Python supplies numerous capabilities and modules for various points, together with easy to advanced duties. For example, to loop over a set and preserve monitor of the indexes of the objects. In such a case, the “enumerate()” operate comes into impact that’s used to retrieve the required rely worth together with the merchandise worth.
This tutorial will clarify a complete information on the “enumerate()” operate utilizing the beneath content material:
What’s the Python “enumerate()” Perform?
The “enumerate()” operate is utilized in Python to rely the objects in an iterable resembling an inventory, tuple, or others and return the rely and the merchandise collectively.
Syntax
enumerate(iterable, begin=0)
Parameters
Within the above syntax:
-
- The “iterable” parameter specifies an iterator object.
- The elective “begin” parameter specifies the “index” worth from the place the counter wants to start out.
- The “commonplace/default” worth is “0”.
Return Worth
The “enumerate()” operate retrieves an enumerate object.
Instance 1: Making use of the “enumerate()” Perform to the Specified Iterator Object
The next instance code demonstrates the working of the Python “enumerate()” operate on a goal object:
list_name = [‘Joseph’, ‘Anna’, ‘Henry’]
enum_obj = enumerate(list_name)
print(enum_obj, ‘n’)
print(checklist(enum_obj))
Within the above code:
-
- The checklist “list_name” is created.
- The “enumerate()” operate takes the checklist “list_name” as an argument and retrieves the enumerated object that accommodates a default counter together with an iterable worth.
- The enumerated object is then reworked into an inventory through the “checklist()” operate.
Output
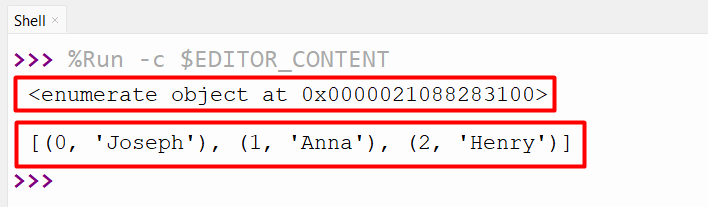
The enumerated object containing the iterable worth together with the default counter has been proven within the above output.
Instance 2: Making use of the “enumerate()” Perform to Iterator Object With the Specified Counter Worth
The beneath code is used so as to add the required counter worth to the enumerated object:
list_name = [‘Joseph’, ‘Anna’, ‘Henry’]
enum_obj = enumerate(list_name, 10)
print(enum_obj, ‘n’)
print(checklist(enum_obj))
Within the above code traces, the default counter worth of the “enumerate()” operate is modified to the required counter worth “10” to start out the counter from that worth.
Output
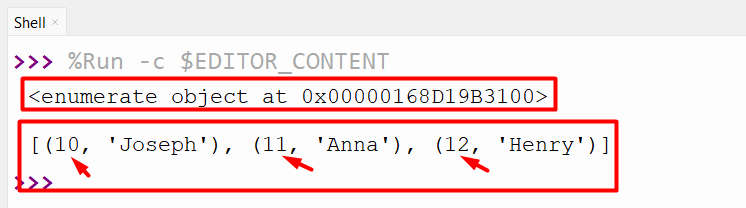
The enumerated object with a specified begin counter worth has been displayed.
Instance 3: Making use of the “enumerate()” Perform With “for” Loop to Loop/Iterate By means of the Enumerate Object
The “for” loop iterates by the enumerated object. Right here is an instance code:
list_name = [‘Joseph’, ‘Anna’, ‘Henry’]
for rely, i in enumerate(list_name):
print(rely, i)
print()
On this code, the “for” loop is used to iterate by the enumerated object and present the iterable worth together with the default counter utilizing the “print()” operate.
Output
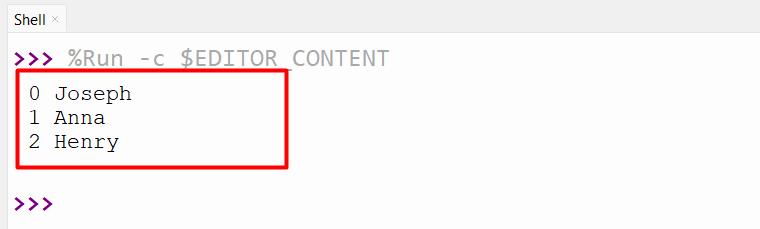
Primarily based on the above output, the enumerated object has been iterated efficiently.
Instance 4: Making use of the “enumerate()” Perform With “for” Loop to Iterate/Loop Over the Enumerate Object With the Specified Counter Worth
The “for” loop can even iterate the enumerated object ranging from the required counter worth. Right here is an instance:
list_name = [‘Joseph’, ‘Anna’, ‘Henry’]
for rely, i in enumerate(list_name, 10):
print(rely, i)
print()
Within the above code block, the required counter worth “10” is handed to the “enumerate()” operate to start out counting values from the required counter until the tip.
Output
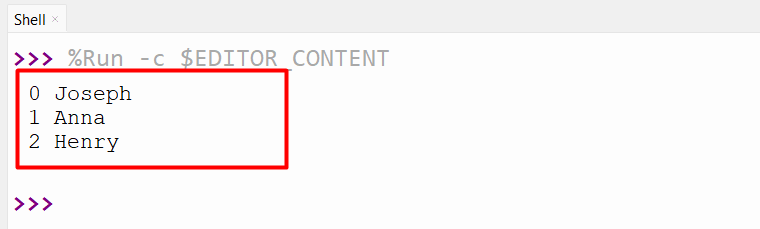
Primarily based on the above output, the enumerated object has been iterated and counted from the required worth.
Conclusion
The “enumerate()” operate in Python is utilized to rely the weather of the required iterable and return the rely and the merchandise collectively. This operate retrieves an enumerated object that accommodates a counter with objects/parts of the iterator. The counter worth may also be modified and handed to the “enumerate()” operate. This submit introduced an in depth information on the “enumerate()” operate utilizing applicable examples.