An RNG or Random Quantity Generator is one thing that’s utilized by a number of applications for varied completely different causes. Nevertheless, oftentimes, the person desires to implement a boolean generator. To do that, the person can make the most of the bool() technique to transform the output of the random quantity generator into boolean values. This bool() technique can be utilized alongside the getrandbits() technique, the selection() technique, and the random() operate inside a conditional assertion.
This submit will comprise the next content material:
Let’s begin with the primary technique.
Methodology 1: Utilizing the getrandbits() Methodology to Generate Boolean Values
The getrandbits() is used to generate bits, mainly integer values, inside a variety specified within the argument of this technique. With this technique, the person can set the vary to 1, which might imply that it may solely generate both a 0 or a 1, after which use the bool() technique to transform the integer to its boolean equal. Nevertheless, to make use of this technique, the person must import the “random” bundle.
To exhibit this technique for producing random boolean worth, take the next code snippet:
import random
randInt = (random.getrandbits(1))
randBool = bool(randInt)
print(randBool)
When this code snippet is executed, it produces the next outcome on the terminal:
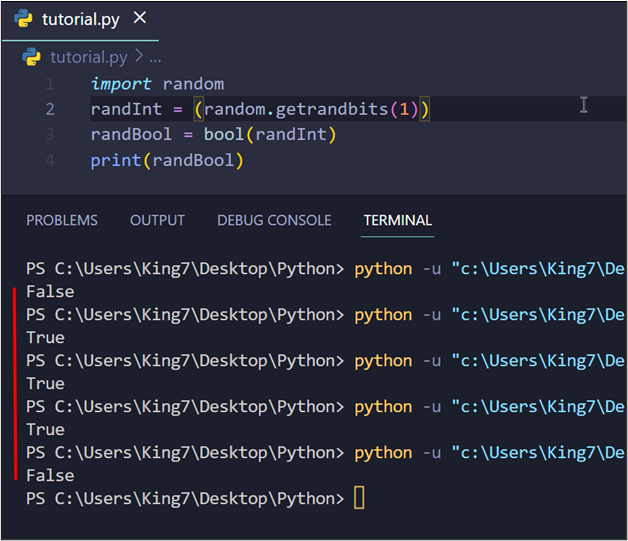
The above picture comprises the output of a number of executions of the code, confirming {that a} random boolean is generated on each execution.
Observe: The getrandbits() technique is the quickest technique of this submit to generate random boolean values.
Methodology 2: Utilizing the selection() Methodology to Generate Boolean Values
The selection() from the “random” bundle is used to decide on a random worth from an inventory of values (strings, tuples, lists, and extra). This technique can be utilized to decide on between True, and False by offering them in an inventory, or to decide on between 0 and 1 after which changing it to a boolean utilizing the bool() technique.
To exhibit the working of the selection() technique to generate random boolean values, check out the next code snippet:
import random
randBool = random.alternative([True, False])
print(randBool)
Upon execution, the next result’s proven on the terminal:
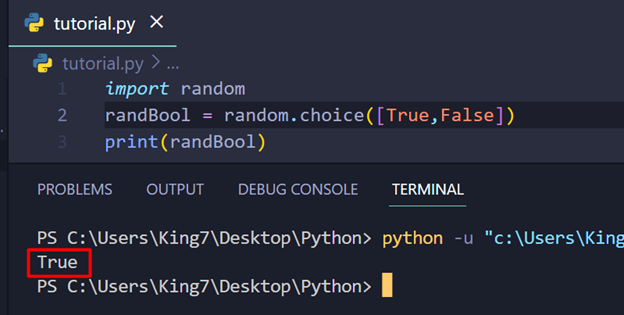
The output verifies {that a} random boolean worth was generated. Alternatively, for the second method with the usage of the selection() technique, check out the below-given code snippet:
import random
randInt = random.alternative([0,1])
randBool = bool(randInt)
print(randBool)
When this code snippet is executed, it shows the next outcome on the terminal:
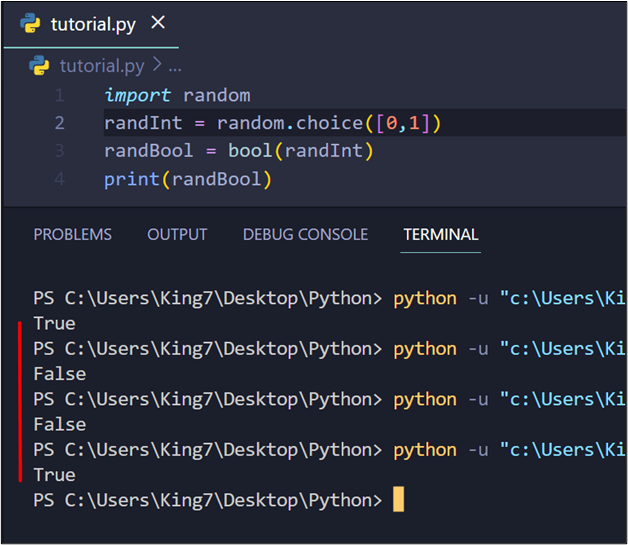
The output is certainly a random boolean generated on every execution of the code.
Methodology 3: Utilizing the random() Methodology With if-condition to Generate Boolean Values
The random() technique will also be used to generate random boolean values. Nevertheless, many of the customers use it mistaken. The customers take the output of the random() technique after which cross it to the bool() technique to transform that worth right into a boolean. The output is certainly a boolean worth, however they created a biased random boolean worth generator utilizing the mistaken method.
The random() technique produces floating level values between 0 and 1, and customers multiply it by 10 to get the worth in integers. However, the values then vary from 0 to 10. When this worth is transformed right into a bool, it provides “False” for under “0”. This implies that there’s a 90% likelihood that the reply goes to be True. Thus, a biased random boolean generator.
To appropriately, use the random() technique to generate boolean values, apply an if-condition like this:
randBool = random.random() > 0.5
print(randBool)
On this code snippet, the situation checks whether or not the worth generated by the random() technique is above 0.5 or not. Based mostly on this, it returns True or False, reaching a 50% likelihood to land True or False. Upon execution, the next is the outcome:
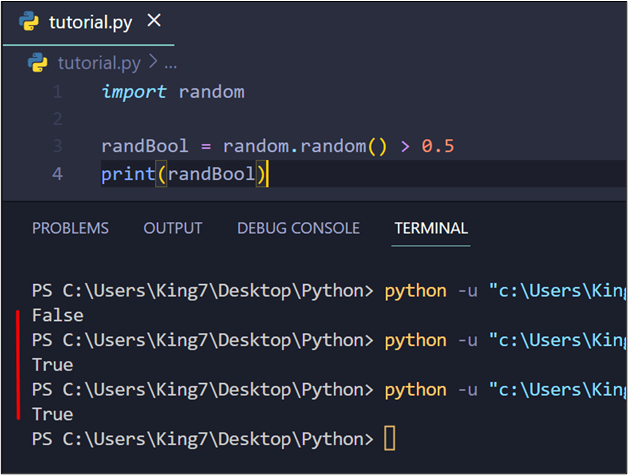
Methodology 4: Utilizing the randint() Methodology to Generate Boolean Values
The randint() technique is used to generate a random integer worth from a given vary. If the offered vary is just 0 and 1, and the output of this technique is handed into the bool() technique, then it’s going to act as a random boolean generator:
import random
randInt = random.randint(0,1)
randBool = bool(randInt)
print(randBool)
When this code is executed it produces the next output on the terminal:
The output is a randomly generated boolean worth for each execution of this code.
Conclusion
Producing Random Boolean Values will be useful in fairly just a few duties, particularly when constructing an RNG system. To do that, the person can make the most of varied strategies () together, such because the getrandbits(), alternative(), random(), and the randint() technique with the bool() technique. This submit has demonstrated the usage of these strategies.