Apache is the world’s hottest, cross-platform HTTP internet server that’s generally utilized in Linux and Unix platforms to deploy and run internet purposes or web sites. Importantly, it’s straightforward to put in and has a easy configuration as effectively.
On this article, we are going to present the best way to test Apache internet server uptime on a Linux system utilizing completely different strategies/instructions defined under.
1. Systemctl Command
systemctl command is a utility for controlling the systemd system and repair supervisor; it’s used it to start out, restart, and cease providers, and past.
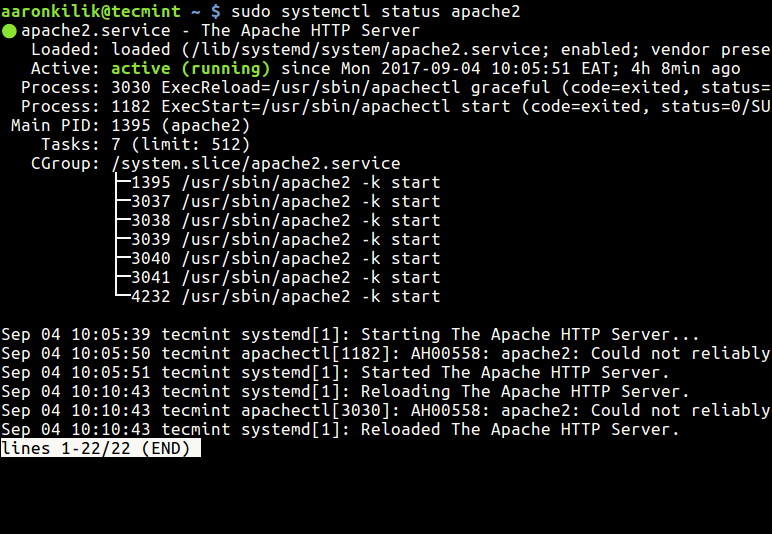
The systemctl standing sub-command, because the title states are used to view the standing of a service, you should use it to test the working standing of your Apache internet server.
$ sudo systemctl standing apache2 #Debian/Ubuntu # systemctl standing httpd #RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
2. Apachectl Command
The apachectl command is used to manage and handle the Apache, which is primarily used for beginning, stopping, and restarting the Apache internet server, in addition to performing different administrative duties.
$ sudo apachectl begin [Start Apache web server] $ sudo apachectl cease [Stop Apache web server] $ sudo apachectl restart [Restart Apache web server] $ sudo apachectl sleek [Gracefully Restart Apache web server] $ sudo apachectl configtest [Check Apache Configuration] $ sudo apachectl -V [Check Apache Version] $ sudo apachectl standing [Check Apache Status]
The apachectl command can be utilized to allow or disable Apache modules, together with the mod_status module, which offers an interface that shows details about the Apache internet server’s present standing and efficiency.
Allow Apache Server Standing in Debian/Ubuntu
The Apache server-status element is enabled by default within the file /and many others/apache2/mods-enabled/standing.conf configuration file.
$ sudo vi /and many others/apache2/mods-enabled/standing.conf
Contained in the <Location /server-status> part, add the next strains to permit entry out of your IP handle or community.
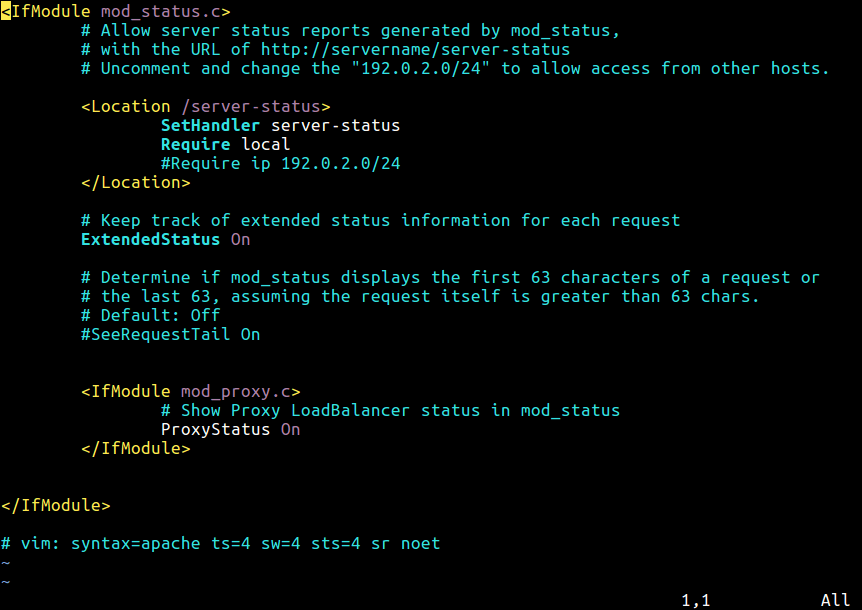
You too can use Require all granted to permit entry from all IPs however be cautious about safety implications.
Save the configuration file and restart the Apache service to use the adjustments:
$ sudo service apache2 restart
Allow Apache Server Standing in RHEL Programs
To allow the Apache server-status element in RHEL-based distributions, create a file under.
# vi /and many others/httpd/conf.d/server-status.conf
and add the next configuration.
<Location "/server-status">
SetHandler server-status
Require ip your_ip_address_or_network
</Location>
Save the file and shut it. Then restart the net server.
# systemctl restart httpd
If you’re primarily utilizing a terminal, then you definately additionally want a command-line internet browser reminiscent of lynx or hyperlinks.
$ sudo apt set up lynx #Debian/Ubuntu # yum set up hyperlinks #RHEL/CentOS
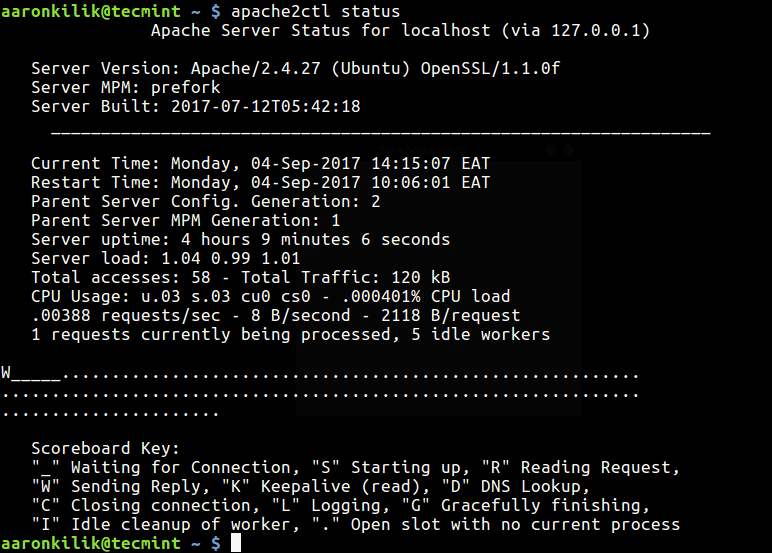
Then run the command under to test the Apache service uptime:
$ apachectl standing
Alternatively, use the URL under to view the Apache internet server standing info from a graphical internet browser:
http://localhost/server-status OR http:SERVER_IP/server-status
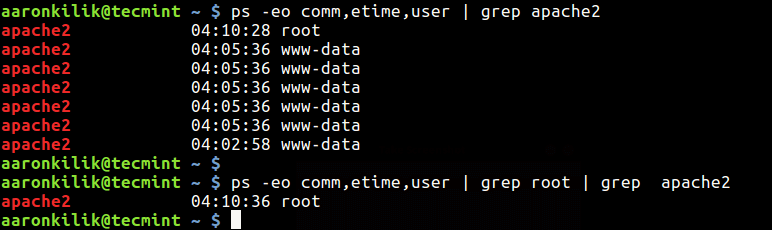
3. ps Command
ps command is used to point out info regarding a collection of the lively processes working on a Linux system, you should use it with the grep command to test Apache service uptime as follows.
Right here, is the flag:
-e– permits collection of each course of on the system.-o– is used to specify output (comm – command, etime – course of execution time, and consumer – course of proprietor).
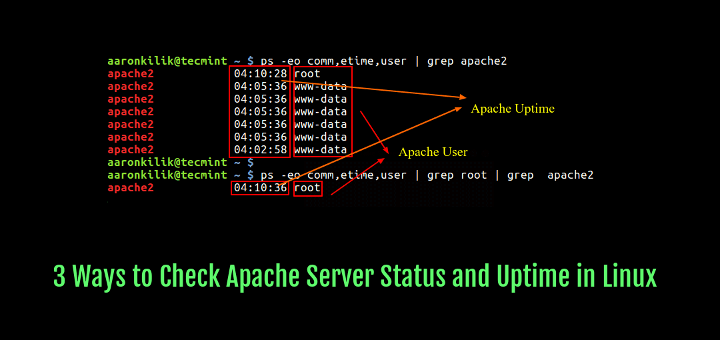
# ps -eo comm,etime,consumer | grep apache2 # ps -eo comm,etime,consumer | grep root | grep apache2 OR # ps -eo comm,etime,consumer | grep httpd # ps -eo comm,etime,consumer | grep root | grep httpd
The pattern output under reveals that the apache2 service has been working for 4 hours, 10 minutes, and 28 seconds (solely think about the one began by root).
Lastly, take a look at extra helpful Apache internet server guides:
On this article, we confirmed you three other ways to test Apache/HTTPD service uptime on a Linux system. In case you have any questions or ideas to share, try this by way of the remark part under.