In Python, working with strings (sequence of characters) is among the necessary options. Strings can comprise any character, together with Unicode characters, corresponding to emojis, accented letters, or symbols. Nonetheless, whereas storing or transmitting strings, we could encounter exceptions/errors by encoding or decoding them. Encoding is the method of changing a string right into a sequence of bytes that may be saved or transmitted and the “encode()” methodology is a built-in methodology of the string class that encodes a string utilizing a particular encoding scheme.
This weblog submit will current an in depth information on the Python “string.encode()” methodology utilizing acceptable examples by masking the next content material:
What’s the Python “string.encode()” Methodology?
In Python, the “string.encode()” methodology encodes a string right into a bytes sequence in accordance with the actual encoding.
Syntax
string.encode(encoding=encoding, errors=errors)
Parameter Worth
Within the above syntax:
-
- The encoding will be specified utilizing the “encoding” parameter with the default worth of “Utf-8”.
- The “errors” parameter can specify learn how to deal with the errors confronted throughout encoding.
The potential values for “errors” are:
-
- “strict”: Elevate an “UnicodeEncodeError” exception if an error happens.
- “ignore”: Ignore the error and proceed encoding.
- “change”: Change the error with a alternative character, corresponding to “?”.
- “xmlcharrefreplace”: Change the error with an XML character illustration.
- “backslashreplace”: Change the error with a backslash escape sequence.
- “namereplace”: Change the error with a Unicode identify.
Return Worth
The “string.encode()” methodology returns a “bytes” object that incorporates the encoded string.
Instance 1: Encoding the String Utilizing “default” Encoding (Utf-8)
The beneath instance code is used to encode the string utilizing the default “Utf-8” encoding:
string = ‘Pythön¶’
print(‘Given String:’, string)
print(‘nEncoded String:’, string.encode())
Within the above code, the “string.encode()” methodology is utilized for encoding the initialized string in accordance with the default encoding worth “Utf-8”.
Output
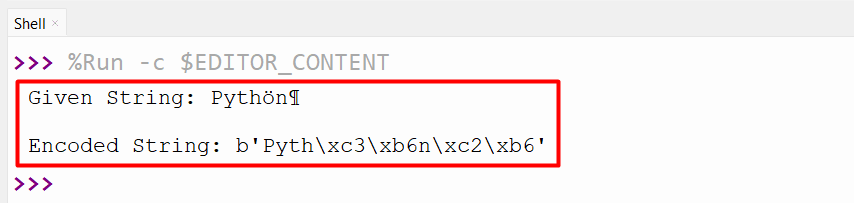
The encoded string has been proven within the above output.
Instance 2: Encoding the String Using the “Errors” Parameter
The beneath code encodes the string by making use of a number of “errors” parameters of the “string.encode()” methodology:
string = ‘Pythön¶’
print(‘Given String:’, string)
print(‘nbackslashreplace Error Methodology:’, string.encode(“ascii”, “backslashreplace”))
print(‘nignore Error Methodology:’, string.encode(“ascii”, “ignore”))
print(‘nreplace Error Methodology:’, string.encode(“ascii”, “change”))
print(‘nxmlcharrefreplace Error Methodology:’, string.encode(“ascii”, “xmlcharrefreplace”))
print(‘nnamereplace Error Methodology:’, string.encode(“ascii”, “namereplace”))
Right here, the outlined string is encoded utilizing the “ascii” encoding scheme and with numerous error parameters corresponding to “backslashreplace”, “ignore”, and many others.
Output
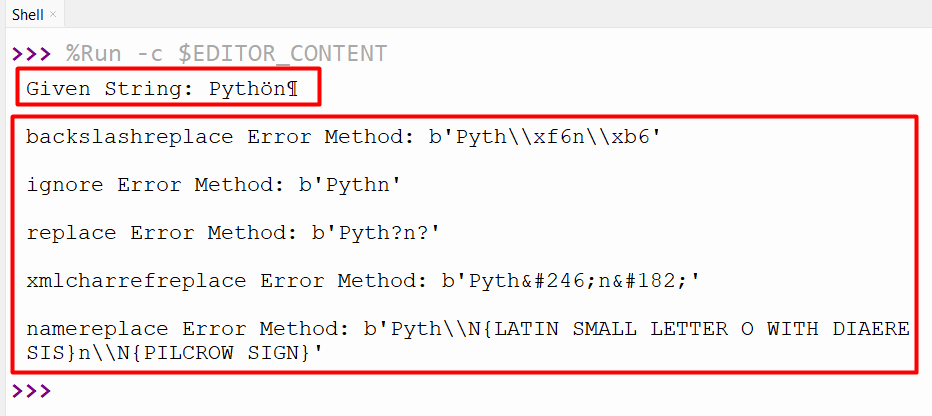
The string has been encoded efficiently, together with the error dealing with.
Conclusion
The “string.encode()” methodology is utilized to encode a specified string right into a bytes sequence relying on the actual encoding. The “encoding” and “errors” parameters are used to specify the encoding for use and the error strategies for use to deal with the error, respectively. This Python write-up offered a complete information on the “string.encode()” methodology utilizing quite a few examples.