The usual utility “os” Python library helps a number of features and modules to work together and work with the working system. It’s utilized for numerous duties similar to accessing/calling file data, eradicating or renaming information, merging information, and others. Whereas working with the desired path or pathnames, the “os.path” module is utilized in Python.
This write-up explains a complete tutorial on the “os.path” module by way of the below-provided content material:
What’s the “os.path” Module in Python?
In Python, the “os.path” module of the “os” library gives numerous features for manipulating file paths. It’s a very useful gizmo for working with information and directories in Python.
We will make the most of the “os.path” module to work with specified paths in numerous working methods. For instance, to verify whether or not the desired path is an current file, the “os.path.isfile()” is used, and to verify whether or not the trail is the listing the “os.path.isdir()” perform is utilized in Python.
Let’s perceive this module in depth utilizing the below-given content material:
Getting the Basename and Listing Title of the Specified Path
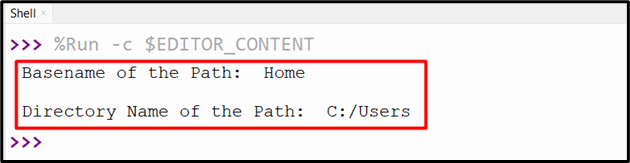
The “os.path” module gives a perform “os.path.basename()” and “os.path.dirname()” to get the bottom title and the listing title of the desired path. For an instance, take a look at the beneath code:
import os
print(‘Basename of the Path: ‘,os.path.basename(“C:/Customers/Dwelling”))
print(‘nDirectory Title of the Path: ‘,os.path.dirname(“C:/Customers/Dwelling”))
The code above generates the next output:
Checking Whether or not the Specified Path is Absolute or Current Listing or Current File or Not
The “os.path.isabs()” perform is used to verify whether or not the desired path is absolute or not. The “os.path.isdir()” and “os.path.isfile()” features are used to find out whether or not the actual path is an current listing or an current file. In Unix, absolute paths begin with a ahead slash. In Home windows, they begin with a backslash after eradicating any drive letter.
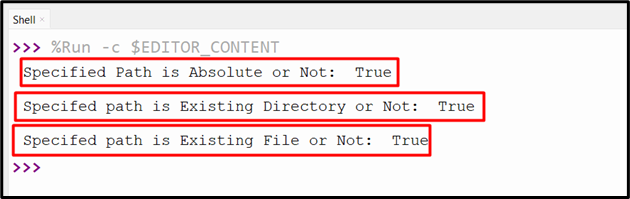
Check out the beneath code to use all of those features on the desired path:
import os
print(‘Specified Path is Absolute or Not: ‘,os.path.isabs(“C:/Customers/Dwelling”))
print(‘nSpecifed path is Current Listing or Not: ‘, os.path.isdir(“C:Customers”))
print(‘nSpecifed path is Current File or Not: ‘, os.path.isfile(“C:/Customers/p/Paperwork/program/new.xml”))
The code above generates the next output:
Normalizing the Case and Paths of the Specified Path
The “os.path.normcase()” of the “os.path” module takes/accepts the desired path as an argument and normalizes the case. To normalize the trail by deleting the additional characters, the “os.path.normpath()” perform is utilized in Python.
Notice: Unix and Mac maintain path names as specified, whereas Home windows converts them to lowercase and replaces ahead slashes with backslashes.
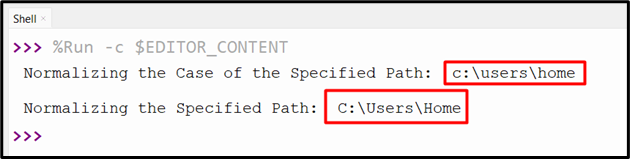
Let’s discover/study this methodology by the beneath instance:
import os
print(‘Normalizing the Case of the Specified Path: ‘, os.path.normcase(“C:/Customers/Dwelling”))
print(‘nNormalizing the Specified Path: ‘, os.path.normpath(“C:/Customers/./Dwelling”))
When the above code is executed, the beneath output shows on the console display screen:
That’s all concerning the os.path module in Python.
Conclusion
In Python, the “os.path” module of the “os” library gives a number of features to work with specified paths in numerous working methods. The “os.path” module has a number of features that carry out numerous operations similar to getting the basename or listing title, checking absolute path, verifying current listing or current file, and others. This write-up offered an entire tutorial on the “os.path” module utilizing quite a few examples.