The “Pandas” library supplies a robust information construction named “DataFrame”, which might retailer tabular information with columns and rows in Python. Many operations may be carried out on DataFrame, similar to including or eradicating information, including or eradicating indexes, sorting columns, and others. To entry or choose particular rows primarily based on some situations, similar to index values, labels, or situations, a number of strategies are utilized in Python.
This tutorial will clarify an in depth information on choosing Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the index.
Tips on how to Get the Pandas DataFrame Rows Based mostly on Indexes in Python?
The next strategies are used to get the Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the index:
Methodology 1: Get the Pandas DataFrame Rows Based mostly on Index Utilizing “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The “DataFrame.iloc[]” technique selects rows and columns by accepting the index or place worth as an argument. This can be utilized to get the Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the index worth. Let’s perceive it by way of the next examples:
Instance 1: Get Single Row Based mostly on Index Utilizing “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The next code is used to get the only row primarily based on the DataFrame index:
import pandas
data_value = {‘Identify’:[“Anna”,“Lily”,“Joseph”,“Henry”],‘Age’:[19,21,14,22],‘Intercourse’:[‘F’,‘F’,‘M’,‘M’],‘Top’:[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value)
print(df, ‘n’)
print(df.iloc[2])
Within the above code:
- The “pandas” and “numpy” modules are imported.
- The “pandas.DataFrame()” takes the dictionary information as an argument and retrieves the Pandas DataFrame.
- The “df.iloc()” technique will get the desired DataFrame row by taking the index worth as an argument.
Output
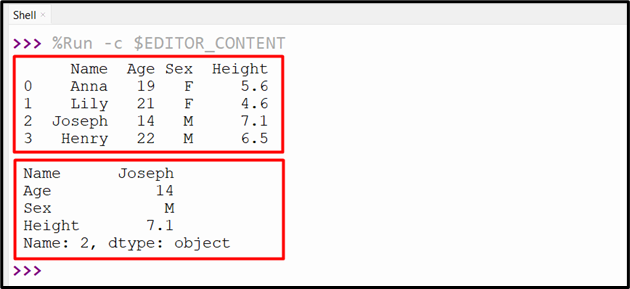
The DataFrame row positioned at index “2” is returned to the console.
Instance 2: Get A number of Rows Based mostly on Index Utilizing “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The beneath code is used to return the a number of rows primarily based on the index:
import pandas
data_value = {‘Identify’:[“Anna”,“Lily”,“Joseph”,“Henry”],‘Age’:[19,21,14,22],‘Intercourse’:[‘F’,‘F’,‘M’,‘M’],‘Top’:[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value)
print(df, ‘n’)
print(df.iloc[[0,3]])
Within the above code:
- The “df.iloc[]” technique takes the a number of index worth as an argument and returns the DataFrame rows primarily based on that index.
Output
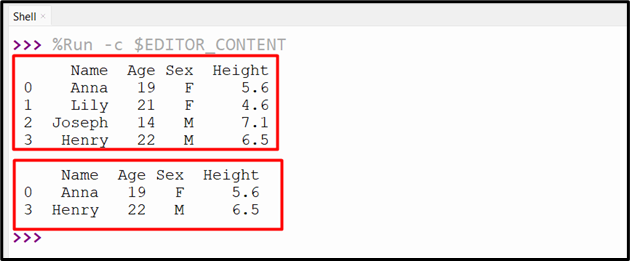
The a number of rows have been retrieved primarily based on the a number of index worth.
Instance 3: Get A number of Rows Based mostly on Index Vary Utilizing “DataFrame.iloc[]”
We are able to additionally get a number of rows primarily based on the precise index vary. Right here is an instance:
import pandas
data_value = {‘Identify’:[“Anna”,“Lily”,“Joseph”,“Henry”],‘Age’:[19,21,14,22],‘Intercourse’:[‘F’,‘F’,‘M’,‘M’],‘Top’:[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value)
print(df, ‘n’)
print(df.iloc[1:5],‘n’)
print(df.iloc[:1],‘n’)
print(df.iloc[:3],‘n’)
print(df.iloc[–1:],‘n’)
Within the above code:
- The “df.iloc[]” technique is used a number of instances to get Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the precise index ranges.
- The “df.iloc[]” technique is used to get the primary, final and first three rows of Pandas DataFrame.
Output
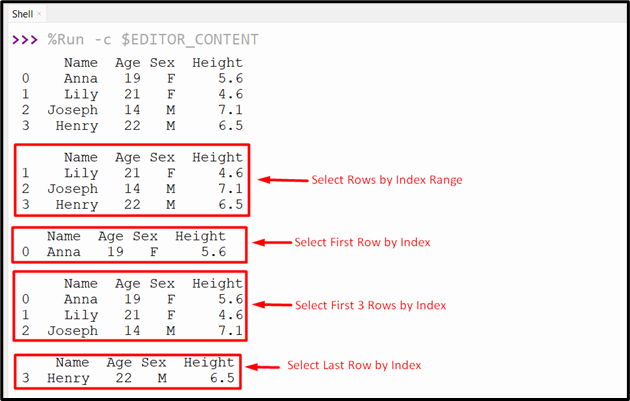
Methodology 2: Get the Pandas DataFrame Rows Based mostly on Index Utilizing “DataFrame.loc[]”
The “DataFrame.loc[]” technique is used to pick out rows primarily based on the index by accepting label(s) or a Boolean array as an argument. Let’s make the most of this technique to get the Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the index worth.
Instance 1: Get Single Row Based mostly on Index Label Utilizing “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The beneath instance is used to get a single row primarily based on the index label:
import pandas
data_value = {‘Identify’:[“Anna”,“Lily”,“Joseph”,“Henry”],‘Age’:[19,21,14,22],‘Intercourse’:[‘F’,‘F’,‘M’,‘M’],‘Top’:[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value,index=[‘a’,‘b’,‘c’,‘d’])
print(df, ‘n’)
print(df.loc[‘c’])
Within the above code:
- The “pandas” module is imported.
- The “pandas.DataFrame()” perform takes the dictionary information and index labels as arguments and retrieves the Pandas DataFrame.
- The “df.loc[]” technique takes the index label “c” as an argument and retrieves the DataFrame rows.
Output
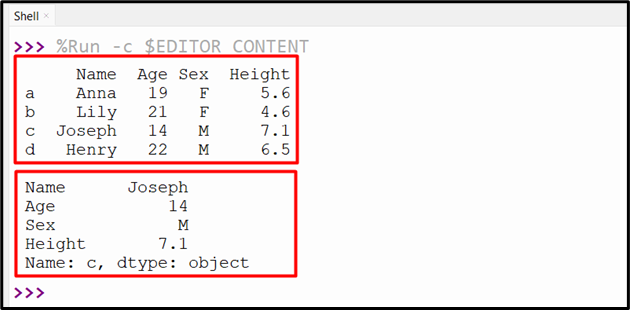
The DataFrame row primarily based on the index label has been retrieved.
Instance 2: Get A number of Rows Based mostly on Index Label Utilizing “DataFrame.loc[]”
Let’s overview the beneath code:
import pandas
data_value = {‘Identify’:[“Anna”,“Lily”,“Joseph”,“Henry”],‘Age’:[19,21,14,22],‘Intercourse’:[‘F’,‘F’,‘M’,‘M’],‘Top’:[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value,index=[‘a’,‘b’,‘c’,‘d’])
print(df, ‘n’)
print(df.loc[[‘d’,‘c’]])
Within the above code:
- The “df.loc[]” technique takes the a number of index labels similar to “d” and “c” as an argument and retrieves the desired DataFrame rows.
Output
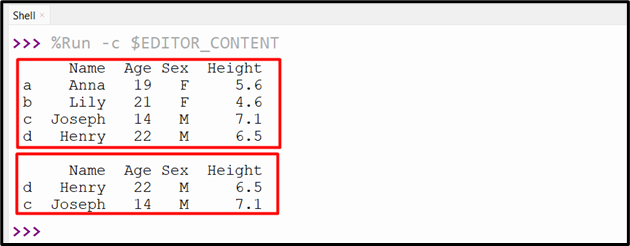
The a number of rows have been retrieved efficiently.
Instance 3: Get Rows Between Index Labels Utilizing “DataFrame.loc[]”
Right here is the code to get rows between index labels:
import pandas
data_value = {‘Identify’:[“Anna”,“Lily”,“Joseph”,“Henry”],‘Age’:[19,21,14,22],‘Intercourse’:[‘F’,‘F’,‘M’,‘M’],‘Top’:[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value,index=[‘a’,‘b’,‘c’,‘d’])
print(df, ‘n’)
print(df.loc[‘b’:‘d’])
Within the above code:
- The “df.loc[]” technique takes the index vary “b:d” as an argument and retrieves the a number of rows primarily based on the precise vary.
Output
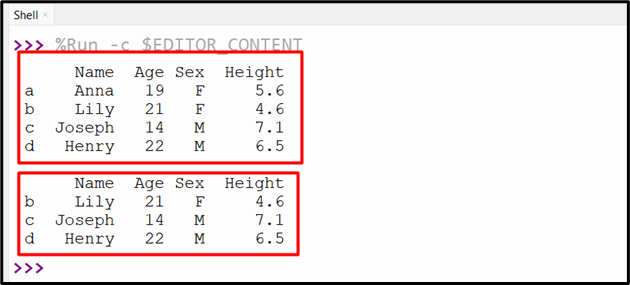
The a number of rows have been retrieved efficiently.
Conclusion
The “DataFrame.iloc[]” and the “DataFrame.loc[]” strategies of the “Pandas” module are used to get the Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the index. The “iloc[]” technique takes the index integer worth, and the “loc[]” technique accepts the index label to get the only or a number of rows of DataFrame. This Python information offered an in depth tutorial on choosing Pandas DataFrame rows primarily based on the index worth utilizing quite a few examples.