The right way to Get Python File Measurement From a System?
Python offers the next strategies for getting file sizes from the system, as follows:
Technique 1: Get the File Measurement Utilizing “os.path.getsize()” Technique
In Python, the “os.path.getsize()” operate retrieves the file measurement in bytes based mostly on the file path. Right here’s an instance:
Instance 1: Get the File Measurement in “Bytes”
The next code is utilized to get the dimensions of the desired file:
import os
file_path = r‘C:UserspDocumentsprogramfilename.txt’
file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
print(f“The dimensions of ‘{file_path}’ is {file_size} bytes.”)
Within the above code:
- The “os” module is imported and the desired file path is outlined as a string, respectively.
- The “os.path.getsize()” operate is utilized to return the file measurement in bytes.
- Lastly the “f-string” is used to print out the file path and measurement, respectively.
Output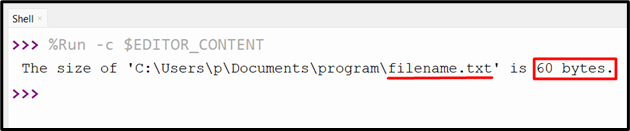
The desired file measurement has been proven within the above output.
Instance 2: Get the File Measurement in “KiloBytes”
To transform the file measurement to “kilobytes”, we have to divide the file measurement in bytes by “1024”. Right here’s an instance code:
import os
file_path =r‘C:UserspDocumentsprogramfilename.txt’
file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
kb_size = file_size / 1024
print(f“The dimensions of ‘{file_path}’ is {kb_size:.2f} KB.”)
On this code snippet:
- Firstly, get the file measurement in bytes utilizing the “os.path.getsize()” methodology.
- As a way to get the dimensions in “kilobytes”, divide the file measurement by “1024”.
Output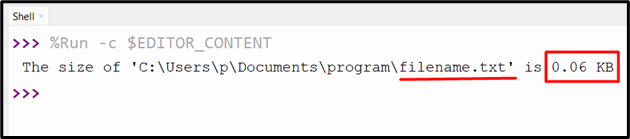
Technique 2: Get the File Measurement Using “os.stat()” Technique
In Python, you may as well retrieve the file measurement through the use of the “os.stat()” methodology, which returns a tuple of file attributes, together with the file’s measurement in bytes.
Instance
Right here is an instance code:
import os
file_path = r‘C:UserspDocumentsprogramfilename.txt’
file_stat = os.stat(file_path)
file_size = file_stat.st_size
print(f“The dimensions of ‘{file_path}’ is {file_size} bytes.”)
Within the above code traces:
- The “os” module is once more imported, however this time the “os.stat()” methodology known as having the file path as its parameter.
- This methodology creates a named tuple of file attributes, together with the file measurement in bytes.
- The “st_size” attribute of the named tuple is accessed to find out the file measurement.
Output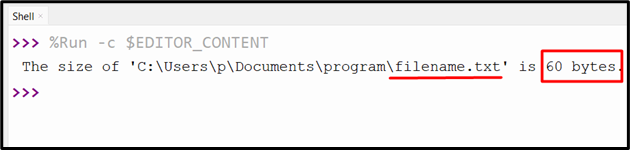
It’s proven above within the snippet how massive the desired file is.
Technique 3: Get the File Measurement Utilizing “pathlib.Path().stat()” Technique
In Python, you may as well use the “pathlib.Path().stat()” methodology to calculate file sizes. It has the identical performance as “os.stat()”, however takes a path object instead of a string.
Instance
Let’s overview the next code:
from pathlib import Path
file_path = Path(r‘C:UserspDocumentsprogramfilename.txt’)
file_stat = file_path.stat()
file_size = file_stat.st_size
print(f“The dimensions of ‘{file_path}’ is {file_size} bytes.”)
In accordance with the above code:
- The “Path” class from the “pathlib” module is imported.
- The “Path” object is created with the file path as its argument and calls the “stat()” methodology on that object to get the file attributes.
- The “st_size” attribute of the named tuple is accessed to find out the file measurement.
Output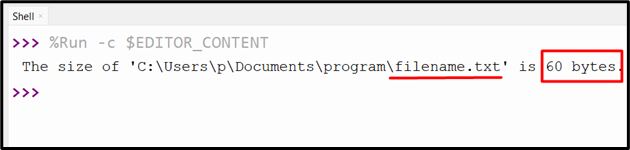
On this output, the dimensions of the desired file is returned appropriately.
Conclusion
There are a number of strategies to find out the file measurement in Python such because the “os.path.getsize()”, “os.stat()”, or the “pathlib.Path().stat()” methodology. The “os.path.getsize()” methodology fetches the file measurement in bytes and kilobytes. The opposite strategies will also be used to get the file measurement in varied sizes. This Python submit delivered varied methods to get the Python file measurement.