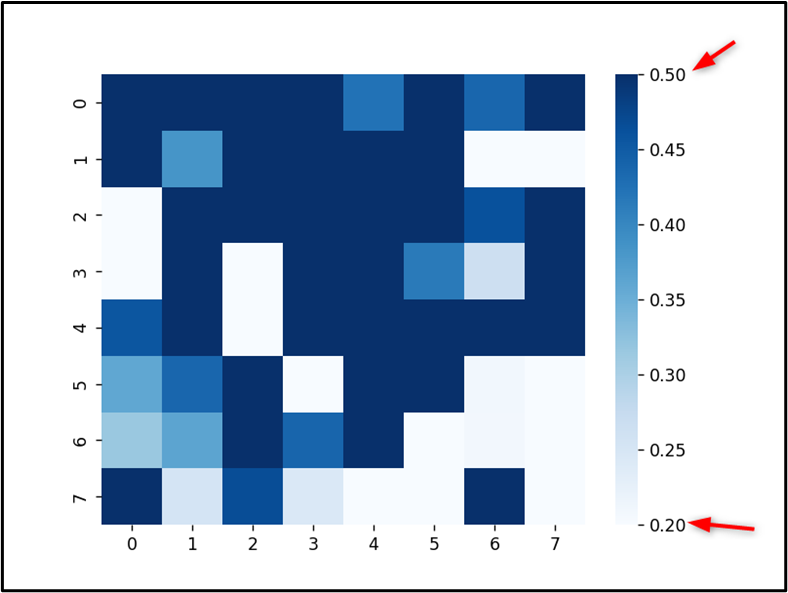
The minimal and most worth of the colorbar of the heatmap has been personalized efficiently.
Instance 4: Implementing a Diverging Colormap on HeatMap
We will implement the diverging colormap on a Seaborn heatmap to symbolize excessive to low and each excessive or low values of curiosity. Let’s perceive this by the under code:
import seaborn
import matplotlib.pyplot
import numpy
numpy.random.seed(0)
information = numpy.random.rand(8, 8)
seaborn.heatmap(information, cmap=“coolwarm”)
matplotlib.pyplot.present()
Within the above code:
- The “seaborn.heatmap()” perform takes the “cmap” as an argument and implements a diverging colormap on a seaborn heatmap.
- The “cmap” is assigned with the default shade scheme “coolwarm”.
Output
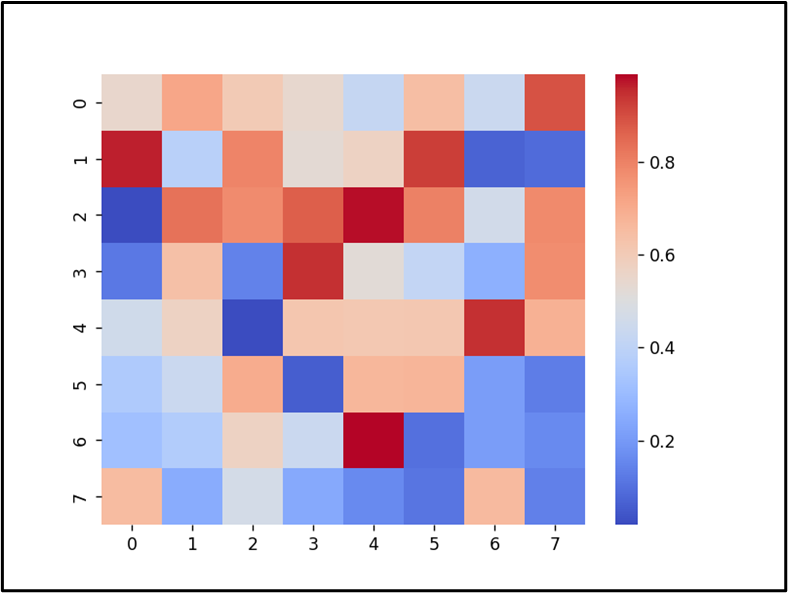
The Seaborn heatmap has been plotted by diverging palette colormap.
Conclusion
The “seaborn.heatmap()” perform of the “Seaborn” module is utilized in Python to plot/create rectangular information within the color-coded matrix type. This perform is used to plot the heatmap with varied colormaps, equivalent to sequential and diverging colormaps. We will additionally set the utmost and minimal worth of the colorbar of the seaborn heatmap by passing the parameter worth to the “heatmap()” perform. This tutorial delivered an in depth information on seaborn heatmap colours utilizing quite a few examples.