Syntax:
- Lambda Expression: (parameters) => expression
- Lambda Assertion: { conditional statement1 statement2 … }
Instance 1:
Create the “fertilizers” checklist that holds 5 strings. Make the most of the lambda expression that returns all of the strings from the checklist.
utilizing System.Linq;
utilizing System.Collections.Generic;
class LambdaExpressionExample {
static public void Most important()
{
// Create Listing of fertilizers
Listing fertilizers = new Listing();
fertilizers.Add(“Urea”);
fertilizers.Add(“nitrogen”);
fertilizers.Add(“potassium”);
fertilizers.Add(“Di-ammonium Phosphate”);
fertilizers.Add(“phosphorus”);
// Use LambdaExpression to pick out all of the fertilizers
var end result = fertilizers.Choose(inp1 => inp1);
foreach (var i in end result)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
Output:

Clarification:
1. Create checklist of string kind named “fertilizers”. Add 5 strings to this checklist.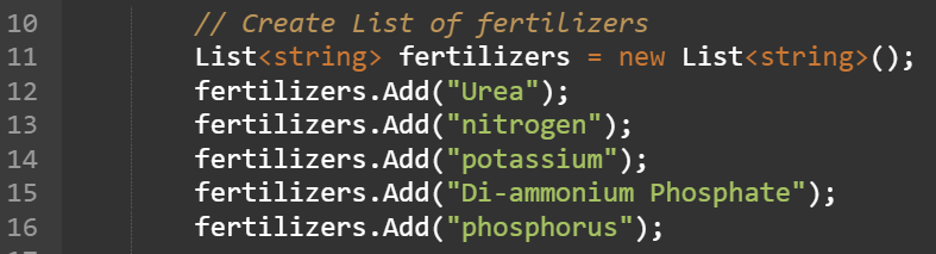
2. Use the lambda expression to pick out all of the fertilizers. Right here, the expression is used with the “Choose” operator. The expression is inp1 => inp1. Then, we use the “foreach” loop to show the strings which can be returned by the lambda expression.
Instance 2:
Use the lambda expression to pick out the fertilizers that embrace “Phosphate”.
utilizing System.Linq;
utilizing System.Collections.Generic;
class LambdaExpressionExample {
static public void Most important()
{
// Create Listing of fertilizers
Listing fertilizers = new Listing();
fertilizers.Add(“Urea”);
fertilizers.Add(“nitrogen”);
fertilizers.Add(“ortho – Phosphate “);
fertilizers.Add(“Di-ammonium Phosphate”);
fertilizers.Add(“phosphorus”);
// Use LambdaExpression to pick out the fertilizers that embrace – “Phosphate”
var end result = fertilizers.The place(inp1 => inp1.Incorporates(“Phosphate”));
foreach (var i in end result)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
Output:
There are two strings that embrace “Phosphate” in them.

Clarification:
1. Create a listing of string kind named “fertilizers”. Add 5 strings to this checklist.
2. Right here, the expression is used with the “The place” operator. The expression is inp1 => inp1.Incorporates(“Phosphate”). Then, we use the “foreach” loop to show the strings which can be returned by the lambda expression.
Instance 3:
Let’s have a listing (order_quantity) that holds three orders. Specify the lambda expression so as to add 5 to every order.
utilizing System.Linq;
utilizing System.Collections.Generic;
class LambdaExpressionExample {
static public void Most important()
{
// Create Listing of portions
Listing order_quantity = new Listing();
order_quantity.Add(5);
order_quantity.Add(7);
order_quantity.Add(8);
// Use LambdaExpression to five to every order.
var end result = order_quantity.Choose(inp1 => inp1 + 5);
foreach (var i in end result)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
Output:
The [5,7,8] checklist is reworked to [10,12,13].

Clarification:
1. Create the checklist of portions of Integer kind.
2. We choose the orders first after which add 5 to every order. So, the “Choose” operator is used. The expression is inp1 => inp1 + 5.
Instance 4:
Create a listing information supply of Occasion kind (with three attributes – Event_Name, Event_Status and Event_Budget) and return the data with the Event_Budget which is bigger than 5000.
utilizing System.Linq;
utilizing System.Collections.Generic;
// Create a category named – ‘Event_Source’ with 5 occasions.
public class Event_Source
{
public static void Most important()
{
// Occasion Listing
IList occasions = new Listing() {
new Occasion() {Event_Name = “Technical Camp”,Event_Status=“Deliberate”,Event_Budget =10000},
new Occasion() {Event_Name = “Advertising and marketing Camp”,Event_Status=“Accomplished”,Event_Budget =5000},
new Occasion() {Event_Name = “Different”,Event_Status=“Deliberate”,Event_Budget =1000},
new Occasion() {Event_Name = “Politics”,Event_Status=“Deliberate”,Event_Budget =13000},
new Occasion() {Event_Name = “Finance”,Event_Status=“Accomplished”,Event_Budget =20000},
};
//Event_Budget larger than 5000.
var end result = occasions.The place(inp1 => inp1.Event_Budget > 5000);
foreach(var i in end result){
Console.WriteLine(“NAME: “+i.Event_Name + ” STATUS: “+i.Event_Status + ” BUDGET: “ +i.Event_Budget);
}
}
}
public class Occasion{
public string Event_Name { get; set; }
public string Event_Status { get; set; }
public int Event_Budget { get; set; }
}
Output:
There are three data within the “occasions” checklist with the Event_Budget larger than 5000.

Clarification:
1. First, we create an “Occasion” class with three attributes.
2. Then, we create a listing of 5 occasions.
3. Utilizing the inp1 => inp1.Event_Budget > 5000 lambda expression, we choose the data with the Event_Budget larger than 5000.
Instance 5:
Make the most of the earlier code and alter the lambda expression. Return the occasions with the Event_Name that ends with “Camp” and with the Event_Status which is “Deliberate”.
//Lambda Expression – Event_Name ends with “Camp” and Event_Status is “Deliberate”.
var end result = occasions.The place(inp1 => inp1.Event_Name.EndsWith(“Camp”) && inp1.Event_Status==“Deliberate”);
foreach(var i in end result){
Console.WriteLine(“NAME: “+i.Event_Name + ” STATUS: “+i.Event_Status + ” BUDGET: “ +i.Event_Budget);
}
Output:
There is just one report that satisfies each situations.

Clarification:
Right here, we specify two situations within the lambda expression. The && (and) operator is used to make the 2 situations as True. The primary situation makes use of the EndsWith() methodology to examine if a string ends with the given string. The second situation makes use of the “Comparability” operator (==) to examine if each the values are equal or not.

Conclusion
In C#, the lambda expression takes the expressions/conditional statements as its physique with out a title. We have to specify the parameters. Then, the expressions are assigned to it. Mainly, these are used to filter the data from the given information supply, rework the weather, and choose the weather from the info supply/ sequence. On this information, we mentioned the 5 completely different examples that choose, filter, and rework the weather utilizing the lambda expression.