Parted is a famend command-line utility designed to facilitate the administration of exhausting disk partitions in a user-friendly method.
With Parted, you possibly can effortlessly carry out duties resembling including, deleting, shrinking, and increasing disk partitions, whereas additionally managing the file programs related to them.
Over time, Parted has undergone vital growth and evolution, introducing varied enhancements and adjustments to its performance. Sure options have been retired, whereas new capabilities have been launched, rendering it a flexible software for partition administration.
This tutorial goals to supply a complete introduction to Parted, masking its elementary ideas and demonstrating sensible examples. In case you are new to Parted, it’s important to notice that any modifications made utilizing Parted are instantly written to the disk.
Subsequently, it’s essential to train warning whereas making an attempt to switch your disk partitions to keep away from unintended penalties or knowledge loss. All through this tutorial, we’ll information you step-by-step, guaranteeing that you simply grasp the fundamentals of Parted and perceive the potential implications of your actions when working with disk partitions.
When you intend to experiment with Parted, it’s endorsed to make the most of a digital machine or an previous pc/laptop computer that doesn’t include any crucial knowledge. When making modifications to a disk partition, it’s essential that the partition is just not actively in use.
Within the case of major partitions, you could take into account booting into rescue mode, which gives a protected surroundings for performing partition-related duties with out interference from the working working system. This precautionary method ensures the integrity of your useful knowledge and minimizes the chance of unintended penalties throughout partition manipulation.
Be aware: You will want to have root entry to the machine you may be engaged on to be able to use parted.
Find out how to Set up Parted on Linux
On many Linux distributions, parted comes pre-installed. If it’s not included in your distro, you possibly can set up it with:
$ sudo apt set up parted [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum set up parted [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/parted [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add parted [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S parted [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper set up parted [On OpenSUSE]
After getting made certain that parted is put in, you possibly can proceed additional to take a look at some real-world examples of parted command in the remainder of this text.
1. Test Parted Model
To watch an analogous message as depicted within the picture beneath, execute the next command. Please be aware that the output could differ barely relying in your particular model of Parted. By default, Parted will function in your major drive, sometimes recognized as /dev/sda, until in any other case specified.
$ parted
If you wish to exit parted, merely kind:
$ give up
2. Checklist Disk Partitions in Linux
Now that parted is began, let’s listing the partitions of the chosen exhausting disk. As talked about earlier, parted chooses your first drive by default. To see the disk partitions run print.
(parted) print
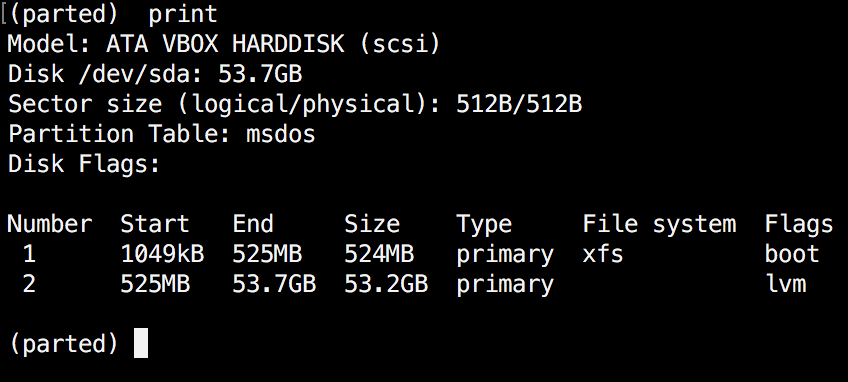
When working print, it’s going to additionally show the exhausting disk info and mannequin. Right here is an instance from an actual exhausting disk (not digital as proven within the picture above) :
(parted) print Mannequin: ATA TOSHIBA MQ01ACF0 (scsi) Disk /dev/sda: 320GB Sector dimension (logical/bodily): 512B/4096B Partition Desk: msdos Quantity Begin Finish Dimension Kind File system Flags 1 1049kB 256MB 255MB major ext2 boot 2 257MB 320GB 320GB prolonged 5 257MB 320GB 320GB logical lvm
Within the instance above, you possibly can see the disk mannequin, capability sector dimension, and partition desk.
3. Change or Swap Partition in Linux
When you’ve got multiple exhausting disk, you possibly can simply swap between disks, by utilizing the “choose” command. Within the instance beneath, I’ll swap from /dev/sda to /dev/sdb which is a secondary drive on my system.
To simply swap between disks you should utilize:
(parted) choose /dev/sdX
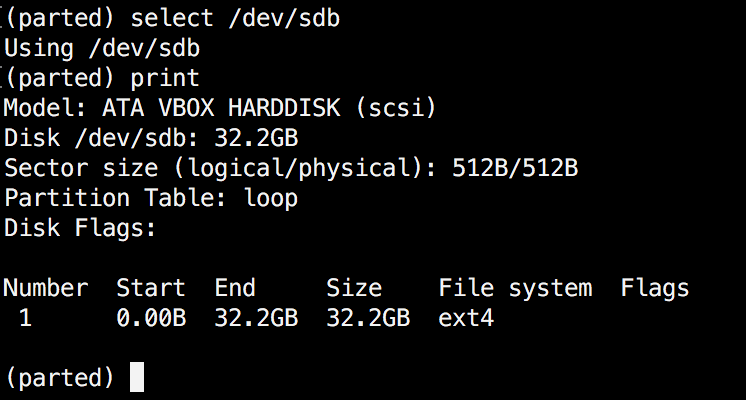
Change "X" with the letter of the disk to which you want to swap.
4. Create Partition in Linux
The parted can be utilized to create major and logical disk partitions. On this instance, I’ll present you how you can create a major partition, however the steps are the identical for logical partitions.
To create a brand new partition, parted makes use of “mkpart“. You can provide it further parameters like "major" or "logical" relying on the partition kind that you simply want to create.
Earlier than you begin creating partitions, it’s vital to just be sure you are utilizing (you may have chosen) the best disk.
Begin by utilizing print:
(parted) print
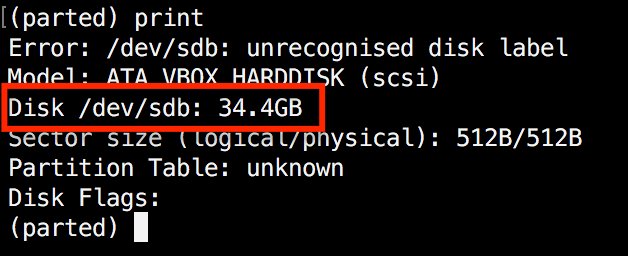
As proven within the above picture, we’re utilizing a digital drive of 34 GB. First, we’ll give the brand new disk a label after which create a partition and set a file system on it.
Now step one is to present the brand new disk a label identify with:
(parted) mklabel msdos
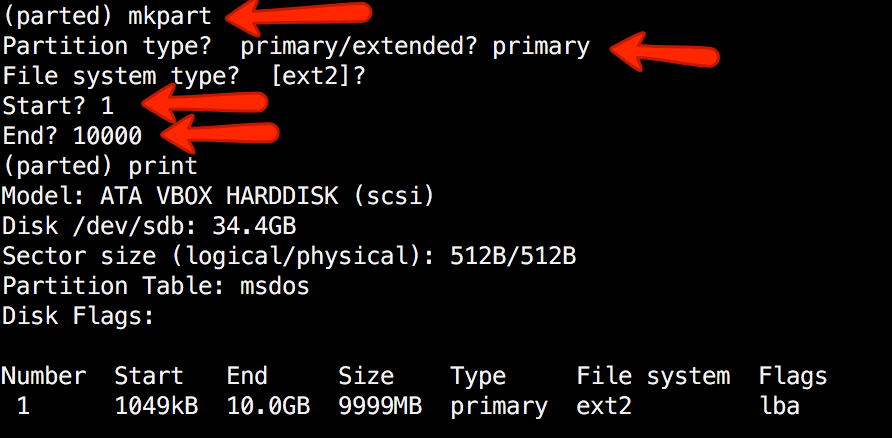
Now create the brand new partition with mkpart. The listed items are in megabytes (MB). We’ll create a 10 GB partition ranging from 1 to 10000:
(parted) mkpart Partition kind? major/prolonged? major File system kind? [ext2]? Begin? 1 Finish? 10000 (parted) print Mannequin: ATA VBOX HARDDISK (scsi) Disk /dev/sdb: 34.4GB Sector dimension (logical/bodily): 512B/512B Partition Desk: msdos Disk Flags: Quantity Begin Finish Dimension Kind File system Flags 1 1049kB 10.0GB 9999MB major ext2 lba
Subsequent, exit parted with "give up" command. We’ll format our new partition within the ext4 file system utilizing mkfs. To make this occur run the next command:
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
Be aware: It’s vital to pick out the best disk and partition when executing the above command!
Now let’s confirm our outcomes, by printing the partition desk on our secondary disk. Beneath file system column, it’s best to see ext4 or the file system kind that you’ve got determined to make use of in your partition:
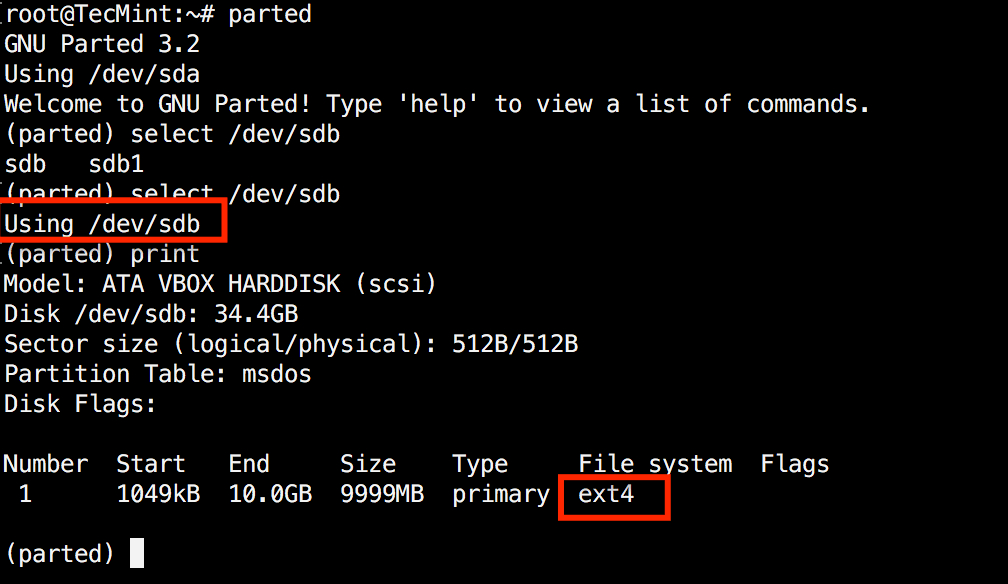
5. Resize Linux Disk Partition
Parted contains a number of helpful features and one in all them is "resizepart". As you may have most likely figured this out by now, "resizepart" helps you resize a partition.
Within the instance beneath, you will note how you can resize an present partition. For the aim of this instance, we will likely be utilizing the sooner created partition.
First, you have to to know the variety of the partition that you may be resizing. This may be simply discovered by utilizing "print":
(parted) print
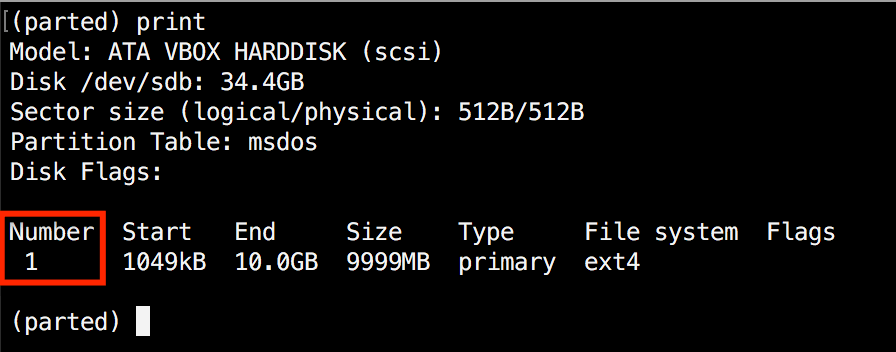
In our instance, the partition quantity is "1". Now run the resizepart command:
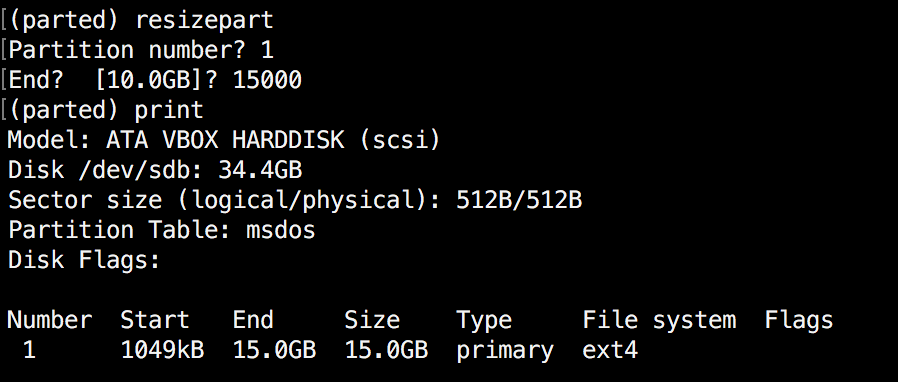
(parted) resizepart
You’ll be requested for the variety of the partition that you’ll resize. Enter its quantity. After that, you may be requested to set the brand new ending level for this partition. Do not forget that by default the items are in MB. In our instance, we’ve set the brand new partition dimension to 15 GB:
(parted) resizepart Partition quantity? 1 Finish? [10.0GB]? 15000
Now confirm the outcomes with "print":
(parted) print
6. Delete Linux Partition
The following factor you’ll be taught is how you can delete a partition out of your exhausting drive. To do that, you have to to make use of the rm command inside parted. To delete a disk partition you have to to know its quantity.
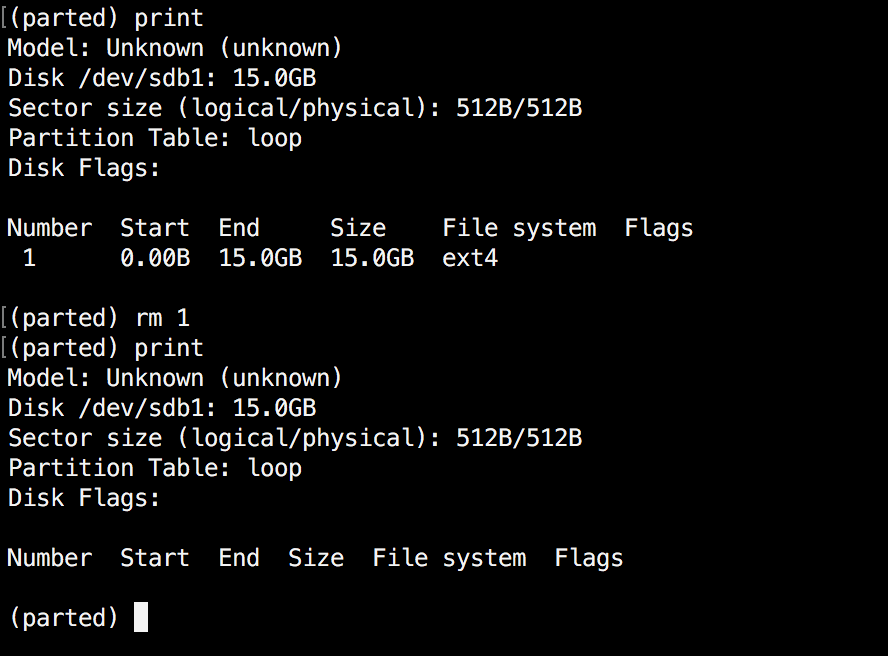
As talked about earlier, you possibly can simply receive this quantity by utilizing "print". In our instance, we’ll delete the partition with a quantity 1 from our secondary drive /dev/sdb1:
(parted) rm 1
Confirm the outcomes by printing the partitions desk:
7. Rescue Linux Disk Partition
Parted helps a “rescue" utility that helps you get well a misplaced partition between a beginning and ending level. If a partition is discovered inside that vary, it’s going to try to revive it.
Right here is an instance:
(parted) rescue Begin? 1 Finish? 15000 (parted) print Mannequin: Unknown (unknown) Disk /dev/sdb1: 15.0GB Sector dimension (logical/bodily): 512B/512B Partition Desk: loop Disk Flags: Quantity Begin Finish Dimension File system Flags 1 0.00B 15.0GB 15.0GB ext4
8 Change Linux Partition Flag
Utilizing parted, you possibly can change the state of a flag for disk partitions. The supported flags are:
- boot
- root
- swap
- hidden
- raid
- lvm
- lba
- legacy_boot
- irst
- esp
- palo
The states will be both "on" or "off". To vary a flag merely run "set" command inside parted:
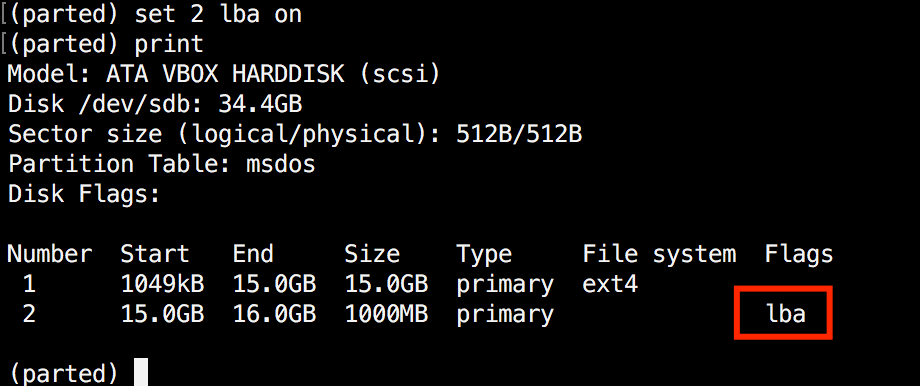
(parted) set 2 lba on
The above command units lba flag to on for the second partition. Confirm the outcomes with print:
Conclusion
Parted is a helpful and highly effective utility that may show you how to handle your disk partitions in Linux programs. As all the time, when working with disk partitions you should be further cautious.
It’s strongly really helpful to undergo parted man pages to be taught how one can customise its output and discover extra details about its capabilities.
When you’ve got any questions or feedback, please don’t hesitate to make use of the remark part beneath.