Bash helps if-else statements so to use logical reasoning in your shell scripts.
The generic if-else syntax is like this:
if [ expression ]; then
## execute this block if situation is true else go to subsequent
elif [ expression ]; then
## execute this block if situation is true else go to subsequent
else
## if not one of the above situations are true, execute this block
fiAs you possibly can discover:
elifis used for “else if” type of situation- The if else situations at all times finish with
fi - using semicolon
;andthenkey phrase
Earlier than I present the examples of if and else-if, let me share widespread comparability expressions (additionally known as take a look at situations) first.
Check situations
Listed below are the take a look at situation operators you need to use for numeric comparability:
| Situation | Equal to true when |
|---|---|
| $a -lt $b | $a < $b ($a is less than $b) |
| $a -gt $b | $a > $b ($a is greater than $b) |
| $a -le $b | $a <= $b ($a is less or equal than $b) |
| $a -ge $b | $a >= $b ($a is greater or equal than $b) |
| $a -eq $b | $a is the same as $b |
| $a -ne $b | $a shouldn’t be equal to $b |
In case you are evaluating strings, you need to use these take a look at situations:
| Situation | Equal to true when |
|---|---|
| “$a” = “$b” | $a is similar as $b |
| “$a” == “$b” | $a is similar as $b |
| “$a” != “$b” | $a is totally different from $b |
| -z “$a” | $a is empty |
There are additionally situations for file kind examine:
| Situation | Equal to true when |
|---|---|
| -f $a | $a is a file |
| -d $a | $a is a listing |
| -L $a | $a is a hyperlink |
Now that you’re conscious of the varied comparability expressions let’s have a look at them in motion in varied examples.
Use if assertion in bash
Let’s create a script that tells you if a given quantity is even or not.
Here is my script named even.sh:
#!/bin/bash
learn -p "Enter the quantity: " num
mod=$(($numpercent2))
if [ $mod -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Quantity $num is even"
fiThe modulus operation (%) returns zero when it’s completely divided by the given quantity (2 on this case).
🚧
Pay particular consideration to house. There have to be house between the opening and shutting brackets and the situations. Equally, house have to be earlier than and after the conditional operators (-le, == and so on).
Here is what it reveals once I run the script:
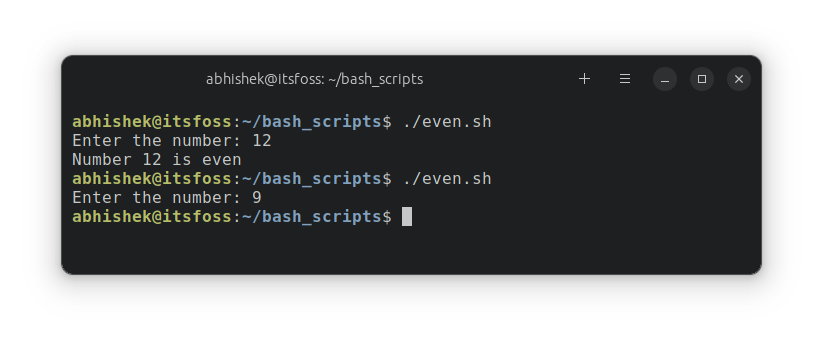
Did you discover that the script tells you when a quantity is even but it surely does not show something when the quantity is odd? Let’s enhance this script with using else.
Use if else assertion
Now I add an else assertion within the earlier script. This manner whenever you get a non-zero modulus (as odd numbers will not be divided by 2), it’s going to enter the else block.
#!/bin/bash
learn -p "Enter the quantity: " num
mod=$(($numpercent2))
if [ $mod -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Quantity $num is even"
else
echo "Quantity $num is odd"
fiLet’s run it once more with the identical numbers:
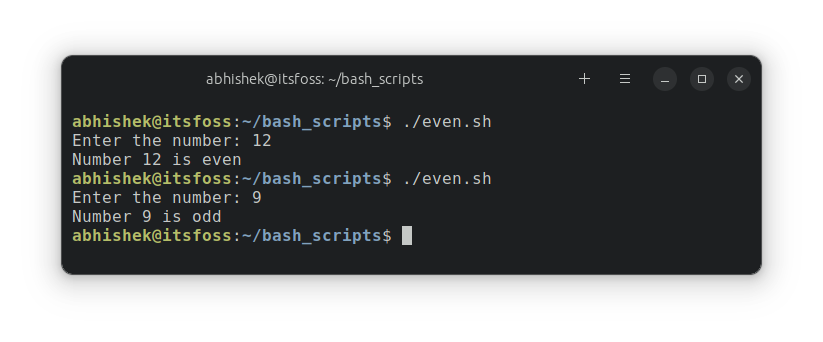
As you possibly can see, the script is best because it additionally tells you if the quantity is odd.
Use elif (else if) assertion
Here is a script that checks whether or not the given quantity is constructive or destructive. In arithmetic, 0 is neither constructive nor destructive. This script retains that truth in examine as nicely.
#!/bin/bash
learn -p "Enter the quantity: " num
if [ $num -lt 0 ]; then
echo "Quantity $num is destructive"
elif [ $num -gt 0 ]; then
echo "Quantity $num is constructive"
else
echo "Quantity $num is zero"
fiLet me run it to cowl all three circumstances right here:
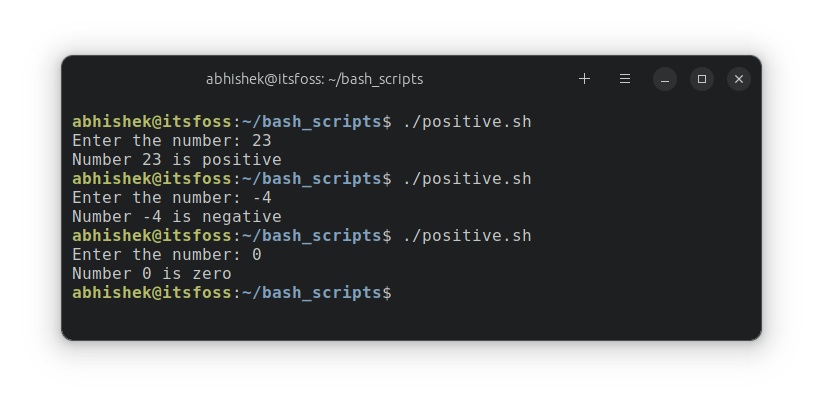
Mix a number of situations with logical operators
Thus far, so good. However are you aware that you could have a number of situations in a single through the use of logical operators like AND (&&), OR (||) and so on? It offers you the power to write down advanced situations.
Let’s write a script that tells you whether or not the given yr is a intercalary year or not.
Do you bear in mind the situations for being a intercalary year? It ought to be divided by 4 however whether it is divisible by 100, it isn’t a intercalary year. Nonetheless, whether it is divisible by 400, it’s a intercalary year.
Here is my script.
#!/bin/bash
learn -p "Enter the yr: " yr
if [[ ($(($year%4)) -eq 0 && $(($year%100)) != 0) || ($(($year%400)) -eq 0) ]]; then
echo "12 months $yr is intercalary year"
else
echo "12 months $yr is regular yr"
fi💡
Discover using double brackets [[ ]] above. It’s obligatory if you’re utilizing logical operators.
Confirm the script by working it with totally different knowledge:
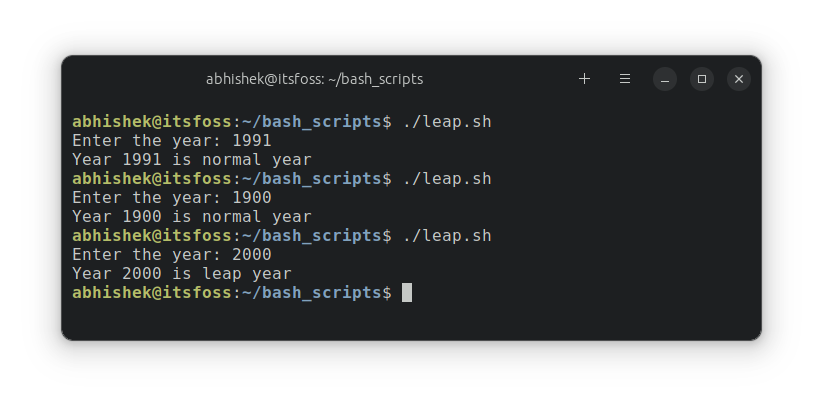
🏋️ Train time
Let’s do some exercise 🙂
Train 1: Write a bash shell script that checks the size of the string supplied to it as an argument. If no argument is supplied, it prints ’empty string’.
Train 2: Write a shell script that checks whether or not a given file exists or not. You may present the total file path because the argument or use it immediately within the script.
Trace: Use -f for file
Train 3: Improve the earlier script by checking if the given file is common file, a listing or a hyperlink or if it does not exist.
Trace: Use -f, -d and -L
Train 3: Write a script that accepts two string arguments. The script ought to examine if the primary string comprises the second argument as a substring.
Trace: Confer with the earlier chapter on bash strings
You could focus on your answer within the Group:
Follow Train in Bash Fundamentals Sequence #7: If Else Statements
In case you are following the Bash Fundamentals collection on It’s FOSS, you possibly can submit and focus on the solutions to the train on the finish of the chapter: Fellow skilled members are inspired to offer their suggestions to new members. Do observe that there might be a couple of reply to a given drawback.

I hope you might be having fun with the Bash Fundamentals Sequence. Within the subsequent chapter, you will study utilizing loops in Bash. Carry on bashing!
