The “Pandas” library makes it easy and environment friendly to work with Python knowledge. Pandas “DataFrames” are like tables of knowledge, with rows and columns. It’s typically essential to pick out solely particular rows from a DataFrame in line with the situation. For instance, decide solely the rows the place the age column worth is larger than 18. To perform this job, varied Pandas strategies can be utilized in Python.
This tutorial presents an in depth information on deciding on rows based mostly on the situation utilizing quite a few examples.
Methods to Choose/Decide Rows By Situation in Pandas DataFrame?
To pick rows based mostly on the actual situation of Pandas DataFrame, totally different strategies are utilized in Python. Listed here are a number of the strategies:
Technique 1: Choose DataFrame Rows By Situation Utilizing Relational Operators Technique
The relation operator technique is used together with the sq. notation syntax to pick out rows of Pandas DataFrame. Within the beneath code, the “==” operator is used to pick out DataFrame rows containing title column values equal to “Henry”.
import pandas
college students = {‘Identify’: [‘Lily’, ‘Joseph’, ‘Henry’, ‘David’],‘Age’: [15, 23, 17, 26], ‘Grades’: [‘A’, ‘B’, ‘A+’, ‘D’]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(college students)
print(df, ‘n’)
output = df[df[‘Name’] == ‘Henry’]
print(output)
The above code execution returns the rows having a “Henry” worth within the Identify column:
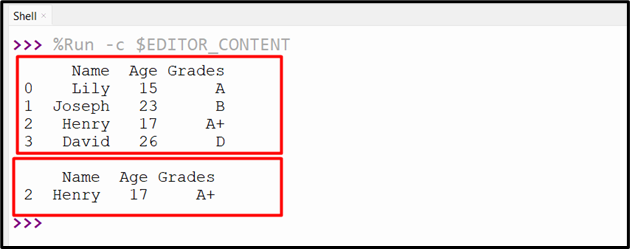
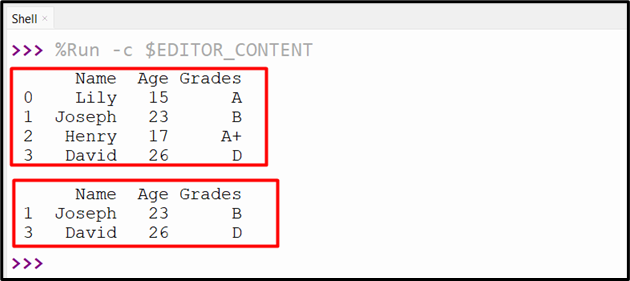
We will additionally make the most of different relation operators to pick out rows based mostly on the desired situation. On this instance, the “>” operator is used to pick out solely these rows which have an age worth better than “18”.
import pandas
college students = {‘Identify’: [‘Lily’, ‘Joseph’, ‘Henry’, ‘David’],‘Age’: [15, 23, 17, 26], ‘Grades’: [‘A’, ‘B’, ‘A+’, ‘D’]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(college students)
print(df, ‘n’)
output = df[df[‘Age’] > 18]
print(output)
When the above code is executed, the next output is proven to the console:
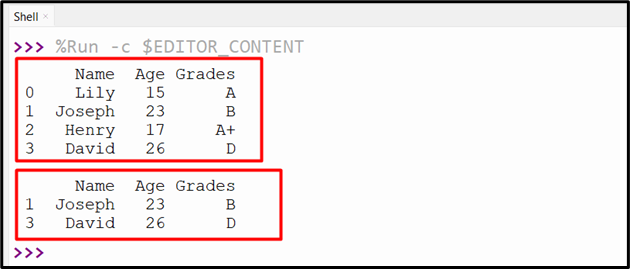
Technique 2: Choose DataFrame Rows By Situation Utilizing “df.isin()” Technique
The “df.isin()” technique of the “pandas” module selects DataFame rows in line with the desired situation. Within the following instance, the “df.isin()” technique selects Pandas DataFrame rows that include the “Grades” column worth “A” or “A+”.
import pandas
college students = {‘Identify’: [‘Lily’, ‘Joseph’, ‘Henry’, ‘David’],‘Age’: [15, 23, 17, 26], ‘Grades’: [‘A’, ‘B’, ‘A+’, ‘D’]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(college students)
print(df, ‘n’)
output = df[df[‘Grades’].isin([‘A’, ‘A+’])]
print(output)
The code produces the beneath output to the console:
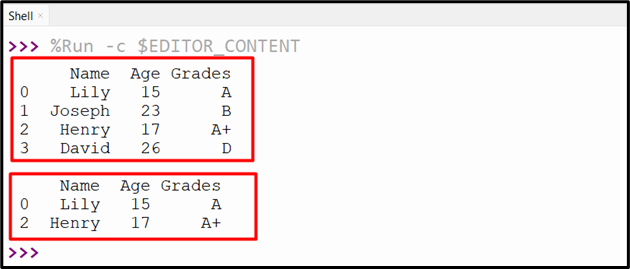
Technique 3: Choose DataFrame Rows By Situation Utilizing “&” Operator
The “&” operator may also be utilized to pick out Pandas DataFrame rows in line with the desired situation. For instance, within the beneath code, the “&” operator is used between two situations which can be used to pick out DataFrame rows. Primarily based on the situations, solely the rows having an “Age” better than “18” and the “Grades” equal to “D” will likely be fetched:
import pandas
college students = {‘Identify’: [‘Lily’, ‘Joseph’, ‘Henry’, ‘David’],‘Age’: [15, 23, 17, 26], ‘Grades’: [‘A’, ‘B’, ‘A+’, ‘D’]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(college students)
print(df, ‘n’)
output = df[(df[‘Age’] > 18) & df[‘Grades’].isin([‘D’])]
print(output)
The above output generates the beneath output:
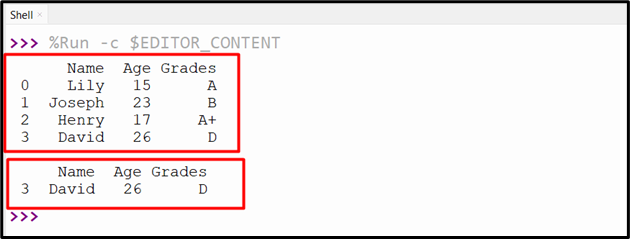
Technique 4: Choose Rows By Situation Utilizing “df.loc[]” Technique
The “df.loc[]” technique takes the index label worth as an argument and returns the information body or rows. This technique is utilized within the following code to pick out the DataFrame rows based mostly on the situation. The situation on this case signifies that the “Age” have to be better or equal to “20”.
import pandas
college students = {‘Identify’: [‘Lily’, ‘Joseph’, ‘Henry’, ‘David’],‘Age’: [15, 23, 17, 26], ‘Grades’: [‘A’, ‘B’, ‘A+’, ‘D’]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(college students)
print(df, ‘n’)
output = df.loc[df[‘Age’] >= 20]
print(output)
This code retrieves the next output to the console:
Conclusion
The relational operators, “df.isin()”, “&” operator, and “df.loc[]” strategies, are used to pick out DataFrame rows based mostly on the actual situations. The entire specified strategies can choose DataFrame rows based mostly on single or a number of situations. This information has offered an in depth tutorial on deciding on rows in line with the situation utilizing quite a few examples.