In Debian-based distributions comparable to Ubuntu, package deal administration performs a vital function in putting in, upgrading, and eradicating software program packages.
One of many basic elements of the package deal administration system is APT (Superior Package deal Instrument), which incorporates numerous utilities for managing packages, one such utility known as apt-cache, which is used for package deal looking, querying, and data retrieval.
What’s apt-cache?
apt-cache is a command-line utility that permits customers to work together with the package deal cache, which comprises metadata, and details about accessible packages, together with their names, descriptions, dependencies, and variations.
By using apt-cache, customers can shortly seek for packages, retrieve package deal data, and carry out different operations associated to package deal administration in Debian-based techniques.
This text explores the utilization of apt-cache with examples that can show you how to to maintain monitor of software program dependencies in your Linux system.
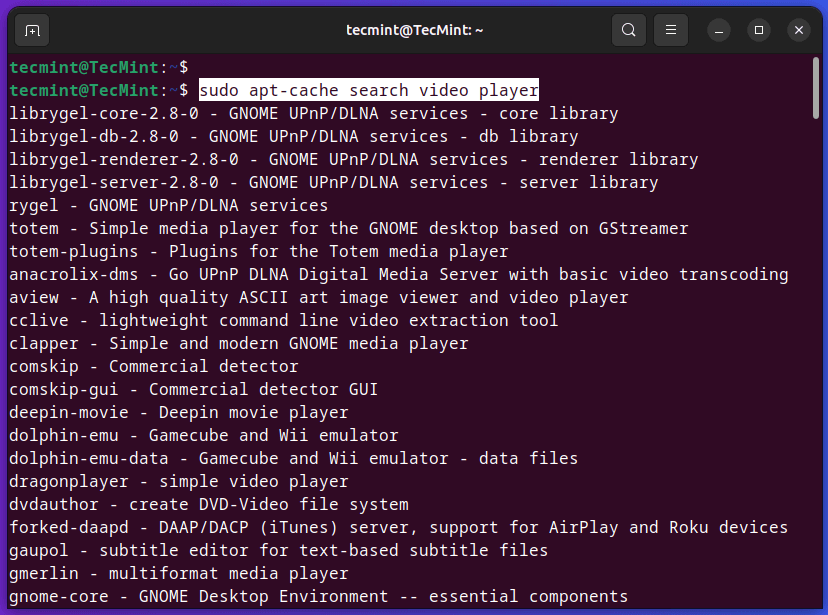
1. Seek for Packages in Ubuntu
The apt-cache search command is used to seek for packages within the package deal cache primarily based on particular key phrases of their names or descriptions.
For instance, in case you’re searching for a video participant, you should use the next command, which can show an inventory of packages whose names or descriptions include the required key phrase.
$ sudo apt-cache search video participant
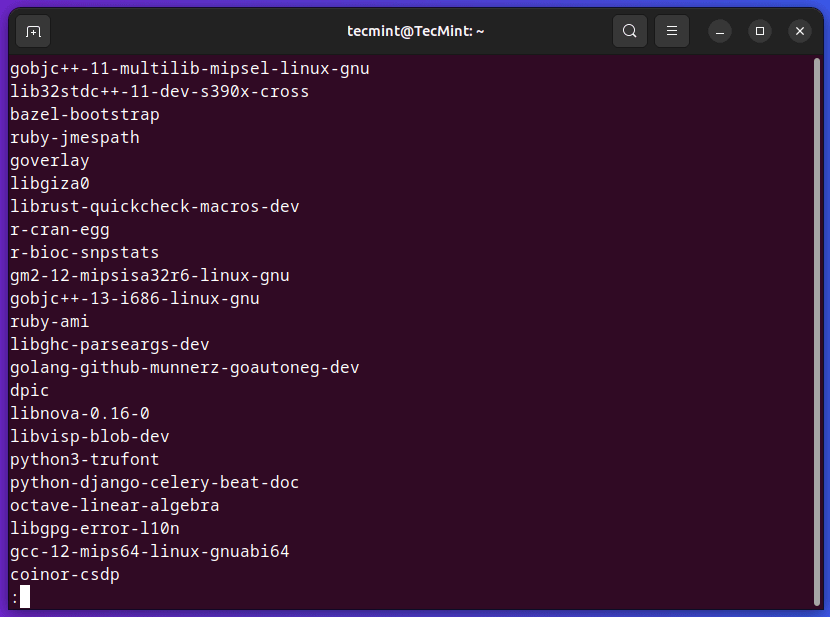
2. Listing Obtainable Packages in Ubuntu
The apt-cache pkgnames command is used to retrieve a complete checklist of package deal names with none descriptions or extra data from the package deal cache.
$ sudo apt-cache pkgnames
The above command will show a protracted checklist of package deal names. For the reason that checklist will be fairly in depth, chances are you’ll need to use instruments like much less or grep to navigate or filter the outcomes.
For instance, you may pipe the output to much less to scroll by the checklist:
$ sudo apt-cache pkgnames | much less
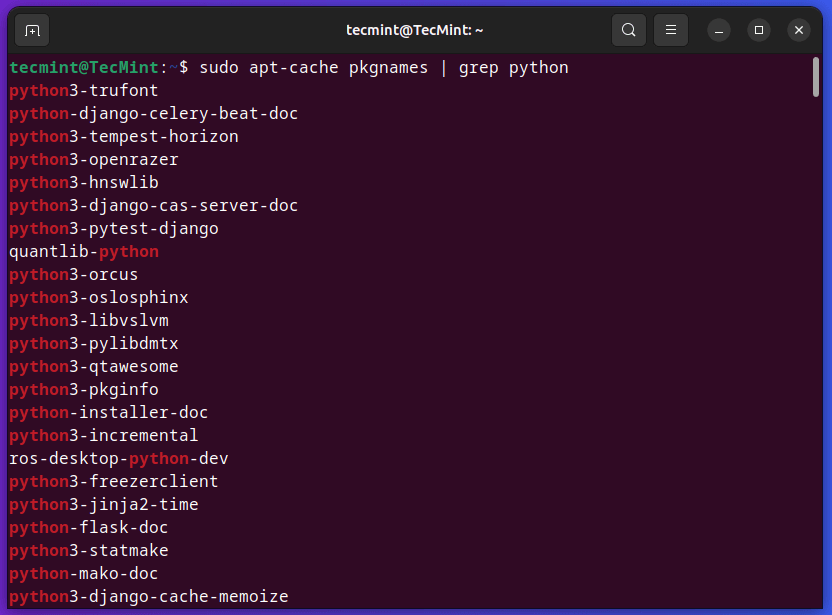
Alternatively, you should use grep to seek for a selected package deal known as Python as proven.
$ sudo apt-cache pkgnames | grep python
3. Discover Particulars of a Package deal in Ubuntu
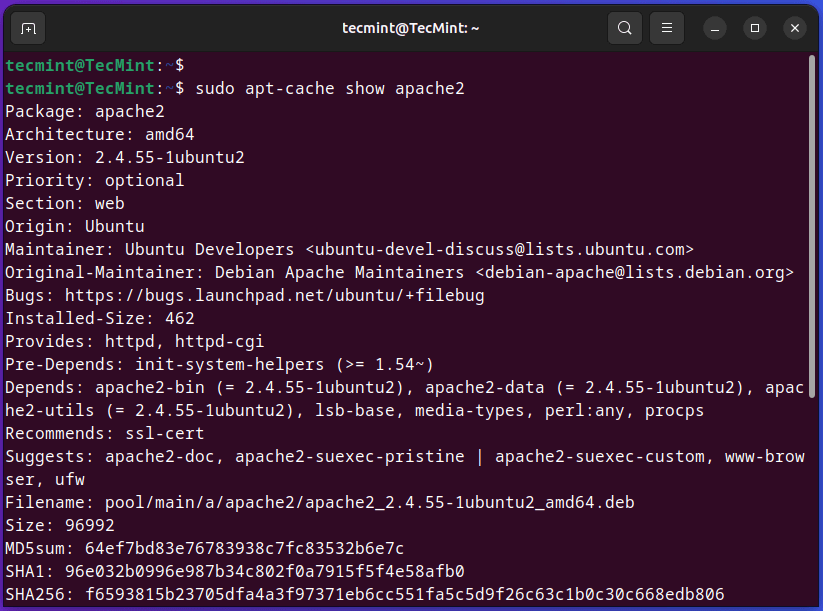
The apt-cache present command is used to show detailed details about a selected package deal comparable to description, model, dependencies, and different particulars from the system package deal cache.
For instance, if you wish to get the whole details about the package deal “apache2“, you should use:
$ sudo apt-cache present apache2
4. Listing Dependencies of a Package deal in Ubuntu
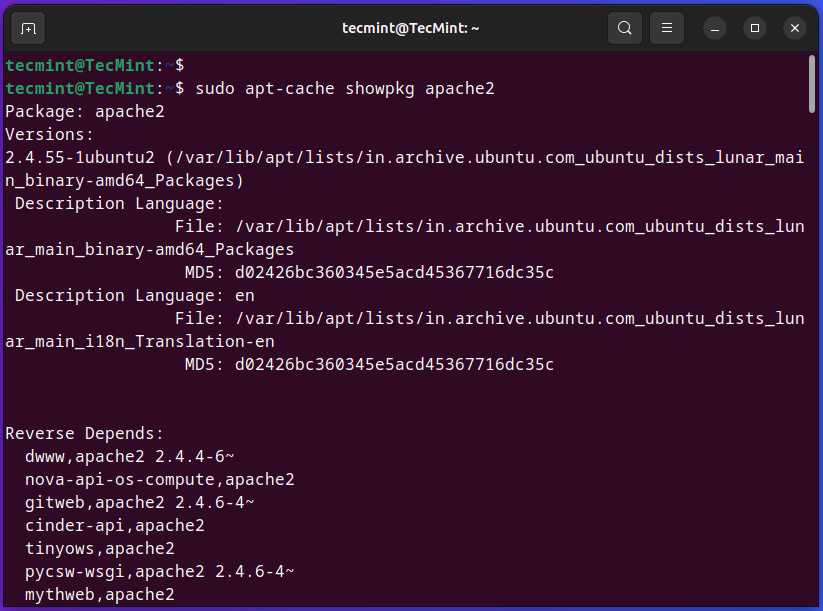
Use the ‘showpkg‘ sub-command to verify the dependencies for explicit software program packages. whether or not these dependencies packages are put in or not.
For instance, use the ‘showpkg‘ command together with package-name to get detailed details about model, dependencies, and reverse dependencies.
$ sudo apt-cache showpkg apache2
5. View Cache Statistics in Ubuntu
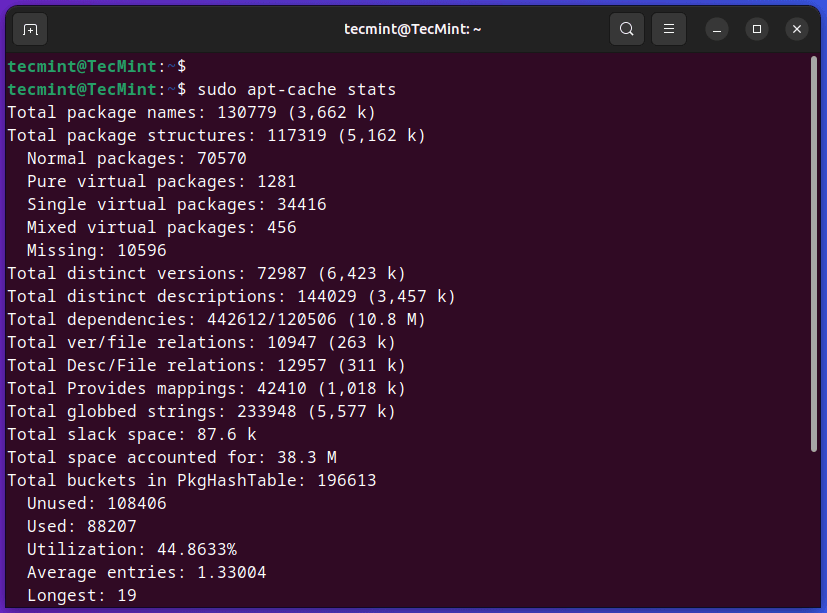
The ‘stats‘ sub-command will show total statistics in regards to the cache. For instance, the next command will show a complete variety of packages discovered within the cache together with the disk house utilization, and different related cache-related data.
$ sudo apt-cache stats
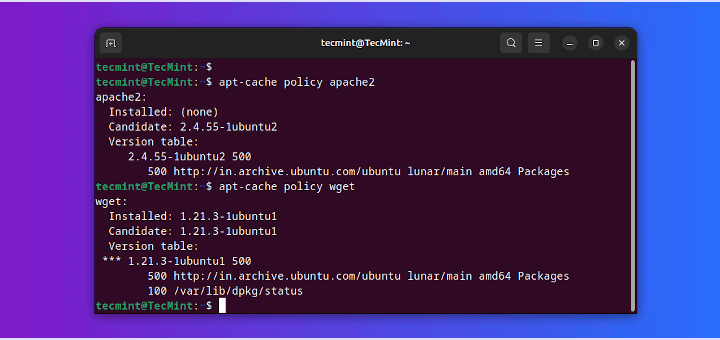
6. Verify a Package deal Set up Standing
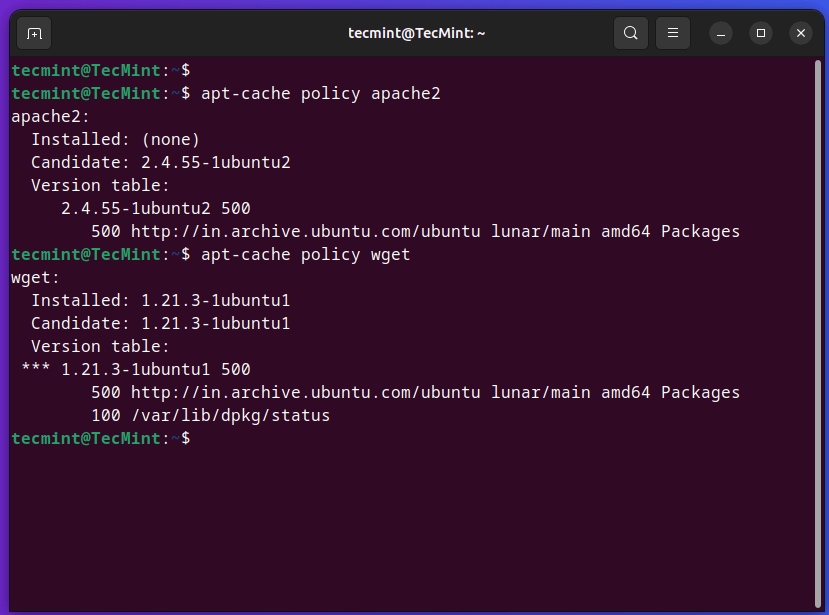
The apt-cache coverage command is used to print detailed details about the package deal set up standing and accessible variations. It supplies an outline of the candidate variations that may be put in, in addition to the presently put in model, if relevant.
$ sudo apt-cache coverage apache2
Conclusion
The apt-cache command gives important performance for looking, querying, and retrieving package deal data in Debian-based techniques.
By leveraging the ability of apt-cache, customers can streamline the set up, upgrading, and elimination of software program packages, enhancing system stability and effectivity within the course of.