Python affords many built-in modules which ship totally different sorts of functionalities and instruments. The “os” is one such module in Python that interacts with the working system and performs frequent duties akin to creating, deleting, shifting, and renaming information and directories. The “os.path.isdir()” operate accepts a path as an argument and retrieves a Boolean worth indicating whether or not the trail corresponds to an present listing or not. This may be helpful for validating consumer enter, checking the standing of a listing, or performing totally different actions based mostly on the trail sort.
This write-up will ship a radical information on Python’s “os.path.isdir()” technique by way of the beneath contents:
What’s the “os.path.isdir()” Methodology in Python?
In Python, the “os.path.isdir()” technique checks whether or not a given path is an present/present listing or not. The strategy will retrieve “True” if the actual path factors to a listing by way of a symbolic hyperlink. In any other case, it returns “False”.
Syntax
Parameters
Within the above syntax, the “path” parameter specifies the path-like object comparable to the file system path.
Return Worth
The “os.path.isdir()” technique retrieves “True” or “False”. If the required path already exists, this technique retrieves “True”; in any other case, it retrieves/returns “False”.
Instance 1: Making use of the “os.path.isdir()” Methodology to Examine Whether or not the Specified Listing Path Exists or Not
The beneath code is utilized to confirm whether or not the outlined path is current or not:
path1 = r‘C:UserspDocumentsprogram’
print(os.path.isdir(path1))
path2 = r‘C:UserspDocumentssample’
print(os.path.isdir(path2))
Within the above code:
-
- The “os.path” module is imported in the beginning.
- The trail worth is assigned to the variables named “path1” and “path2”, respectively.
- The “os.path.isdir()” technique takes the “path” as an argument in each circumstances to retrieve the corresponding Boolean worth “True” or “False” based mostly on the existence of the required listing i.e., “program” and “pattern” within the path.
Output
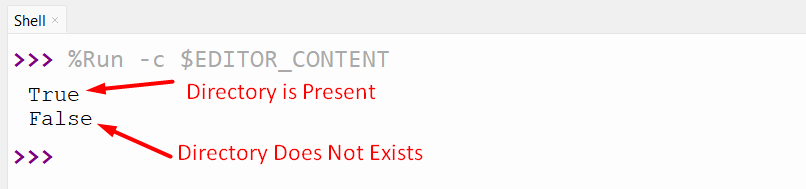
Right here, the Boolean values point out whether or not the required listing path exists or not.
Instance 2: Making use of the “os.path.isdir()” Methodology to Examine Whether or not the Specified Listing Exists or Not within the Present Working Listing
The next code is used to test the listing existence within the present working listing using its identify:
import os.path
path1 = ‘Python’
print(os.path.isdir(path1))
Within the above code:
-
- The “os.path” module is imported in the beginning.
- The listing identify that must be checked is assigned to a variable named “path1”.
- The “os.path.isdir()” technique takes the listing identify i.e., “Python” as an argument and retrieves “True” or “False” based mostly on the existence of a listing within the present working listing.
Output
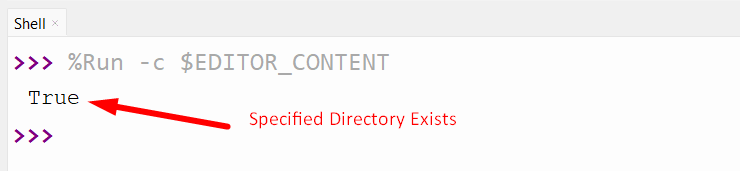
Conclusion
The “os.path.isdir()” technique of the “os” module is utilized to test whether or not a given/specified path is an present/present listing or not. Within the case of symbolic hyperlinks, the tactic will return “True“. This technique takes solely the identify of the listing as an argument and retrieves “True” or “False” based mostly on its existence. This Python information introduced an in-depth tutorial on the “os.path.isdir()” technique utilizing quite a few examples.