One vital factor to grasp beneath Linux System/Server Administration is bundle administration utilizing totally different bundle administration instruments.
Completely different Linux distributions set up purposes in a pre-compiled bundle containing binary information, configuration information, and details about the applying’s dependencies.
Package deal administration instruments assist System/Server Directors in some ways corresponding to:
- Downloading and putting in software program.
- Compile software program from supply.
- Preserving monitor of all software program put in, updates, and upgrades.
- Dealing with dependencies.
- and likewise holding different details about put in software program and lots of extra.
On this information, we’re going to take a look at the apt command examples, that are mostly utilized in Debian-based Linux distributions, corresponding to Ubuntu, to handle software program packages.
The apt is a command-line-based bundle administration device that’s used to handle bundle set up, upgrades, and removing in Debian-based Linux distributions, corresponding to Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and others.
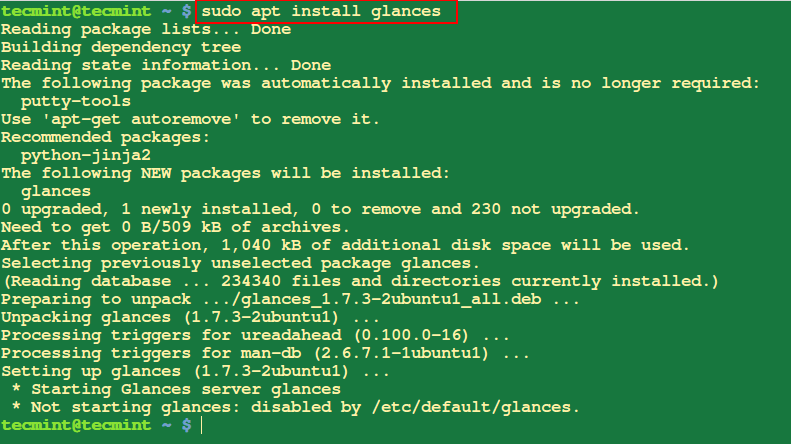
1. Set up Package deal in Ubuntu
To put in a bundle named “glances“, you’ll use the ‘apt set up‘ command which is able to set up a bundle together with the wanted dependencies.
$ sudo apt set up glances
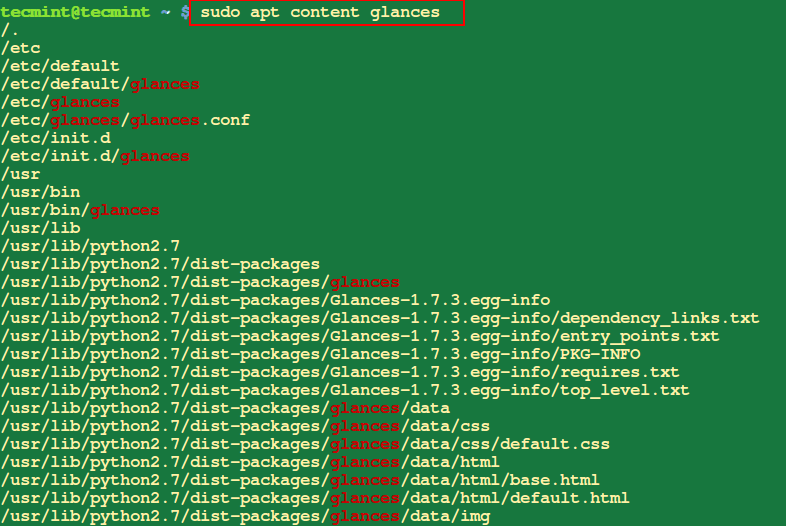
2. View Put in Information From a Package deal
The next ‘apt content material‘ command will show a listing of information and directories which might be put in in your system as a part of the desired bundle referred to as glances.
$ sudo apt content material glances
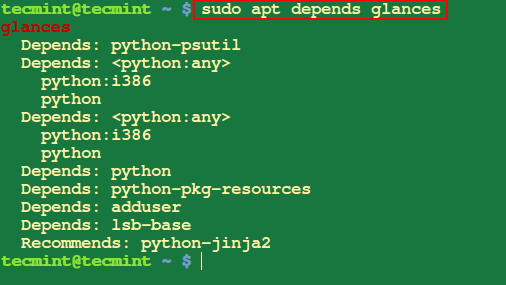
3. Examine the Dependencies of a Package deal in Ubuntu
To view the dependencies of a bundle you need to use the apt relies upon command, which shows a listing of the dependencies of the desired bundle referred to as glances.
$ sudo apt relies upon glances
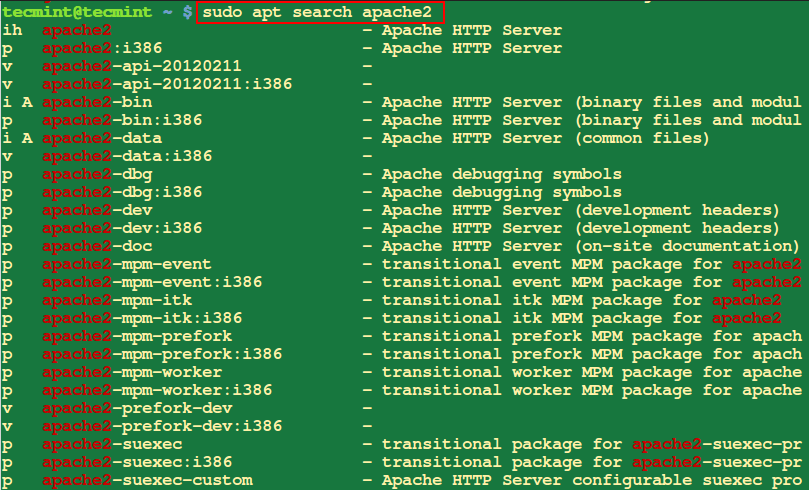
4. Seek for a Package deal in Ubuntu
The apt search command is used to seek for packages within the repositories obtainable based mostly on key phrases of their names or descriptions.
For instance, to seek for packages associated to the apache2 internet server, you’ll use the next command:
$ sudo apt search apache2
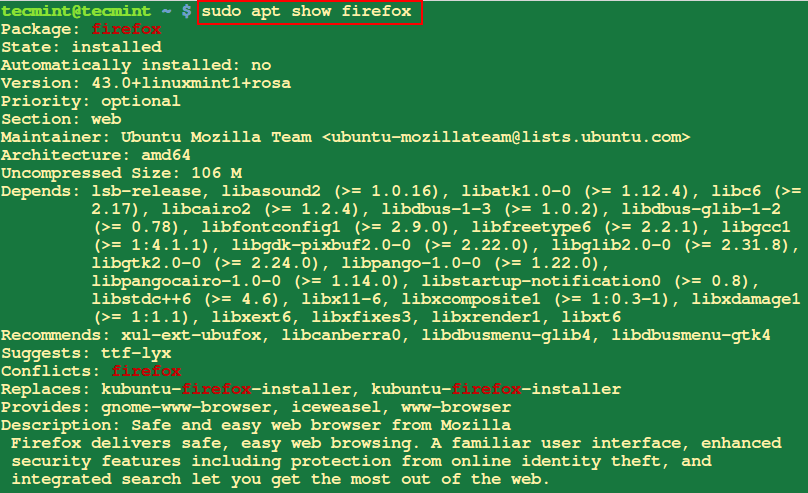
5. Present Info A couple of Package deal in Ubuntu
The apt present command is used to show detailed details about a selected bundle, which incorporates its model, dimension, description, dependencies, and different related particulars.
$ sudo apt present firefox
6. Examine Package deal for Any Damaged Dependencies
Typically throughout bundle set up, you could get errors regarding damaged bundle dependencies, to examine that you simply wouldn’t have these issues run the command beneath with the bundle identify.
$ sudo apt examine firefox

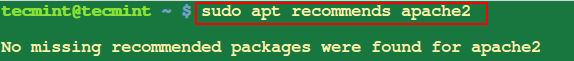
7. Record Lacking Dependencies of Package deal
To view the really helpful lacking packages for the apache2 bundle, you need to use the apt recommends command as proven.
$ sudo apt recommends apache2
8. Examine the Model of Put in Package deal on Ubuntu
The apt model command means that you can examine the put in model and availability of a bundle within the repositories.
$ sudo apt model firefox

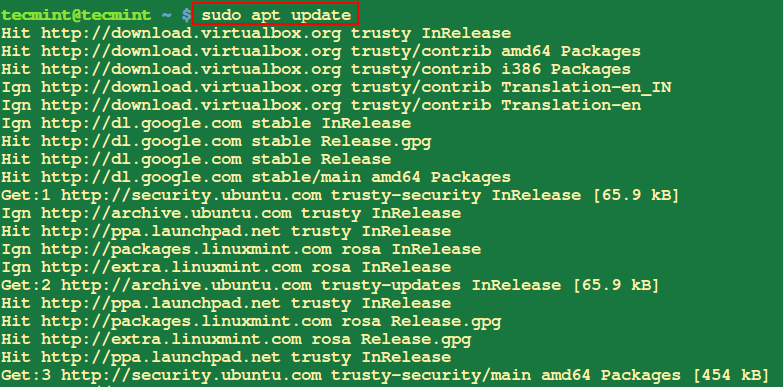
9. Replace All Packages On Ubuntu
The apt replace command will make it easier to to obtain a listing of packages from totally different repositories included in your system and updates them when there are new variations of packages and their dependencies.
$ sudo apt replace
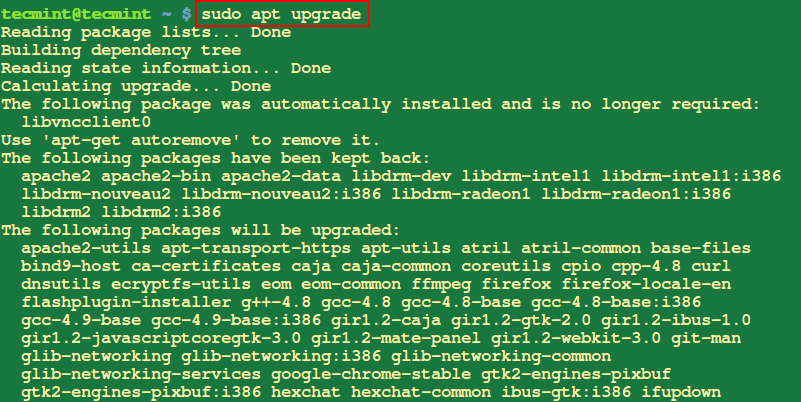
10. Improve Ubuntu System
The apt improve command is used to improve put in packages on a system to their newest obtainable variations. It retrieves the most recent bundle variations from the repositories and installs them, changing any older variations which might be presently put in.
$ sudo apt improve
11. Take away Unused Packages in Ubuntu
The apt autoremove command is used to take away packages that have been robotically put in as dependencies however are now not wanted by some other bundle in your system.
These packages might have been put in previously to fulfill the dependencies of different packages, but when these dependencies are now not current, the packages grow to be pointless.
$ sudo apt autoremove
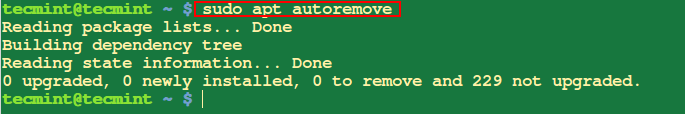
12. Clear Apt Cache in Ubuntu
The apt autoclean or apt clear command is used to wash up the native repository cache by eradicating previous bundle information which might be now not wanted.
$ sudo apt autoclean or $ sudo apt clear
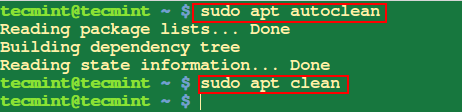
13. Utterly Take away a Package deal in Ubuntu
While you run apt with take away, it solely removes the bundle information however configuration information stay on the system. Subsequently, you’ll have to use purge to take away a bundle and its configuration information.
$ sudo apt purge glances
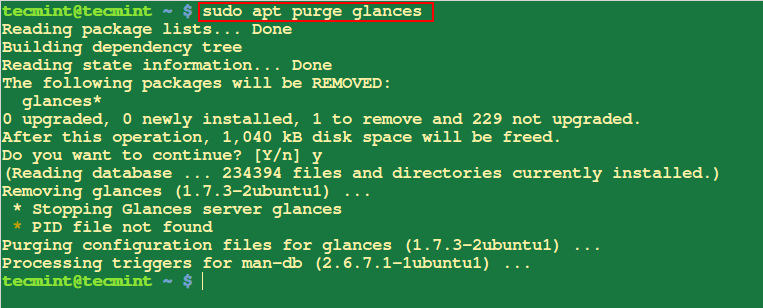
14. Set up Deb Package deal in Ubuntu
To set up a .deb bundle file, run the command beneath with the filename as an argument as follows:
$ sudo apt deb atom-amd64.deb
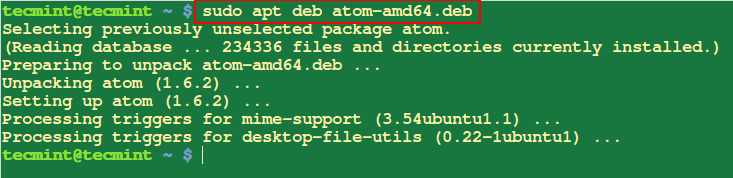
15. Uninstall Packages in Ubuntu
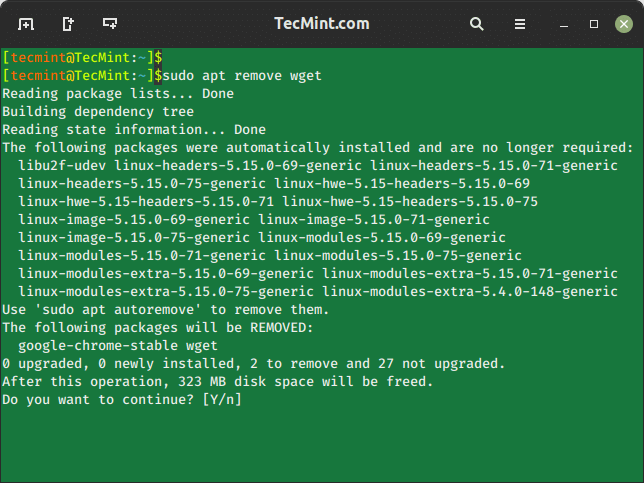
The apt take away command is used to uninstall or take away a selected bundle out of your system.
$ sudo apt take away wget
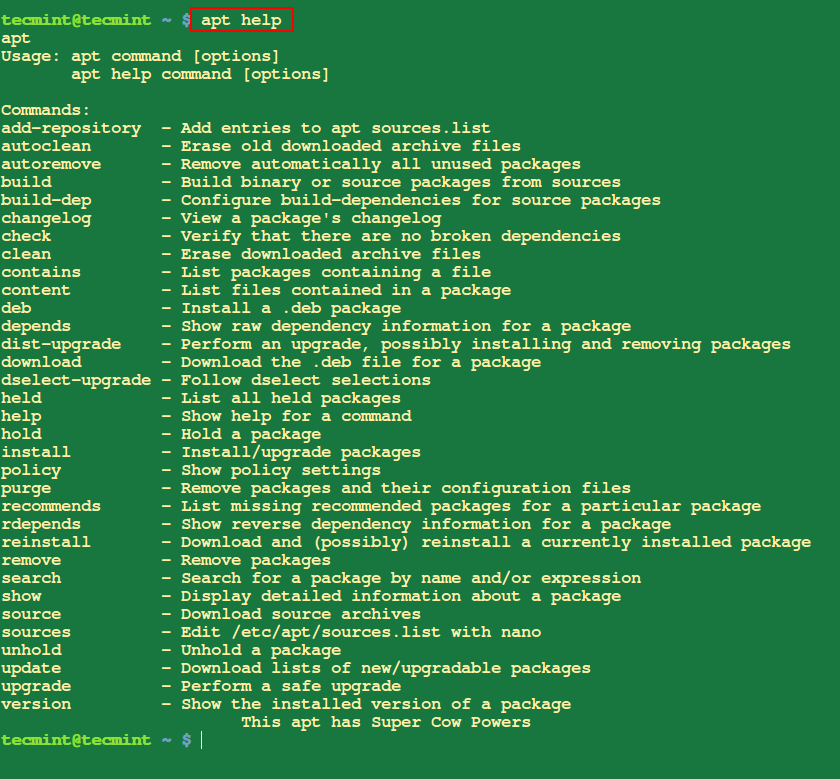
16. APT Command Assist
The apt assist command gives a built-in assist system that may present data on the way to use varied apt instructions and their choices.
$ apt assist
Abstract
Do not forget that good Linux bundle administration might help you keep away from breaking your system. There are such a lot of different bundle administration instruments that you need to use in Linux.
You possibly can share with us what you utilize and your expertise with it. I hope the article is useful and for any extra data, depart a remark within the remark part.
![Learn how to Use apt Instructions in Ubuntu/Debian [16 Examples] Learn how to Use apt Instructions in Ubuntu/Debian [16 Examples]](https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/apt-Command-Examples.png)