An important function of Python is the flexibility to set attribute values within the class by referring to the created class objects at runtime. Attributes are variables or features that belong to an object and could be accessed/known as by the dot notation, reminiscent of “object.attribute”. The “setattr()” is a built-in operate in Python that units or assigns an object’s attribute worth.
This publish will clarify a whole information on the “setattr()” operate utilizing quite a few examples by way of the next supported content material:
What’s the “setattr()” Perform in Python?
In Python, the “setattr()” operate is used to assign the desired attribute worth of the goal object.
Syntax
setattr(object, attribute, worth)
Parameters
Within the above syntax:
-
- The “object” parameter specifies an object whose attribute must be set.
- The “attribute” parameter signifies the attribute identify.
- The “worth” parameter denotes the worth we need to assign to the attribute.
Return Worth
The “setattr()” operate returns no worth.
Instance 1: Making use of the “setattr()” Perform to Set the Attribute Worth
The beneath code is used to set/modify the attribute worth of the desired object:
identify = “Joseph”
age = 55
top = 9.5
p1 = college students()
print(‘Earlier than Setting Attribute: ‘, p1.age)
setattr(p1, ‘age’, 40)
print(‘After Setting Attribute: ‘,p1.age)
Within the above code, the “setattr()” operate takes the created class (college students) object “p1”, attribute “age”, and worth “40” as its arguments, respectively, and modifies the goal worth accordingly.
Output
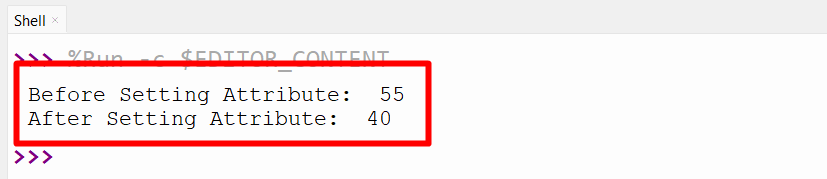
The attribute worth has been modified efficiently.
Instance 2: Making use of the “setattr()” Perform to Set the Not Existent Attribute Worth
The beneath code reveals how the “setattr()” operate works with the attribute that isn’t discovered:
identify = “Joseph”
age = 55
top = 9.5
p1 = college students()
setattr(p1, ‘identify’, ‘Lily’)
print(p1.identify)
setattr(p1, ‘intercourse’, ‘male’)
print(p1.intercourse)
Within the above code strains, the “setattr()” operate units the brand new worth to the attribute “identify” that’s current within the class. After that, the “setattr()” operate additionally assigns the worth to the attribute “intercourse” that isn’t contained within the class.
Output
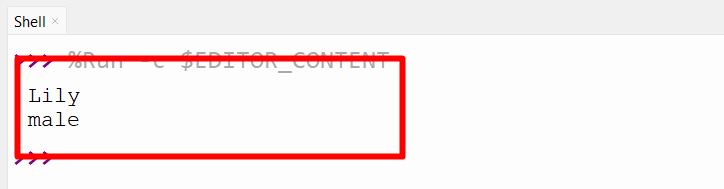
As seen, the non-existent attribute is created and returned based mostly on its set worth utilizing the “setattr()” operate.
Instance 3: Various Method of Setting an Attribute of Python Object
The beneath code is used to set/assign an attribute utilizing the “dot” notation syntax with the “self” parameter:
class college students:
def __init__(self, identify, age, top):
self.identify = identify
self.age = age
self.top = top
p1 = college students(‘Joseph’, 43, 5.5)
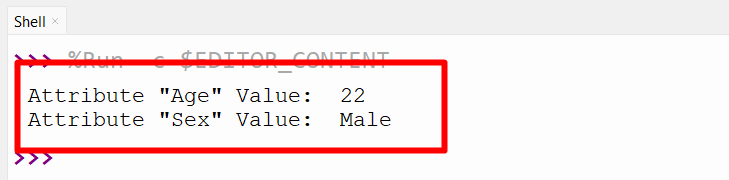
p1.age = 22
p1.intercourse = ‘Male’
print(‘Attribute “Age” Worth: ‘, p1.age )
print(‘Attribute “Intercourse” Worth: ‘, p1.intercourse)
Within the above code block, the “attribute” named “age” that exists within the class is about/modified, and the “attribute” named “intercourse” that doesn’t exist is created and assigned a worth utilizing the dot syntax. Lastly, each attributes are returned.
Output
Conclusion
Python’s “setattr()” operate units the desired object’s attribute worth. This operate creates an attribute that isn’t contained within the class. The “setattr()” operate modifies the attribute of the Python object by accepting the article, attribute, and worth as its arguments, respectively. This tutorial offered an in depth publish on Python’s “setattr()” operate utilizing a number of examples.