The “bytearray” sort is a mutable sequence of bytes that can be utilized to govern binary information. In Python, the “bytearray()” technique is used to retrieve a “bytearray” object that lies within the vary of “0” to “256”. This write-up presents an in depth information on Python “bytearray()” technique by protecting the next contents:
What’s the “bytearray()” Methodology in Python?
The “bytearray()” technique in Python returns a “bytearray” object. A “bytearray” object is a changeable integer sequence starting from “0” to “256”. Which means that every aspect of a “bytearray” object is usually a single byte or a personality.
Syntax
bytearray(supply, encoding, errors)
Parameter
Within the specified syntax:
- The “supply” parameter/attribute is usually a string, a bytes object, an integer, or an iterable object.
- The “encoding” parameter specifies the encoding to make use of when changing a string to a “bytearray” object.
- The “errors” parameter specifies what to do if the encoding fails.
A number of Situations of “supply” Parameter
There are a number of methods to initialize the array with the “supply” parameter, as follows:
- If the “supply” parameter is a “string”, the bytearray object can be initialized with the bytes of the string.
- If the “supply” parameter/attribute is a specified “bytes” object, the bytearray object can be initialized with the bytes of the bytes object.
- If the “supply” parameter is an “integer”, the bytearray object can be initialized with an empty bytearray of the desired measurement.
- If the “supply” parameter is an “iterable” object, the bytearray object can be initialized with the bytes of the iterable object.
Return Worth
The retrieved worth of the “bytearray()” technique is a “bytearray” object.
Instance 1: Making use of the “bytearray()” Methodology to Retrieve Arrays of Bytes From the Specified Worth
The beneath code is used to retrieve the “bytearray” object from the desired worth:
print(bytearray(string_value, ‘utf-8’), ‘n‘)
int_value = 10
print(bytearray(int_value), ‘n‘)
list_1 = [20, 15, 35, 95]
print(bytearray(list_1))
Within the above code:
- The “string”, “integer”, and “listing” are initialized within the code.
- The “bytearray()” technique takes the desired worth as an argument and retrieves the corresponding byte array object in every case.
Output
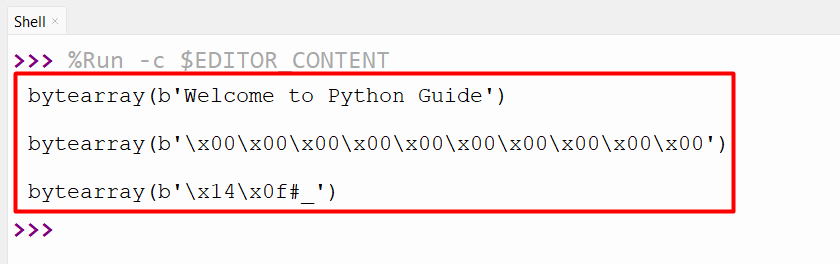
The byte-array object of the string, integer, and listing are proven on this output.
Instance 2: Making use of the “bytearray()” Methodology to Retrieve Arrays of Bytes From Byte Object
The beneath instance code is used to use the “bytearray()” technique to return arrays of bytes from byte objects:
print(arr1)
On this code, the “bytearray()” technique takes the “byte” object as an argument and retrieves the byte-array object.
Output
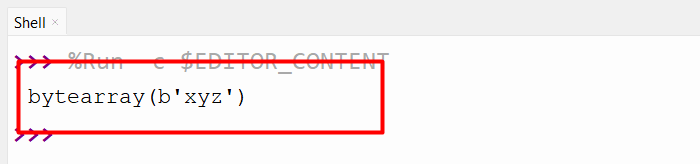
The byte-array object has been returned appropriately.
Conclusion
In Python, the built-in “bytearray()” technique is utilized to retrieve a bytearray object which is an array of specified bytes. This technique returns a changeable sequence of integers within the “0” to “256” vary. The “bytearray()” technique may be utilized to retrieve arrays of bytes from string, integer, iterable, and byte objects. This tutorial introduced a complete information on Python’s “bytearray()” technique utilizing a number of examples.