Itemizing information is among the most generally undertaken duties by strange Linux customers and system directors. In Linux, the ls command, brief for “record” is used to record or show the contents of a listing.
This might both be your present listing or some other listing on the system. The command shows each information and subdirectories and normally distinguishes between completely different file varieties utilizing shade codes.
With none command-line choices, the ls command will merely record all of the listing contents. Nonetheless, it supplies an array of useful command-line choices to control the output and show the specified output.
On this article, we’ll be discussing the fundamentals of ls command examples with all of the out there numerous command choices that it supplies in Linux.
ls Command Choices in Linux
The ls command takes the next syntax:
$ ls [ options ] /path/to/listing
The choices part represents the command-line arguments that may be handed to control the output of the command.
On this tutorial, we are going to cowl the next ls command arguments.
| Choices | Description |
ls -m |
Lists listing contents separated by a comma. |
ls -Q |
Shows listing contents enclosed by citation marks. |
ls -l |
Shows information in a long-list format. |
ls -lh |
Show file measurement in a human-readable format. |
ls -g |
Omits group possession column. |
ls -F |
Provides a ahead slash to directories. |
ls -i |
Show inode variety of information and directories. |
ls -a |
Show all information together with hidden information. |
ls *. |
Filters information based on the file extension. |
ls -la |
Shows all information and directories in lengthy record format. |
ls -R |
Show information and directories recursively. |
ls -r |
Kind Recordsdata in reverse. |
ls -X |
Kind information alphabetically by file extension. |
ls -tl |
Show information based on file creation date and time. |
ls -n |
Checklist UIDs and GIDs. |
1. Checklist Recordsdata and Directories in Linux
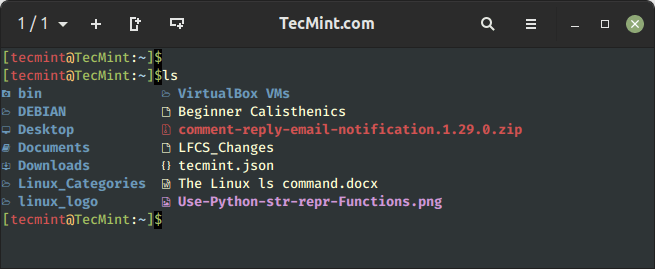
Working ls command with out passing any command-line choices or arguments, the ls command merely lists the listing contents in alphabetical order. Right here we received’t be capable of view particulars like file varieties, measurement, modified date and time, permission and hyperlinks, and so on.
$ ls
2. Lengthy Itemizing of Recordsdata in Linux
The -l command choice enables you to print out detailed details about the listing contents in a columnar format that features measurement, modified date and time, file or listing title and proprietor of the file, and its permission.
$ ls -l
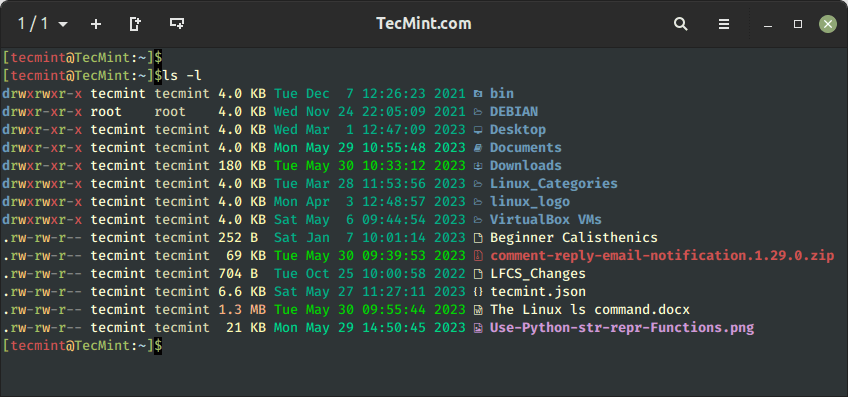
Ranging from the far left, we have now:
- 1st column – File/listing permissions.
- 2nd column – Variety of hyperlinks.
- third column – Title of the proprietor.
- 4th column – Title of the group that the file belongs to.
- fifth column – File measurement in bytes.
- sixth column to eighth column – Final modification date.
- ninth column – File / Listing title.
3. Checklist Hidden Recordsdata and Directories
Hidden information are particular information that retailer consumer settings and configuration information, that are utilized by working packages and providers for studying and storing info.
For instance. the .bashrc file is a script that incorporates consumer settings and configurations of the presently logged-in consumer, which embody command aliases, shell historical past, the coloring of the terminal font, and so on.
The .bash_logout file is executed once you sign off of your bash classes. It’s primarily used for cleanup functions i.e. finishing up any operations that must be carried out when you exit the bash shell.
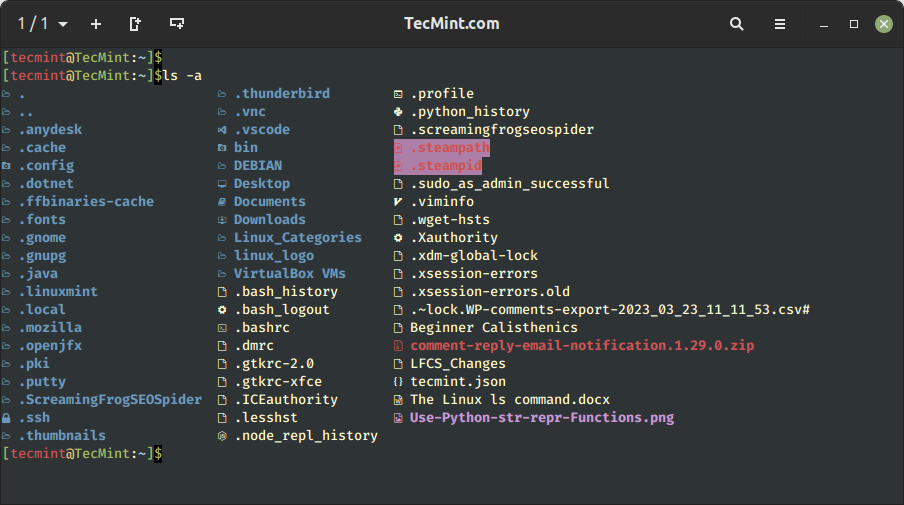
To record hidden information, move the -a choice as proven, which shows each hidden information and directories.
$ ls -a
4. Checklist All Recordsdata in Linux
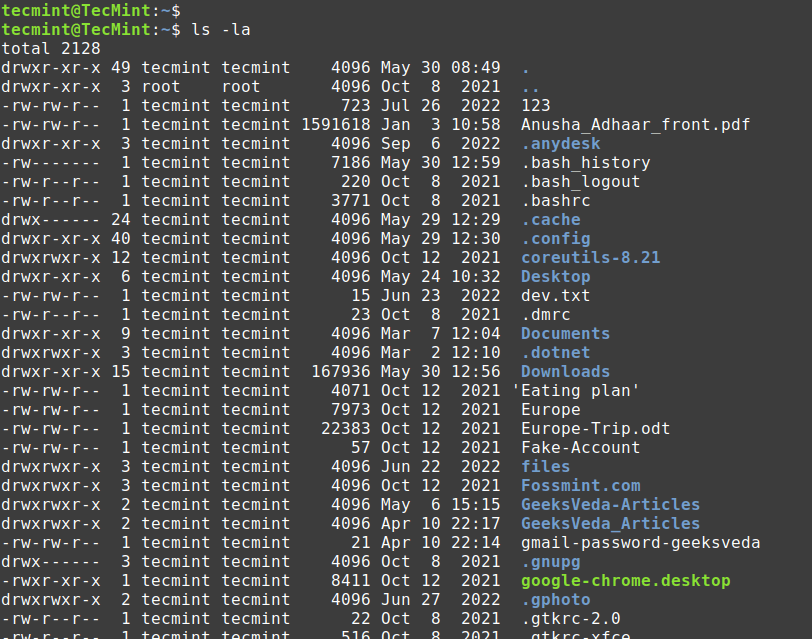
As you may have observed the -a choice not solely lists hidden information however all of the information and directories. For higher viewing, you should use the -la choice
$ ls -la
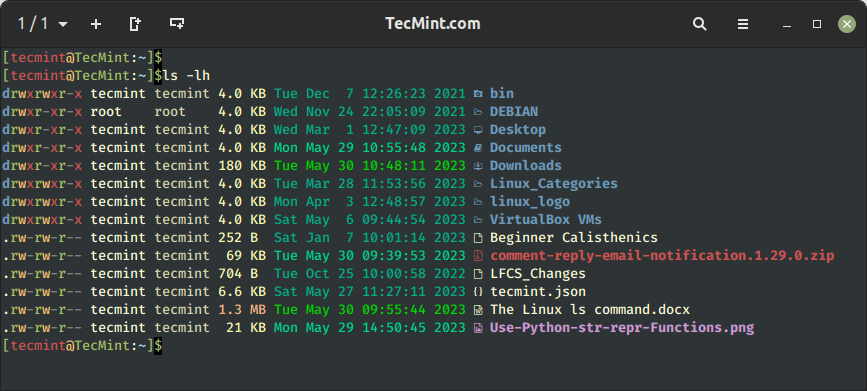
5. Show File Dimension in a Human-readable Format
To current the output in a greater format, add the -h flag to print the file measurement in a human-readable format. From the output, the file measurement is displayed in Kilobytes, Megabytes, and Gigabytes. By all means, this appears to be like extra presentable.
$ ls -lh
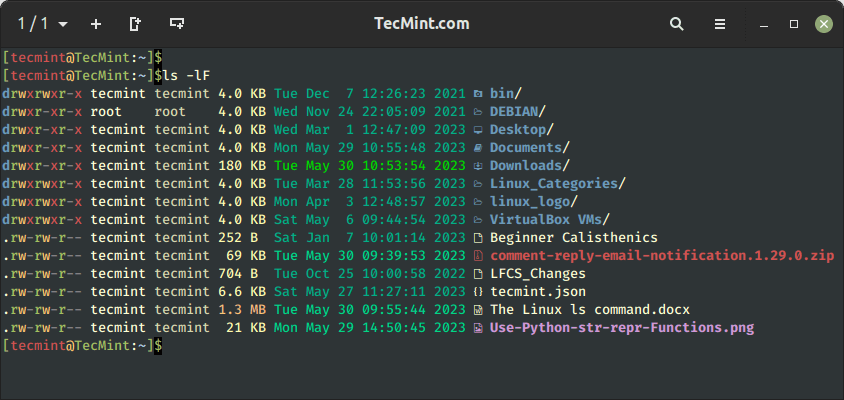
6. Distinguish Directories and Recordsdata in Linux
When working the ls command, it’s not at all times straightforward to make a transparent distinction between information and directories. The -F choice provides a ahead slash (/) to directories, making it simpler for them to face out from the remainder of the information.
$ ls -F
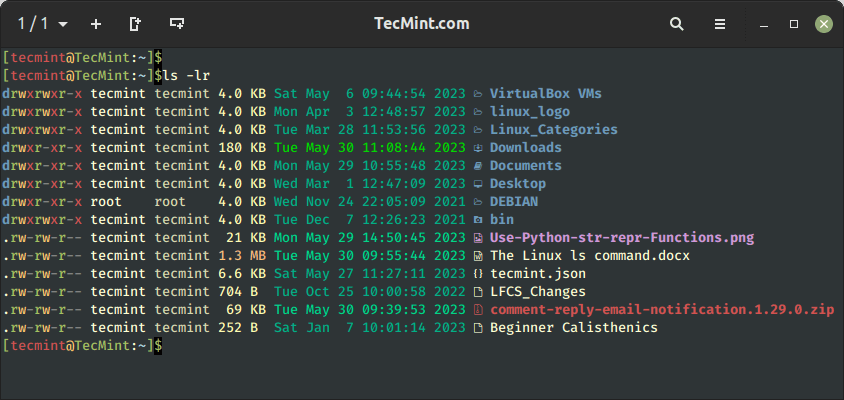
7. Sorting Recordsdata in Reverse Order
By default, the ls command kinds information and directories alphabetically (From A – Z). You possibly can choose to type the listing contents in reverse order utilizing the -r choice.
$ ls -lr
As well as, you’ll be able to type the file extensions alphabetically utilizing the -X flag.
$ ls -X
8. Checklist Recordsdata Recursively in Linux
The -R flag lists information recursively. First, the command lists all of the information and directories in your present listing, then proceeds to show information contained in particular person directories and subdirectories.
$ ls -R
Within the following instance, the information in particular person directories have been listed as nicely.
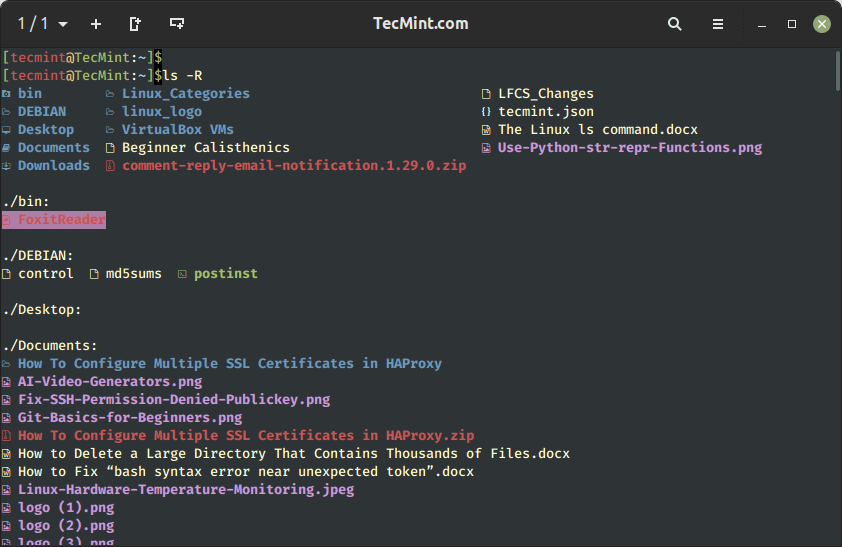
9. Kind Recordsdata By Modification Time in Linux
The ls -ltr command exhibits the information within the lengthy itemizing format in reverse sorted by modification time, which implies it’s going to show detailed details about every file or listing in reverse order based mostly on their final modified date/time stamp.
$ ls -ltr
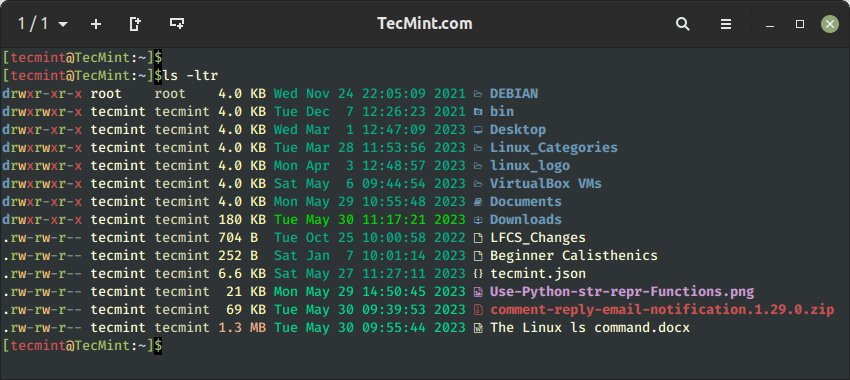
10. Kind Recordsdata By Latest to Oldest in Linux
You possibly can type information by time and date utilizing the -t choice, which kinds the information so as ranging from the latest to the oldest.
$ ls -tl
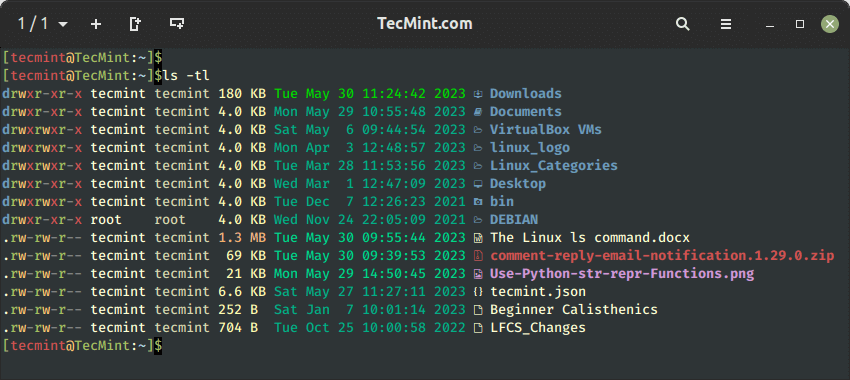
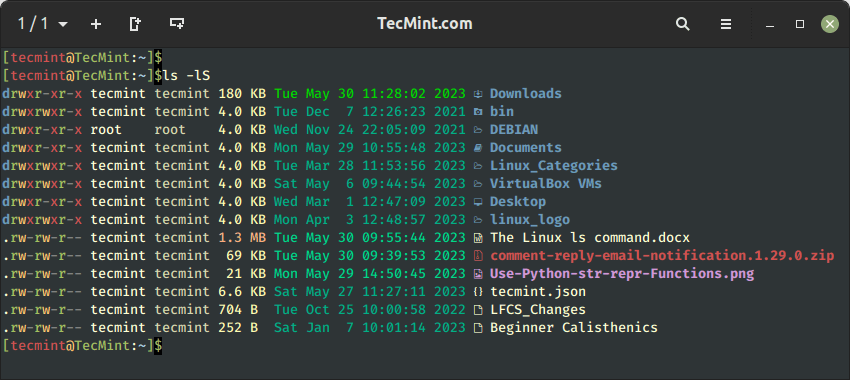
11. Kind Recordsdata by File Dimension in Linux
With a mix of -lS choice, it’s going to shows file measurement in descending order (greatest to smallest in measurement).
$ ls -lS
12. Checklist File Inode Quantity in Linux
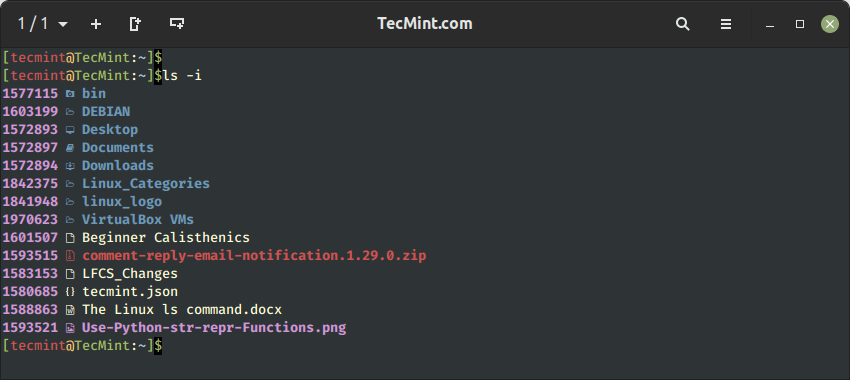
You possibly can show the information and directories’ inode numbers utilizing the -i choice as proven.
$ ls -i
13. Checklist Recordsdata and Directories Separated by Commas
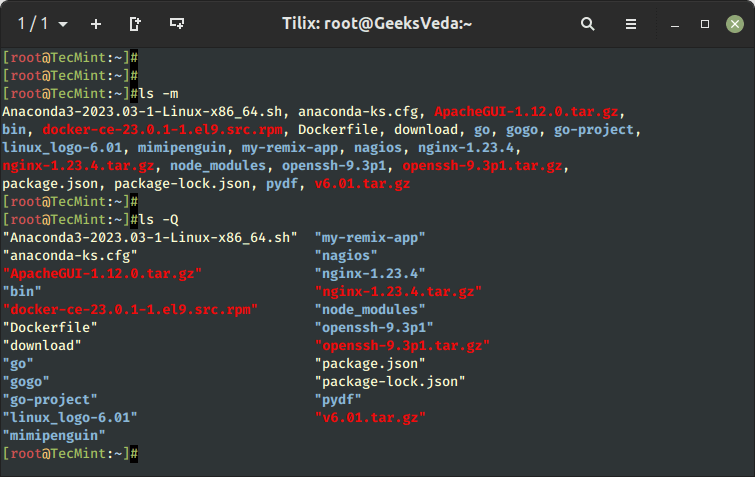
The -m flag lists the listing contents one after the opposite separated by a comma.
$ ls -m
With the -Q flag, all of the listing contents are enclosed by double citation marks as proven.
$ ls -Q
14. Omit Group Possession in a Lengthy-Checklist Format
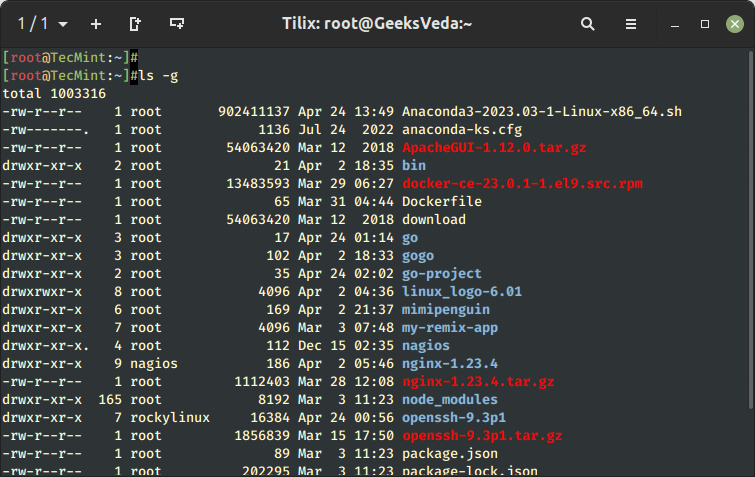
When used with the -l command choice, the ls command prints each consumer and group possession of the file. You possibly can choose to omit the group column by passing the -g choice.
$ ls -g
15. Checklist Particular File Varieties or Extensions
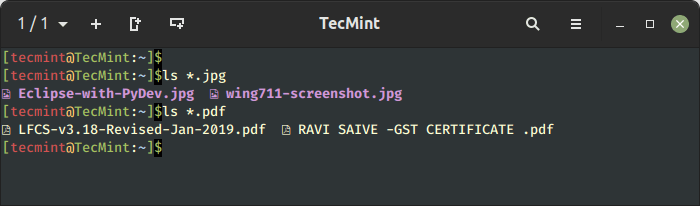
To record particular file varieties or extensions, use the wildcard notation (*) adopted by the file extension.
For instance, to show all information with a .jpg extension, run the command:
$ ls *.jpg
Equally, to record all PDF information, run the command:
$ ls *.pdf
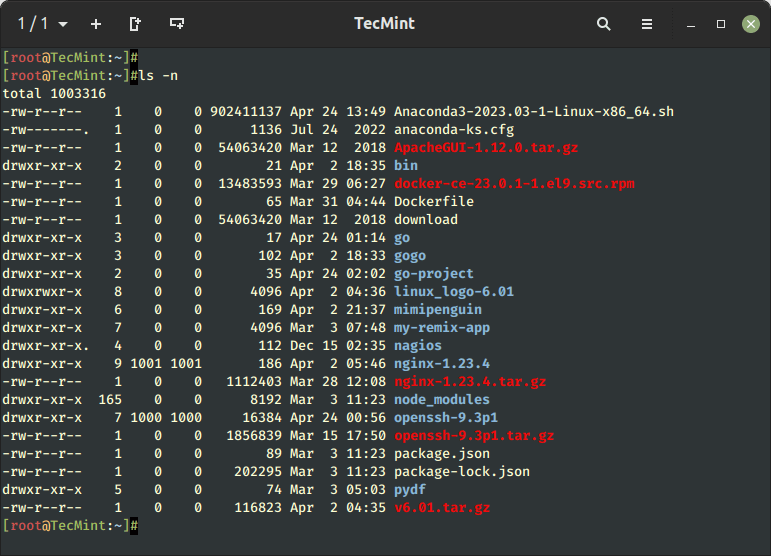
16. Checklist the UID and GID of Recordsdata
To show the UID and GID of information and directories, use the -n choice as proven.
$ ls -n
17. Examine ls Command Model
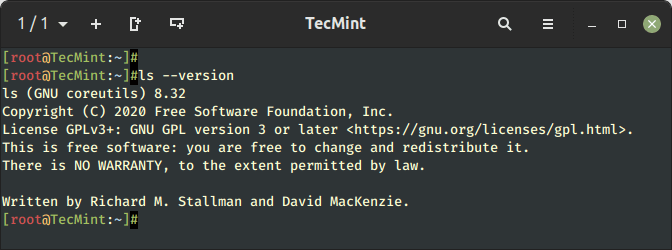
If you’re a bit of curious and need to test the model of the ls command, you are able to do in order follows:
$ ls --version
From the output, you’ll be able to see that we’re working ls model 9.1.
18. Present ls Command Assist Web page
The ls program supplies a wealth of command-line choices. What we have now lined are simply among the generally used ones. For a complete record of all of the command choices, run the next command:
$ ls --help
Optionally, you’ll be able to go to the person pages by working:
$ man ls
19. Checklist Listing Info in Linux
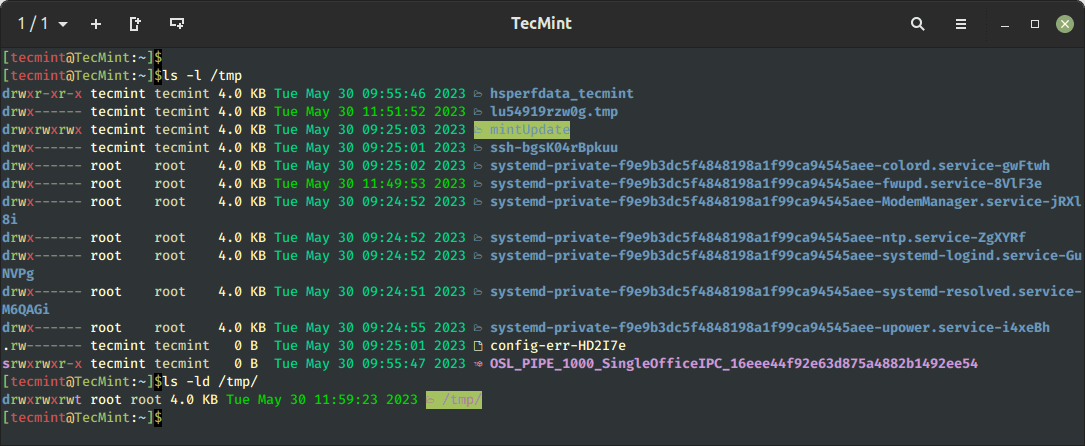
With the ls -l command record information underneath listing /tmp. Whereby with -ld choices, it’s going to show info of the /tmp listing.
$ ls -l /tmp $ ls -ld /tmp/
20. Create ls Command Aliase
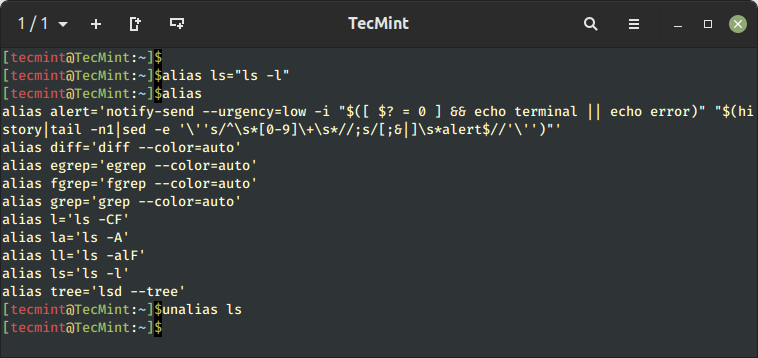
We’ve got made an alias for the ls command once we execute the ls command it’s going to take the -l choice by default and show an extended itemizing as talked about earlier.
$ alias ls="ls -l"
To view quite a few aliases out there in your system, use the beneath alias command and the identical will be unalias as proven beneath instance.
$ alias
To take away an alias beforehand outlined, simply use the unalias command.
$ unalias ls
On this information, we have now demonstrated the best way to use the ls command to view the contents of a folder or listing. As well as, we went a step additional and explored command choices that can be utilized with the ls command in Linux.
In our subsequent article, we’ll cowl extra superior ls instructions with their examples. Additionally, I counsel you undergo some interview questions on the ls command, and likewise if we’ve missed something within the record, please replace us by way of the remark part.