The programming languages use numerous encoding schemes to signify information. Considered one of them is “ASCII”, which refers to “American Commonplace Code for Info Interchange”. ASCII encodes English characters utilizing numbers from “0” to “127” and permits safe information transmission over the community. This information will exhibit using the Python “string.isascii()” technique using acceptable examples.
The beneath contents shall be lined on this write-up:
- What’s the “isascii()” Technique in Python?
- Checking ASCII Characters Utilizing the “isascii()” Technique.
- Checking ASCII Characters Utilizing the “isascii()” Technique With the “if/else” Assertion.
What’s the “string.isascii()” Technique in Python?
Python makes use of the “string.isascii()” technique to find out if a string incorporates “ASCII” characters or not. It checks for Unicode values that correspond to ASCII values.
Syntax
Parameters
The “string.isascii()” technique doesn’t take any parameter values.
Return Worth
The return worth of the tactic is a boolean because it retrieves “True” if the string is empty/clean or all chars within the string are “ASCII”. It retrieves “False” for any “non-ASCII” characters.
Observe: The complete ASCII desk may be discovered right here. Characters discovered on this desk shall be handled as ASCII characters, whereas the opposite characters present in a string will generate the “False” consequence.
Instance 1: Checking ASCII Characters Utilizing the “string.isascii()” Technique
The beneath code is utilized to find out if the enter string incorporates “ASCII” characters or not:
print(‘String of Alphabets is ASCII: ‘,mystr.isascii())
mystr = “189456”
print(‘nString of Numbers is ASCII: ‘,mystr.isascii())
mystr = “!@#$%”
print(‘nString of Symbols is ASCII: ‘,mystr.isascii())
mystr = “”
print(‘nEmpty String is ASCII: ‘,mystr.isascii())
mystr = “Åßç”
print(‘nString of Non-ASCII Characters is ASCII: ‘, mystr.isascii())
Within the above code, the “string.isascii()” technique retrieves “True” if the string is an ASCII character and “False” if it’s not an ASCII character.
Output
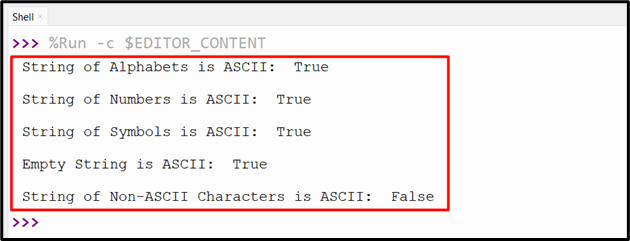
On this consequence, the “ASCII” and “non-ASCII” characters have been checked utilizing the “isascii()” technique accordingly.
Instance 2: Checking ASCII Characters Utilizing the “string.isascii()” Technique With the “if/else” Assertion
Let’s overview this code and test the Unicode ASCII characters primarily based on a situation:
str1 = ‘Python Information’
if str1.isascii():
print(‘”%s” is ASCII string.’ %(str1))
else:
print(‘”%s” will not be an ASCII string.’ %(str1))
Within the above code, the “string.isascii()” technique is utilized together with the “if/else” situation to confirm whether or not the enter string incorporates ASCII characters or not. The “else” assertion shows the message if the initialized string doesn’t comprise an ASCII character.
Output
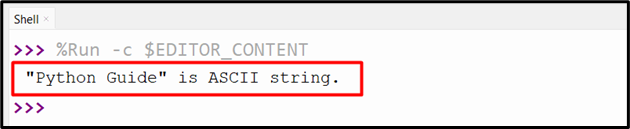
In response to the above output, the initialized string is an “ASCII” string.
Conclusion
The “string.isascii()” technique in Python checks whether or not a string incorporates an “ASCII” (American Commonplace Code for Info Interchange) character or not. On this technique, “True” and “False” values are returned relying on whether or not the initialized string incorporates the ASCII characters or not. The aim of this information was to offer an entire and complete overview of Python’s “string.isascii()” technique with examples.