The apt-get command was the first package deal administration command utilized in Debian-based Linux distributions previous to the introduction of the apt command.
With the apt-get command, you possibly can set up, take away, improve, search, and handle packages in your system. Nonetheless, ranging from Ubuntu 16.04 and Debian 9, the apt command grew to become the really useful command-line software for package deal administration, though apt-get continues to be accessible and purposeful.
What’s apt-get Command?
The apt-get command is a robust and free package deal administration command line program, that’s used to work with Ubuntu’s APT (Superior Packaging Instrument) library to carry out the set up of recent software program packages, eradicating present software program packages, upgrading of present software program packages, and even used to upgrading the whole working system.
The syntax for the apt-get command is as follows:
$ sudo apt-get <choices> <command>
Right here, <choices> characterize any further flags or modifiers you need to use with the command, and <command> specifies the motion you wish to carry out, akin to putting in, upgrading, eradicating, or trying to find packages.
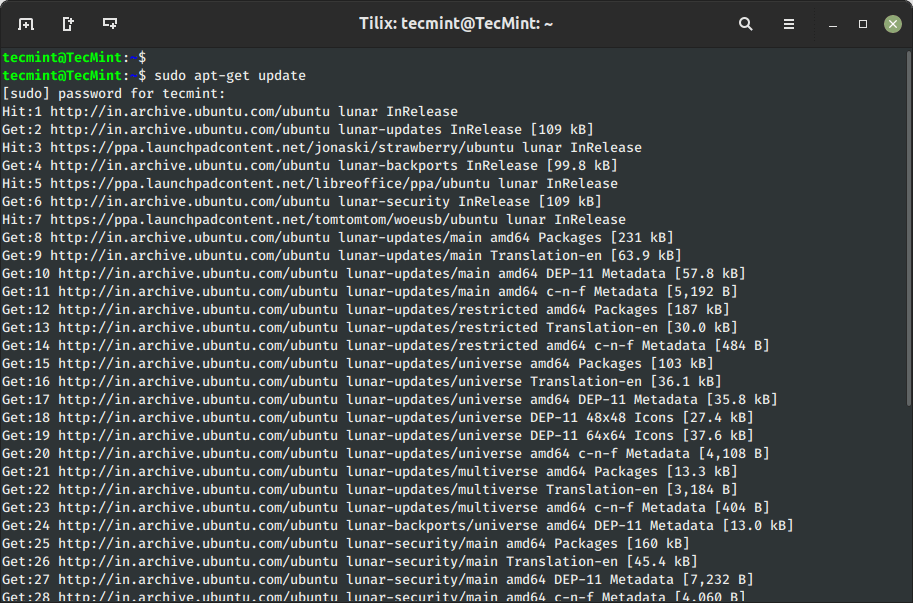
1. Replace Ubuntu System Packages
The ‘replace‘ command is used to resynchronize the package deal index information from the sources laid out in /and many others/apt/sources.listing file. The replace command fetched the packages from their areas and replace the packages to newer variations.
$ sudo apt-get replace
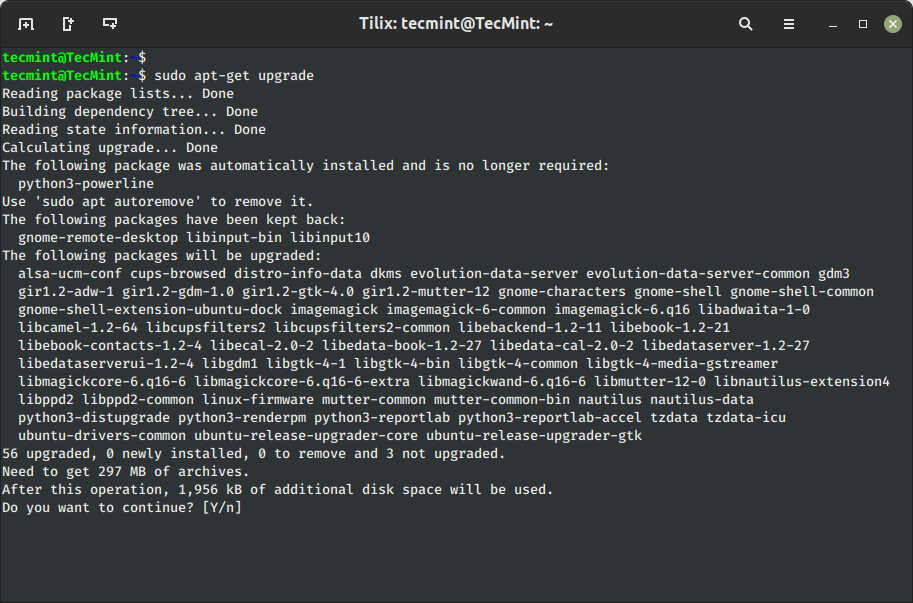
2. Improve Ubuntu System Packages
The ‘improve‘ command is used to improve all of the at present put in software program packages on the system. Below any circumstances at present put in packages are usually not eliminated or packages that aren’t already put in neither retrieved nor put in to fulfill improve dependencies.
$ sudo apt-get improve
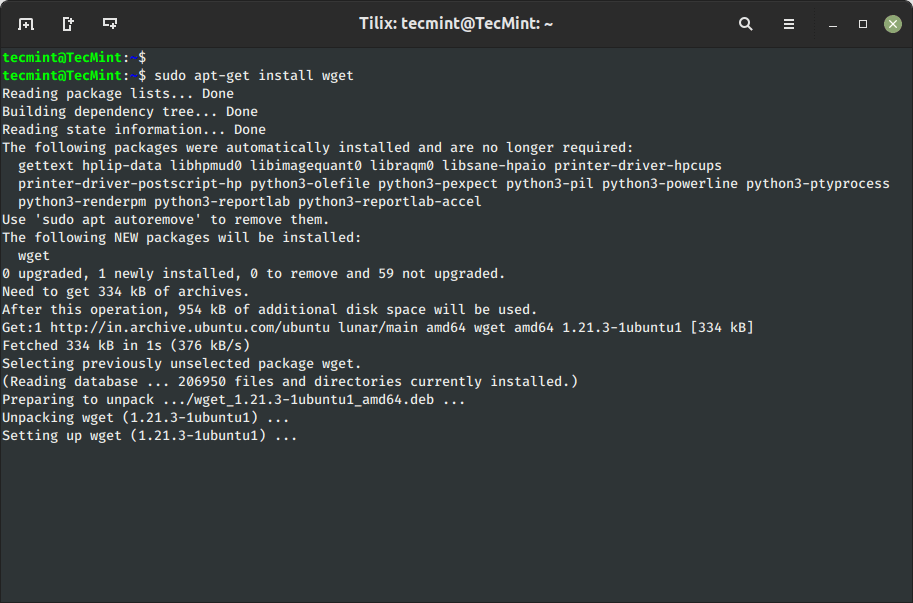
3. Set up Bundle in Ubuntu
The ‘set up‘ sub command is tracked by a number of packages wishing for set up or upgrading from the repositories. For instance, to put in or replace the package deal named wget, you possibly can run:
$ sudo apt-get set up wget
Alternatively, it’s also possible to use the apt-cache command to seek for a package deal earlier than putting in within the system package deal cache based mostly on a given search time period akin to identify or description.
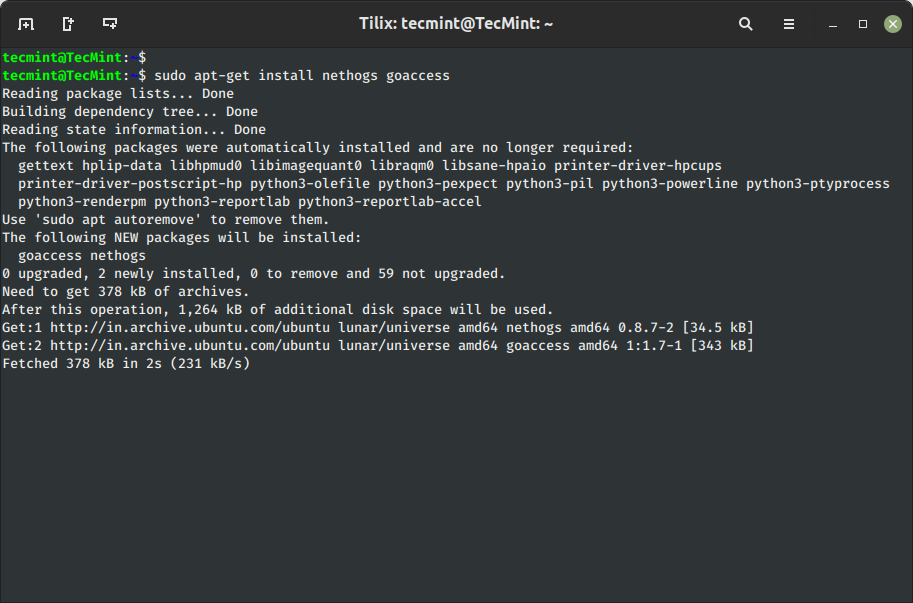
4. Set up A number of Packages in Ubuntu
You may add a couple of package deal identify together with the command with the intention to set up a number of packages on the identical time. For instance, the next command will set up packages ‘nethogs‘ and ‘goaccess‘.
$ sudo apt-get set up nethogs goaccess
5. Set up A number of Packages Utilizing Wildcard
With the assistance of standard expression, you possibly can add a number of packages with one string. For instance, we use * wildcard to put in a number of packages that comprise the ‘*identify*‘ string, the identify could be ‘package-name‘.
$ sudo apt-get set up '*identify*'
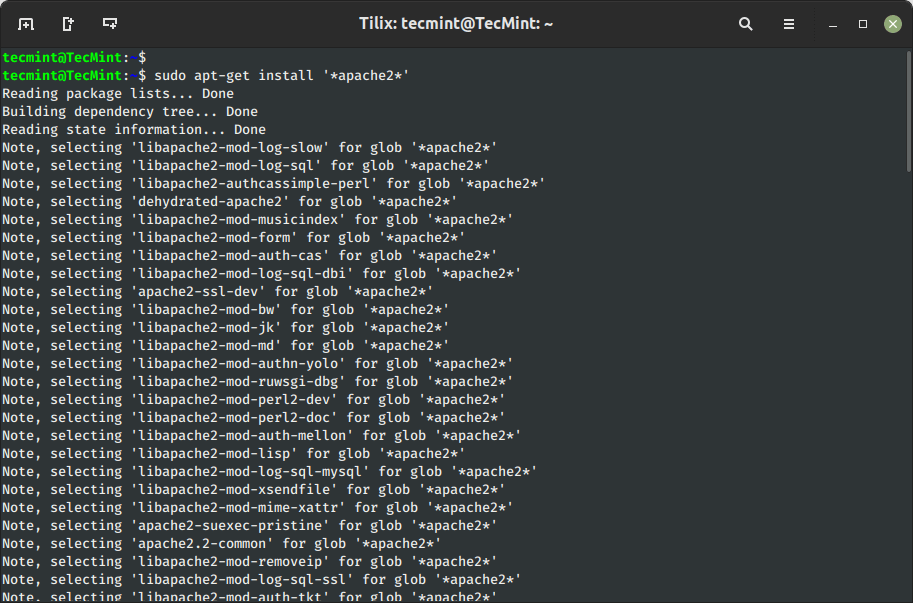
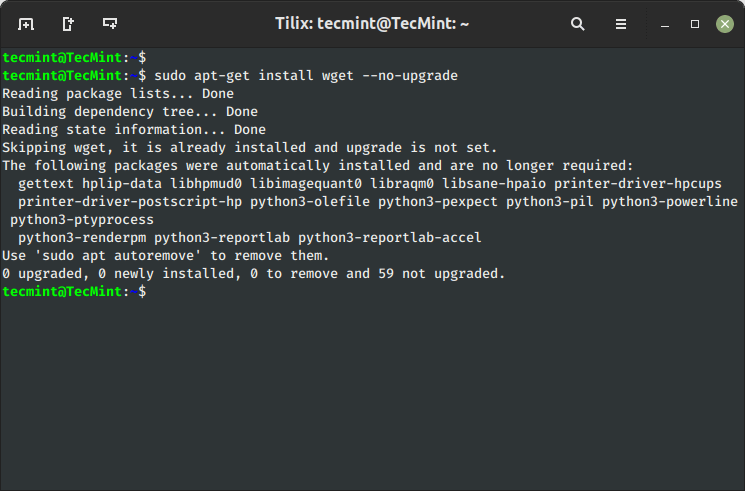
6. Set up Bundle With out Upgrading
Utilizing sub ‘--no-upgrade‘ command will forestall already put in packages from upgrading.
$ sudo apt-get set up packageName --no-upgrade
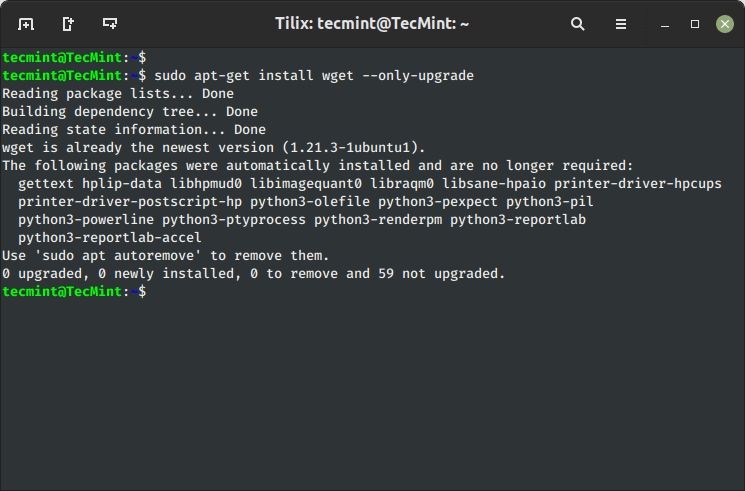
7. Replace a Single Bundle
The ‘--only-upgrade‘ command doesn’t set up new packages but it surely solely upgrades the already put in packages and disables new set up of packages.
$ sudo apt-get set up packageName --only-upgrade
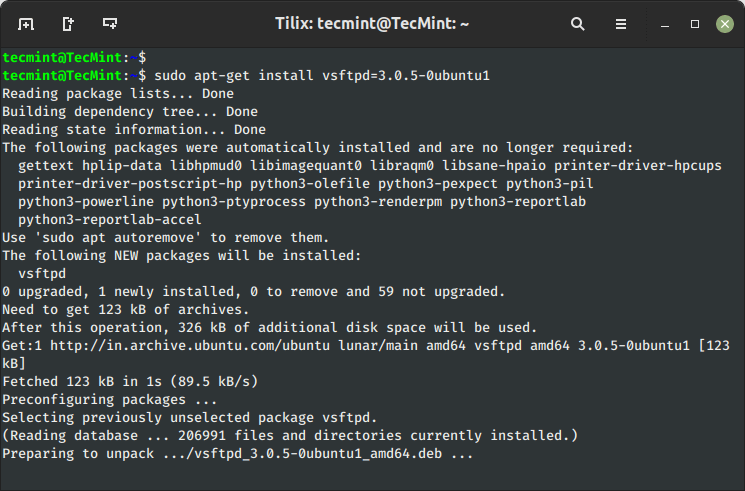
8. Set up Particular Bundle Model on Ubuntu
Let’s say you want to set up solely particular variations of packages, merely use the ‘=‘ with the package deal identify and append desired model.
$ sudo apt-get set up vsftpd=3.0.5-0ubuntu1
9. Uninstall Bundle With out Configuration
To uninstall software program packages with out eradicating their configuration information (for later re-use of the identical configuration), use the take away command as proven.
$ sudo apt-get take away vsftpd
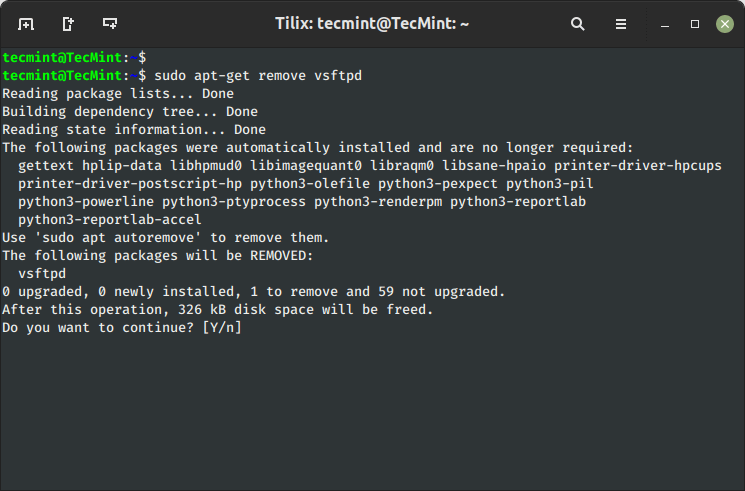
10. Utterly Take away Bundle with Configuration
To take away software program packages together with their configuration information, use the ‘purge‘ sub-command as proven under.
$ sudo apt-get purge vsftpd
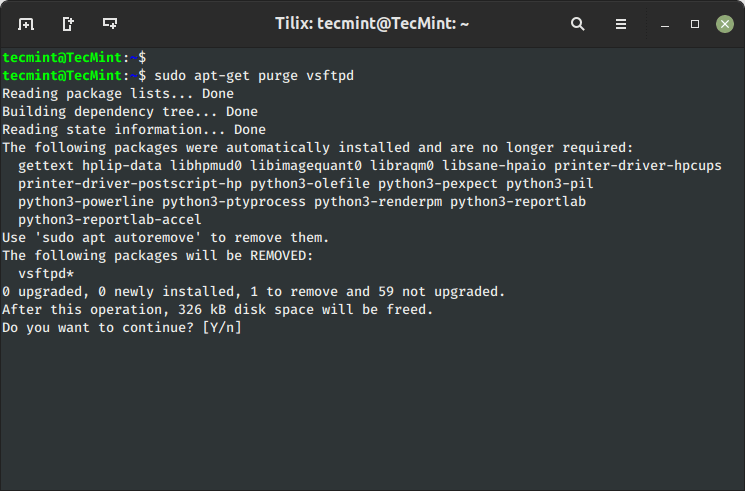
Alternatively, you possibly can mix each instructions collectively as proven under.
$ sudo apt-get take away --purge vsftpd
11. Clear Apt Cache to Save Disk Area
The ‘clear‘ command is used to liberate the disk area by cleansing retrieved (downloaded) .deb information (packages) from the native repository.
$ sudo apt-get clear OR $ sudo apt-get autoclean
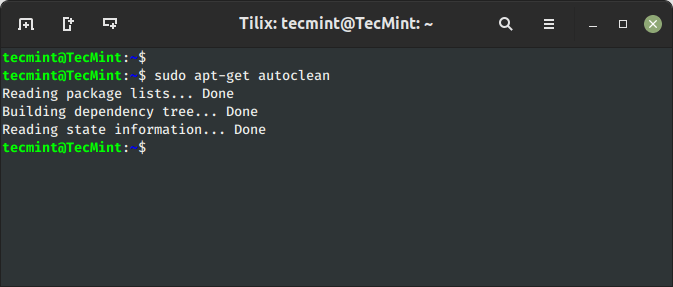
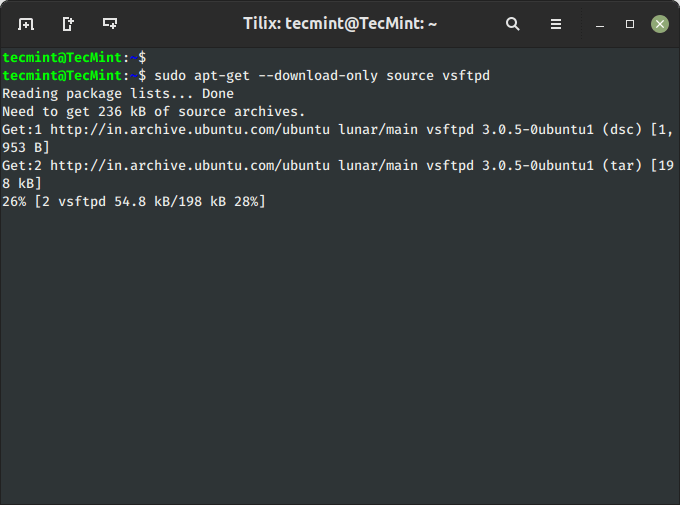
12. Obtain Supply Code of a Bundle in Ubuntu
To obtain solely the supply code of a selected package deal, use the choice ‘--download-only supply‘ with ‘package-name‘ as proven.
$ sudo apt-get --download-only supply vsftpd
13. Obtain and Extract Supply Bundle in Ubuntu
To obtain and unpack the supply code of a package deal to a selected listing, sort the next command.
$ sudo apt-get supply vsftpd
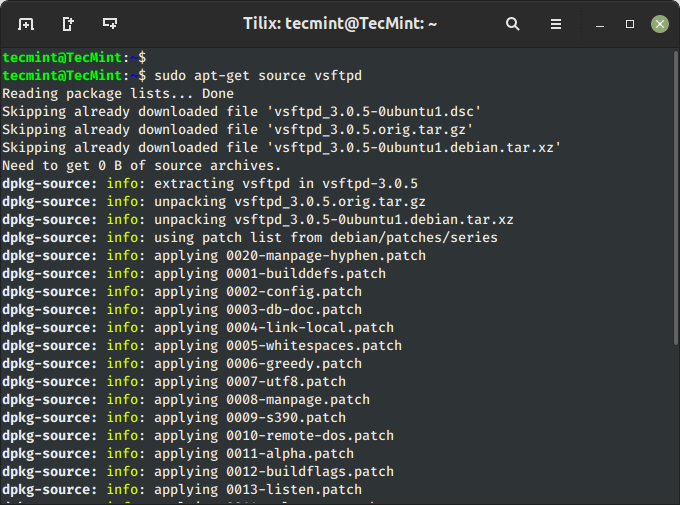
You could encounter one widespread error “E: You have to put some ‘deb-src’ URIs in your sources.listing” when making an attempt to obtain the supply code of a package deal from the repositories.
14. Compile Ubuntu Bundle from Supply
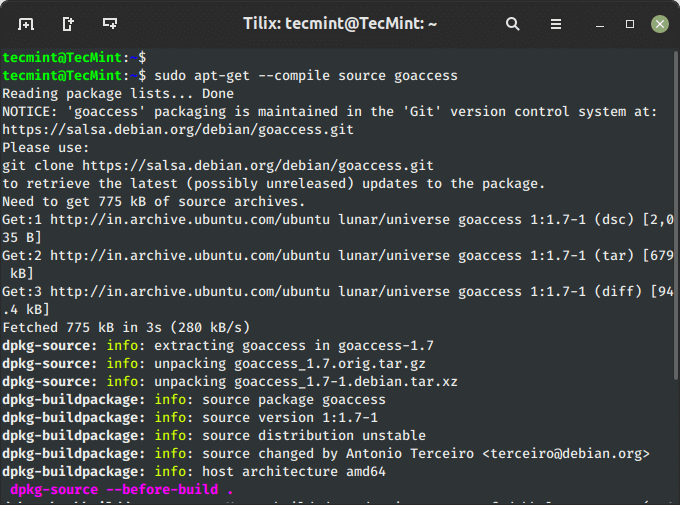
It’s also possible to obtain, unpack and compile the supply code on the identical time, utilizing the choice ‘--compile‘ as proven under.
$ sudo apt-get --compile supply goaccess
15. Obtain Bundle With out Putting in
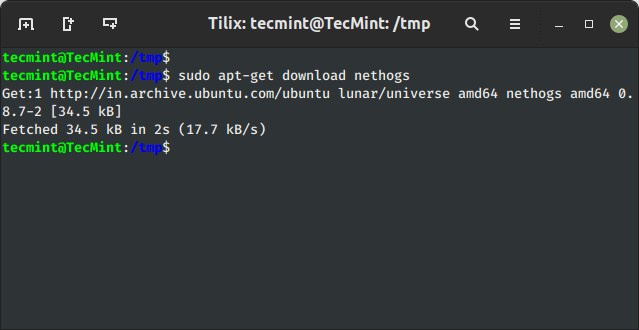
Utilizing the ‘obtain‘ possibility, you possibly can obtain any given package deal with out putting in it. For instance, the next command will solely obtain the ‘nethogs‘ package deal to the present working listing.
$ sudo apt-get obtain nethogs
16. View Bundle Changelog in Ubuntu
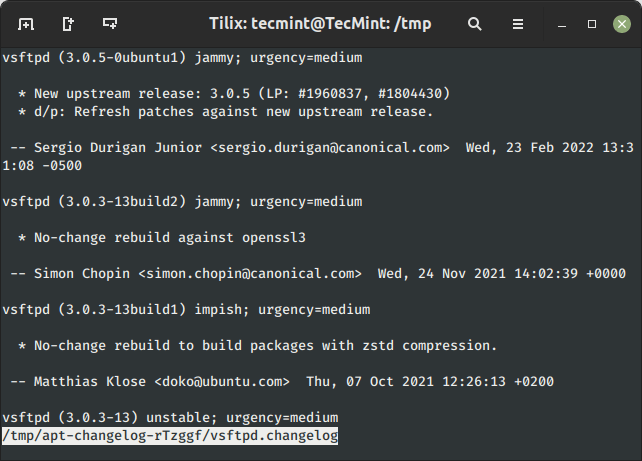
The ‘changelog‘ flag downloads a package deal change-log and reveals the package deal model that’s put in.
$ sudo apt-get changelog vsftpd
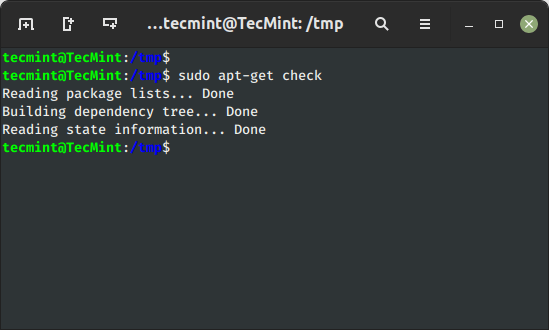
17. View Damaged Dependencies in Ubuntu
The ‘examine‘ command is a diagnostic software, which is used to replace the package deal cache and examine for damaged dependencies.
$ sudo apt-get examine
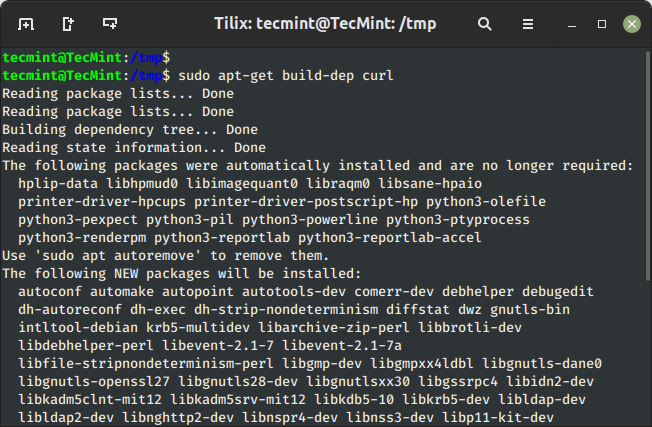
18. Set up Construct Dependencies of Bundle
The ‘build-dep‘ command searches the native repositories within the system and installs the construct dependencies for the curl package deal. If the package deal doesn’t exist within the native repository it is going to return an error code.
$ sudo apt-get build-dep curl
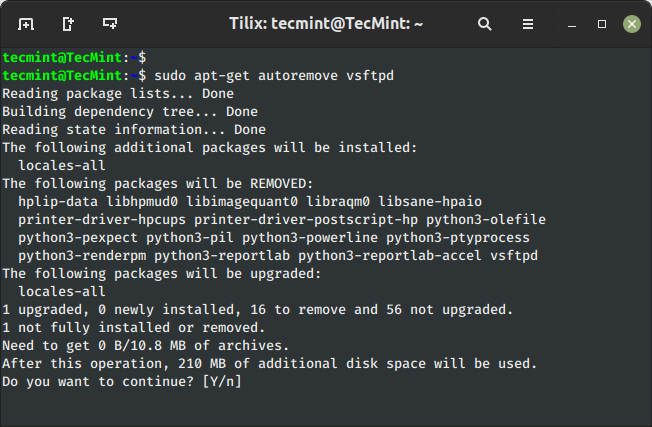
19. Auto Take away Put in Packages
The ‘autoremove‘ sub-command is used to auto-remove packages that have been actually put in to fulfill dependencies for different packages however have been now not required. For instance, the next command will take away an put in package deal with its dependencies.
$ sudo apt-get autoremove vsftpd
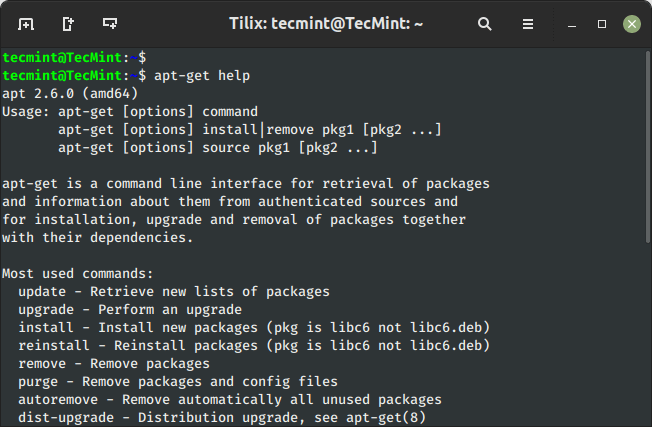
20. apt-get Command Assist
The apt-get assist command shows the built-in assist documentation with the accessible choices to make use of with the apt-get command.
$ sudo apt-get assist
I’ve lined many of the accessible choices with the apt-get command, however nonetheless, there are extra choices accessible, you possibly can examine them out utilizing ‘man apt-get‘ from the terminal.
I hope you loved studying this text, If I’ve missed something and you want to me so as to add to the listing. Please be happy to say this within the remark under.
Learn Additionally : 20 Helpful Linux YUM Instructions for Bundle Administration
![Learn how to Use ‘apt-get’ Command in Ubuntu [20 Examples] Learn how to Use ‘apt-get’ Command in Ubuntu [20 Examples]](https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/apt-get-Command-Examples.png)