There isn’t a constraint on the kind of worth that may be saved inside an inventory in Python. Which means that the listing variable in Python can truly retailer one other listing, or a number of lists as the weather of the listing. Nevertheless, when new programmers are getting began with the listing inside an inventory, they typically get confused. Subsequently, this submit will work as a information and clarify tips on how to create an inventory inside one other listing in Python.
Let’s get began with the primary methodology to create an inventory inside an inventory.
Technique 1: Utilizing the Record Initializer
The simplest and most basic means of making an inventory and even a nested listing is by utilizing the listing initializer notation “[ ]”. For the nested listing, merely use the sq. brackets on the inside listing once more. To reveal this, let’s create a nested listing of numbers utilizing the next strains of code:
listVar= [ [1,2,3,4] , [5,6,7,8] ]
As you’ll be able to see, the listing “listVar” comprises two parts, and each of those parts are particular person lists containing numeric values. To confirm this, merely print out the primary ingredient of the listVar variable and print out its sort by utilizing the kind() methodology as properly:
print(listVar[1])
print(sort(listVar[1]))
When that is executed, it produces the next output on the terminal:
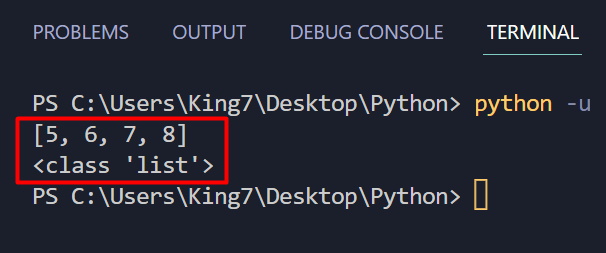
As you’ll be able to see, the values of the primary ingredient (listVar) have been printed and the kind is proven as “listing”.
Furthermore, two separate lists can be utilized to create a nested listing by utilizing the listing initializing notation. To reveal this, use the next code snippet:
listVar_2 = [5,6,7,8]
listVar_1= [listVar_1, listVar_2]
print(listVar_1)
When this code is executed, it produces the next outcome on the terminal:
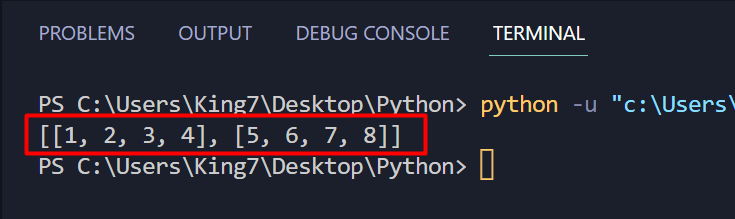
The output verifies that you’ve created a nested listing or an inventory of lists utilizing the initializing listing notation.
Technique 2: Utilizing the append() Technique
The append() methodology can be utilized to append an inventory to a different listing. To reveal this methodology, take the next code snippet:
listVar_2 = [5,6,7,8]
listVar_3= [10,20,30]
listVar_3.append(listVar_1)
listVar_3.append(listVar_2)
print(listVar_3)
On this above code snippet:
-
- Three totally different listing variables are created and the aim is to append() the primary two lists into the third listing variable.
- The append() methodology known as on the third listing “listVar_3” utilizing the dot-operator and within the argument the lists “listVar_1” and the “listVar_2” is handed.
- Lastly, the listVar_3 is printed on the terminal.
When this code is executed, it produces the next outcome on the terminal:
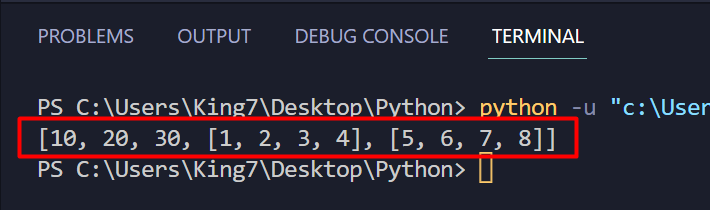
Within the output, you’ll be able to observe that the primary three parts are numeric values. Nevertheless, the fourth and the fifth variables are particular person lists, that means you’ve got efficiently created an inventory of lists.
Conclusion
If you’re in search of a technique to create an inventory of lists in Python, then in that case, make the most of the listing initialization notation, which makes use of sq. brackets to create lists, or use the append() methodology to append already present lists into one other listing. Each of those strategies have been demonstrated completely on this article.