Recordsdata are important for storing and processing information, and Python supplies many built-in capabilities and modules to deal with these information. The “search()” technique is one such very important file operation in Python. It’s utilized to maneuver/switch the file pointer to a particular place within the file, which could be useful for studying or writing the information at a sure location.
This submit will current an in depth information on the “file.search()” technique by overlaying the next supported content material:
Python “file.search()” Technique
The “file.search()” technique is utilized to learn or write information at a selected place in a file. This technique strikes the file deal with, which is sort of a cursor that marks the place the information can be accessed, to a distinct location within the file.
Syntax
file.search(offset[, from_where])
Parameter
Within the above syntax, the “file” is the file pointer, “offset” is the place to maneuver ahead, and “from_where” is the purpose of reference. The “from_where” argument can take three values:
- “0”: implies that the file’s reference level is at first.
- “1”: implies that the file’s reference level is on the present file place.
- “2”: implies that the file’s reference level is on the file finish.
The “from_where” argument is assigned as “0” by default.
Return Worth
The “search()” technique retrieves a worth representing the cursor’s new place within the file.
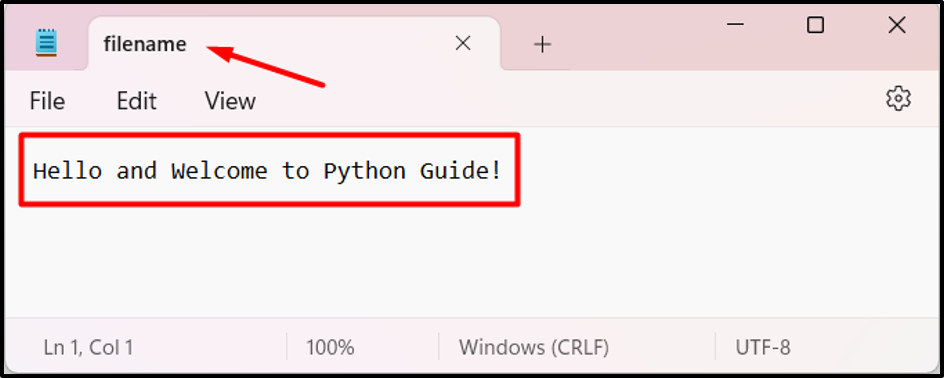
File to be Evaluated
We now have a file named “filename.txt” that comprises the next textual content and can be evaluated all through the information:
Instance 1: Utilizing the “file.search()” Technique to Change the Place of the File Deal with
Right here is an instance code to alter the place of the file deal with:
file = open(“filename.txt”, “r”)
print(file.search(20))
print(file.readline())
file.shut()
In keeping with the above code:
- The “search()” technique takes the integer worth as an argument and strikes the desired variety of positions ahead by referring to the supplied file.
- The “readline()” technique is utilized to learn the information from the outlined place till the tip of the desired file.
Output
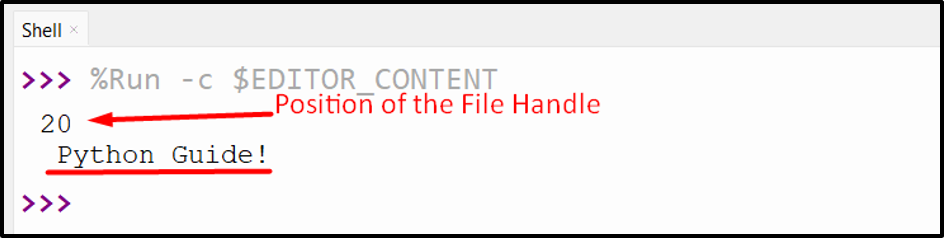
The place of the file deal with and the information from the present place till the tip has been displayed within the above snippet.
Instance 2: Utilizing the “file.search()” Technique With Unfavourable Offset
The beneath code is used to alter the file deal with place of the file opened in binary mode using the “file.search()” technique:
file = open(“filename.txt”, “rb”)
print(file.search(–24, 2))
print(file.readline())
file.shut()
Within the above code:
- The “open()” operate opened the file “txt” in “rb” mode.
- The “search()” technique takes the adverse offset and the reference level worth as its arguments, respectively and strikes the file deal with from place “-24” relative to the tip of the file.
- The “readline()” technique is then utilized to learn the remainder of the road.
Output
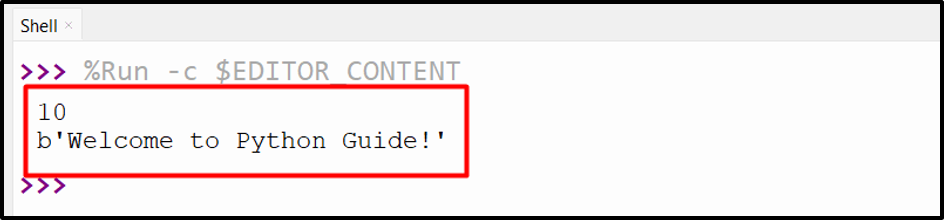
Based mostly on the above output, the desired information from the textual content file is learn from the desired place.
Conclusion
The “file.search()” technique in Python is utilized to maneuver or modify the place of the file deal with pointer in keeping with the actual offset worth. This technique can learn a sure part/portion of a file or write at a selected portion of the file. The adverse offset together with the tip reference level worth could be utilized to maneuver the pointer to the desired location ranging from the tip of the file. This weblog introduced an in depth information on Python’s “search()” technique utilizing the related examples.