“Renaming recordsdata” is a typical activity in varied programming functions, and Python gives an environment friendly and versatile method for conducting this. By means of its sturdy file-handling capabilities, Python permits builders to discover varied methods for “renaming recordsdata”, each regionally and remotely.
This text goals to delve into the intricacies of “file renaming” in Python, discussing important strategies to equip the reader with a complete understanding of this topic.
File Techniques and Paths
Earlier than diving into “file renaming”, it’s essential to develop an understanding of file techniques and paths. Python’s “os” module gives a set of features that permit us to work together with the underlying working system, enabling file path manipulations. By using strategies like “os.path()” and “os.chdir()”, builders can navigate directories and entry recordsdata utilizing absolute or relative paths.
Tips on how to Rename Recordsdata in Python?
By using functionalities like “os.rename()” or “shutil.transfer()”, builders can modify the identify or extension of a file in a given listing. Moreover, by using looping buildings and conditional statements, it’s doable to automate the renaming course of for a batch of recordsdata. A number of the approaches embody the next:
Strategy 1: Renaming the File Utilizing the “os.rename()” Perform
To rename a single file utilizing Python, make use of the “os.rename()” perform by passing the unique and desired file names as arguments. Integration with person enter, exception dealing with, and file existence checks will probably be demonstrated to make sure robustness and keep away from errors.
Syntax
On this syntax, the supply tackle of the file to be renamed is given as “src”, and the vacation spot is given as “dst”.
Suppose, now we have this file named “linuxHint.txt” that must be renamed:
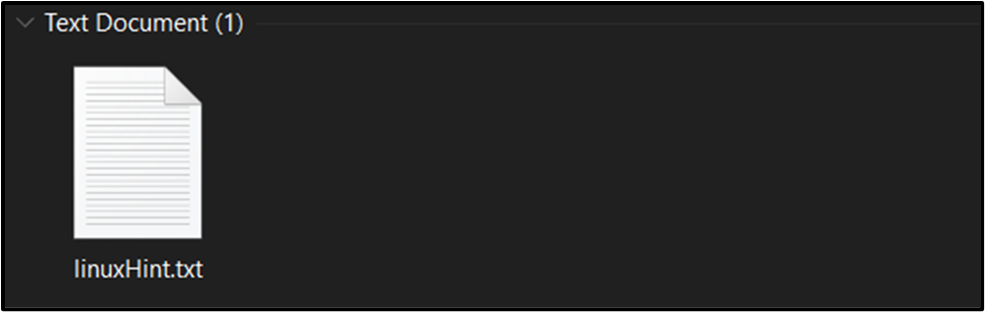
Now, to rename this file, contemplate the next code:
old_name = “D:linuxHint.txt”
new_name = “D:linux.txt”
os.rename(old_name, new_name)
print(“File renamed”)
Within the above code traces, import the “os” module first after which specify the present and new file names. It’s such that the file is renamed from “linuxHint.txt” to “linux.txt” utilizing the “os.rename()” perform.
Output
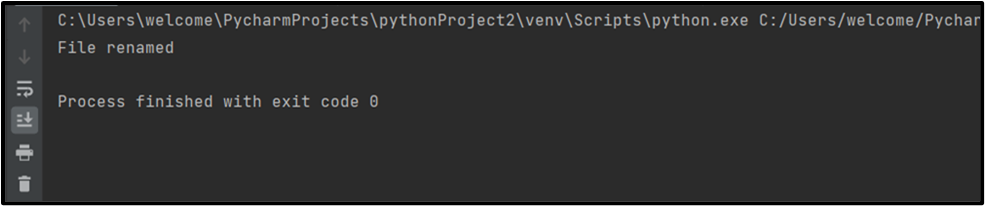
Renamed File
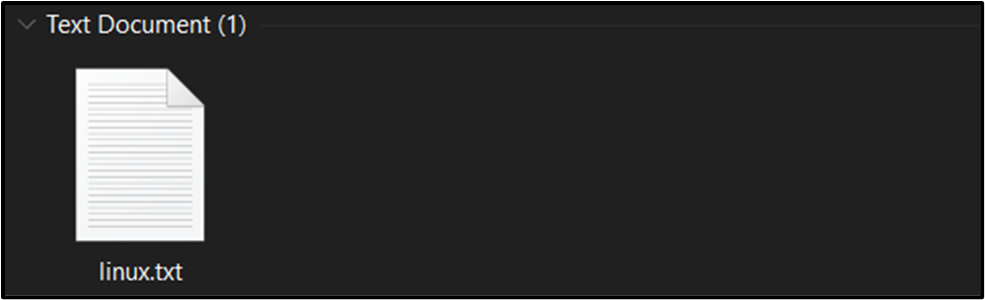
Strategy 2: Renaming the File Utilizing the “shutil” Module
The “shutil” module in Python presents superior file-handling functionalities, together with renaming recordsdata throughout totally different directories. With strategies comparable to “shutil.transfer()”, it’s doable to maneuver recordsdata whereas concurrently renaming them, facilitating listing restructuring or group duties:
Syntax
shutil.transfer(supply, vacation spot, copy_function = copy2)
Parameters
supply: A string containing the supply file’s location.
vacation spot: A string containing the listing’s path info.
copy_function: Non-compulsory. Copy2 is the default worth for this parameter. For this argument, we will additionally make the most of various copy features like copy and replica tree.
Now take a look at the code instance:
import shutil
old_name = “D:linux.txt”
new_name = “D:linuxHint.txt”
shutil.transfer(old_name, new_name)
print(“File renamed.”)
The above code block first imports the “shutil” module after which specifies the outdated and new file names. The file is then renamed from “linux.txt” to “linuxHint.txt” by way of the “shutil.transfer()” methodology.
Output
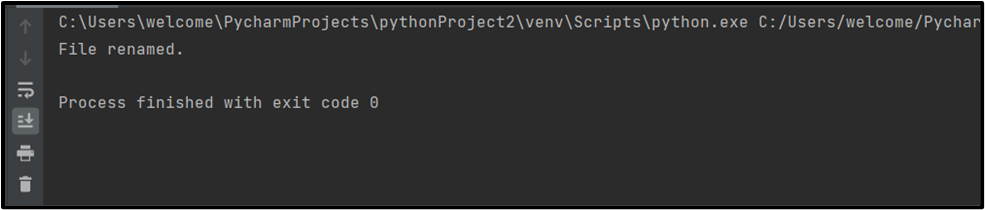
Renamed File
Strategy 3: Renaming A number of Recordsdata Utilizing the “os.listdir()” Perform
In real-world eventualities, builders might have to deal with a number of recordsdata concurrently. Python permits for bulk renaming via varied methods, such because the “os.listdir()” perform to get a listing of the recordsdata in a listing, and you’ll then cycle via the recordsdata to rename them.
Syntax
path: Non-compulsory. Path of the listing.
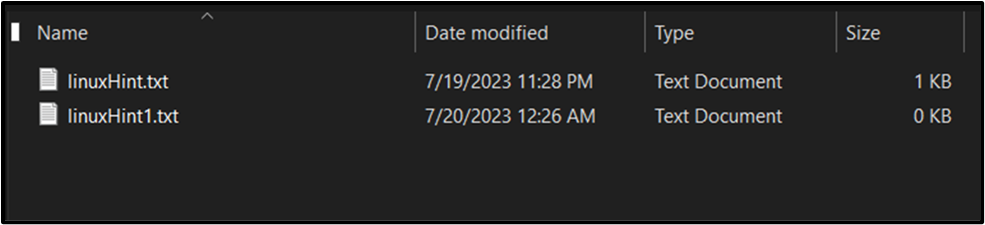
Following are the recordsdata that must be renamed:
To rename a number of recordsdata, overview the below-given code:
import os
dir = “D:linuxhint”
pre = “new_”
for file_name in os.listdir(dir):
if file_name.endswith(“.txt”):
new_name = pre + file_name
os.rename(os.path.be a part of(dir, file_name), os.path.be a part of(dir, new_name))
print(“Recordsdata renamed.”)
This code snippet will rename any textual content recordsdata—these with the “.txt” extensions—discovered within the specified listing, “D:linuxhint“. The vacation spot listing and a prefix string “new_” are initially set, which will probably be appended to the beginning of every renamed file. The “os.listdir()” perform is then utilized by the script to loop via every file within the listing.
It creates a brand new identify for each file with a “.txt” extension by including the prefix to the unique file identify. The file within the listing is then renamed utilizing the “os.rename()” perform, changing the outdated identify with the brand new identify. It prints the message “Recordsdata renamed.” as soon as all of the goal recordsdata have been renamed.
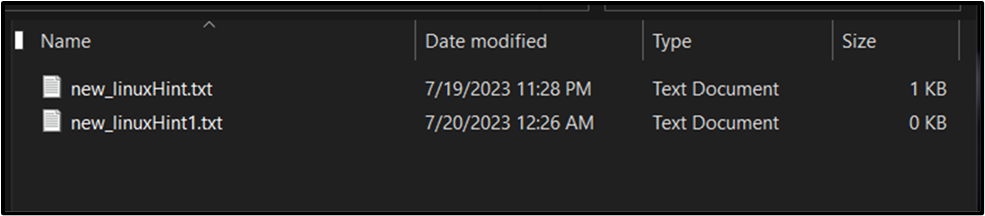
Output
Renamed A number of Recordsdata
Conclusion
Mastering file renaming in Python empowers builders to effectively handle file operations each regionally and remotely. By utilizing the “os.rename()” perform, or “shutil.transfer()” methodology, customers can rename the recordsdata utilizing Python. Python additionally permits for a number of renaming of recordsdata by way of the “os.listdir()” perform to get a listing of the recordsdata in a listing, and you’ll then cycle via the recordsdata to rename them.