Rsync (Distant Sync) is probably the most generally used command for copying and synchronizing recordsdata and directories remotely in addition to regionally in Linux/Unix methods.
With the assistance of the rsync command, you possibly can copy and synchronize your knowledge remotely and regionally throughout directories, disks, and networks, carry out knowledge backups, and mirror between two Linux machines.

This text explains 16 fundamental and superior makes use of of the rsync command to switch your recordsdata remotely and regionally in Linux-based machines. You don’t should be a root consumer to run the rsync command.
Benefits of Rsync Command
It gives a number of benefits, together with:
- Environment friendly File Switch – rsync makes use of a delta switch algorithm, which implies it solely transfers the variations between supply and vacation spot recordsdata, which considerably reduces the quantity of knowledge transferred, making it environment friendly for syncing giant recordsdata or directories.
- Distant File Synchronization – rsync helps each native and distant file transfers over SSH, which permits synchronization between native and distant methods or mirroring directories throughout a number of machines.
- Incremental Backups – rsync is well-suited for incremental backups, because it create and replace backups effectively by transferring solely new or modified recordsdata.
- Preserves File Permissions – rsync can protect numerous file attributes, similar to permissions, possession, timestamps, and symbolic hyperlinks, which ensures that the copied recordsdata retain their unique traits on the vacation spot.
- Bandwidth Management – rsync means that you can restrict the bandwidth utilization throughout file transfers, because it makes use of compression and decompression methodology whereas sending and receiving knowledge on each ends.
- Quicker – rsync may be sooner than scp (Safe Copy) for transferring recordsdata, particularly when syncing giant directories or when coping with recordsdata which have already been partially transferred or exist on the vacation spot.
Rsync Command Syntax
The rsync command follows the next syntax:
# rsync [OPTIONS] SOURCE DESTINATION
Right here’s an evidence of the totally different parts and choices used with rsync instructions:
-v– Verbose output, displaying detailed details about the switch.-r– copies knowledge recursively (however doesn’t protect timestamps and permission whereas transferring knowledge.-a– archive mode, which permits copying recordsdata recursively and it additionally preserves symbolic hyperlinks, file permissions, consumer & group ownerships, and timestamps.-z– Compress recordsdata throughout switch to cut back community utilization.-h– human-readable, output numbers in a human-readable format.-P– Present progress in the course of the switch.SOURCE– Specifies the supply file(s) or listing to be transferred, which generally is a native or a distant location.DESTINATION– Specifies the vacation spot path the place the recordsdata or directories will likely be copied. Just like the supply, it may be a neighborhood path or a distant location.
Set up Rsync in Linux System
We are able to set up the rsync package deal with the assistance of the next package deal supervisor as per your Linux distribution.
$ sudo apt set up rsync [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum set up rsync [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/rsync [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add rsync [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S rsync [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper set up rsync [On OpenSUSE]
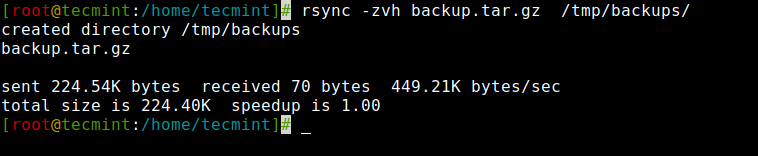
1. Copy/Sync File Domestically
To repeat or sync a file regionally, you should use the next command that can sync a single file on a neighborhood machine from one location to a different location.
Right here on this instance, a file title backup.tar must be copied or synced to /tmp/backups/ folder.
[[email protected]]# rsync -zvh backup.tar.gz /tmp/backups/ created listing /tmp/backups backup.tar.gz despatched 224.54K bytes obtained 70 bytes 449.21K bytes/sec whole measurement is 224.40K speedup is 1.00
Within the above instance, you possibly can see that if the vacation spot is just not already existed rsync will create a listing robotically for the vacation spot.
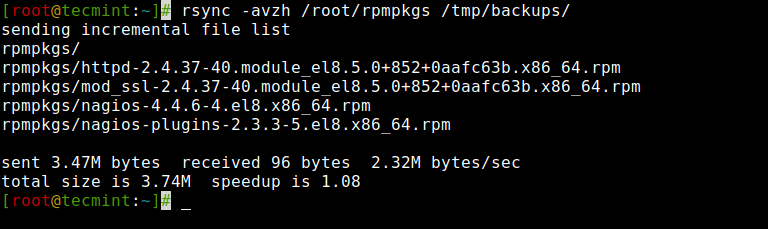
2. Copy/Sync Listing Domestically
The next command will switch or sync all of the recordsdata from one listing to a distinct listing in the identical machine.
Right here on this instance, /root/rpmpkgs incorporates some rpm package deal recordsdata and also you need that listing to be copied inside /tmp/backups/ folder.
[[email protected]]# rsync -avzh /root/rpmpkgs /tmp/backups/ sending incremental file listing rpmpkgs/ rpmpkgs/httpd-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/mod_ssl-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/nagios-4.4.6-4.el8.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/nagios-plugins-2.3.3-5.el8.x86_64.rpm despatched 3.47M bytes obtained 96 bytes 2.32M bytes/sec whole measurement is 3.74M speedup is 1.08
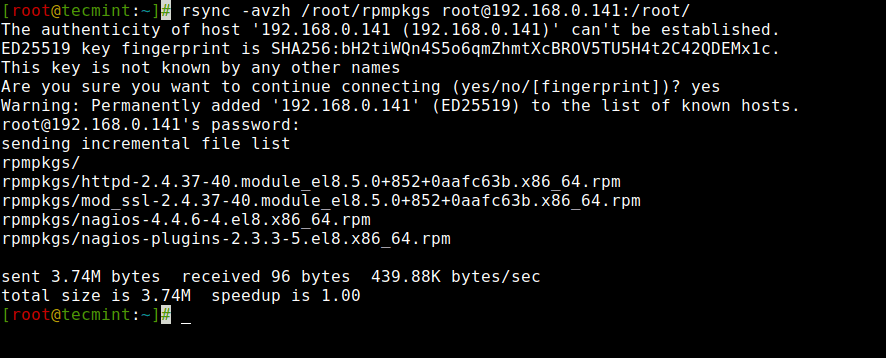
3. Copy a Listing from Native to Distant Server
To repeat a listing from a neighborhood server to a distant server, you should use the next command, which can sync a listing from a neighborhood to a distant machine.
For instance, if there’s a folder in your native laptop “rpmpkgs” that incorporates some RPM packages and in order for you that native listing’s content material sends to a distant server, you should use the next command.
# rsync -avzh /root/rpmpkgs [email protected]:/root/ The authenticity of host '192.168.0.141 (192.168.0.141)' cannot be established. ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:bH2tiWQn4S5o6qmZhmtXcBROV5TU5H4t2C42QDEMx1c. This key is just not recognized by some other names Are you positive you wish to proceed connecting (sure/no/[fingerprint])? sure Warning: Completely added '192.168.0.141' (ED25519) to the listing of recognized hosts. [email protected]'s password: sending incremental file listing rpmpkgs/ rpmpkgs/httpd-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/mod_ssl-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/nagios-4.4.6-4.el8.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/nagios-plugins-2.3.3-5.el8.x86_64.rpm despatched 3.74M bytes obtained 96 bytes 439.88K bytes/sec whole measurement is 3.74M speedup is 1.00
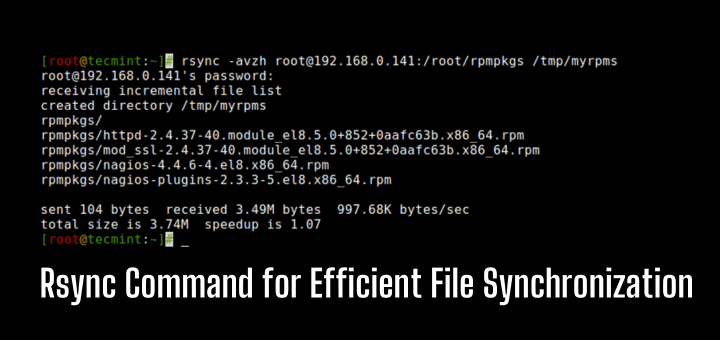
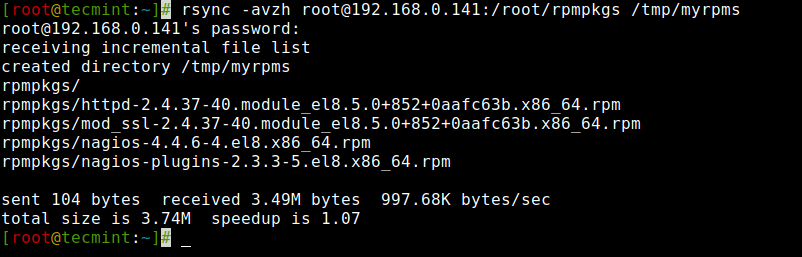
4. Copy a Listing from Distant to Native Server
This command will allow you to sync a distant listing to a neighborhood listing. Right here on this instance, a listing /root/rpmpkgs which is on a distant server is being copied into your native laptop in /tmp/myrpms.
# rsync -avzh [email protected]:/root/rpmpkgs /tmp/myrpms [email protected]'s password: receiving incremental file listing created listing /tmp/myrpms rpmpkgs/ rpmpkgs/httpd-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/mod_ssl-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/nagios-4.4.6-4.el8.x86_64.rpm rpmpkgs/nagios-plugins-2.3.3-5.el8.x86_64.rpm despatched 104 bytes obtained 3.49M bytes 997.68K bytes/sec whole measurement is 3.74M speedup is 1.07
5. Rsync Over SSH
With rsync, we will use SSH (Safe Shell) for knowledge switch, utilizing SSH protocol whereas transferring our knowledge you may be ensured that your knowledge is being transferred in a secured reference to encryption in order that no one can learn your knowledge whereas it’s being transferred over the wire on the web.
Additionally after we use rsync we have to present the consumer/root password to perform that specific process, so utilizing the SSH choice will ship your logins in an encrypted method in order that your password will likely be protected.
To make use of rsync over SSH, you should use the -e choice to specify the distant shell command, which is often ssh as proven.
# rsync [OPTIONS] -e ssh /path/to/supply [email protected]:/path/to/vacation spot
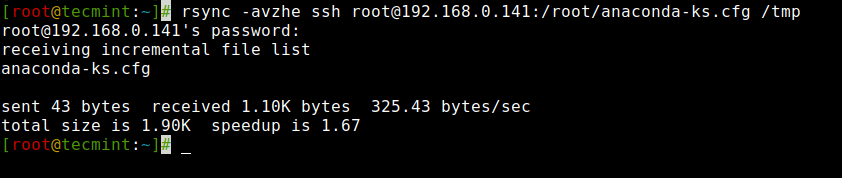
6. Copy a File from a Distant Server to a Native Server with SSH
To synchronize a file from a distant server to a neighborhood server, you possibly can specify a protocol with rsync utilizing the “-e” choice with the protocol title you wish to use.
Right here on this instance, We will likely be utilizing the “ssh” with the “-e” choice and carry out knowledge switch.
# rsync -avzhe ssh [email protected]:/root/anaconda-ks.cfg /tmp [email protected]'s password: receiving incremental file listing anaconda-ks.cfg despatched 43 bytes obtained 1.10K bytes 325.43 bytes/sec whole measurement is 1.90K speedup is 1.67
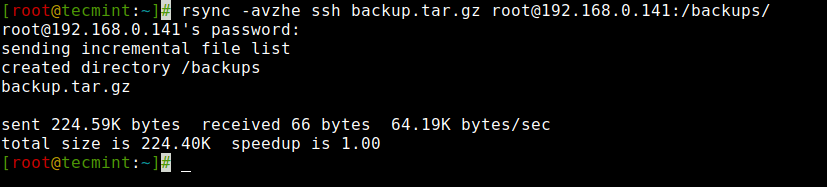
7. Copy a File from a Native Server to a Distant Server with SSH
To synchronize a file from a neighborhood server to a distant server utilizing SSH, you possibly can leverage the next command as proven.
# rsync -avzhe ssh backup.tar.gz [email protected]:/backups/ [email protected]'s password: sending incremental file listing created listing /backups backup.tar.gz despatched 224.59K bytes obtained 66 bytes 64.19K bytes/sec whole measurement is 224.40K speedup is 1.00
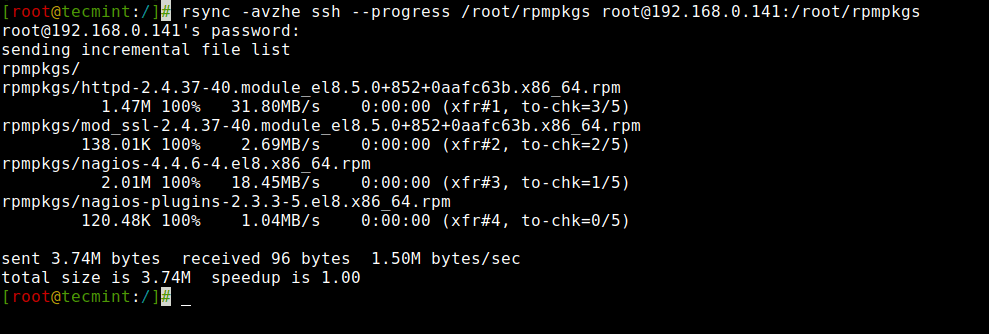
8. Present Progress Whereas Transferring Information with Rsync
To indicate the progress whereas transferring the info from one machine to a distinct machine, we will use the ‘--progress' choice, which shows the recordsdata and the time remaining to finish the switch.
# rsync -avzhe ssh --progress /root/rpmpkgs [email protected]:/root/rpmpkgs [email protected]'s password: sending incremental file listing rpmpkgs/ rpmpkgs/httpd-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm 1.47M 100% 31.80MB/s 0:00:00 (xfr#1, to-chk=3/5) rpmpkgs/mod_ssl-2.4.37-40.module_el8.5.0+852+0aafc63b.x86_64.rpm 138.01K 100% 2.69MB/s 0:00:00 (xfr#2, to-chk=2/5) rpmpkgs/nagios-4.4.6-4.el8.x86_64.rpm 2.01M 100% 18.45MB/s 0:00:00 (xfr#3, to-chk=1/5) rpmpkgs/nagios-plugins-2.3.3-5.el8.x86_64.rpm 120.48K 100% 1.04MB/s 0:00:00 (xfr#4, to-chk=0/5) despatched 3.74M bytes obtained 96 bytes 1.50M bytes/sec whole measurement is 3.74M speedup is 1.00
9. Embrace Information with Specific Extension with Rsync
To incorporate particular recordsdata or patterns throughout a rsync operation, you should use the --include choice with an extension that matches all recordsdata.
# rsync -avz --include="*.txt" /path/to/supply/ [email protected]:/path/to/vacation spot/
Within the supplied instance, rsync will embrace solely recordsdata with the .txt extension from the /path/to/supply/ listing in the course of the switch.
10. Exclude Information with Specific Extension with Rsync
Equally, to exclude a particular extension throughout a rsync operation, you should use the --exclude choice with a wildcard sample.
# rsync -avz --exclude="*.ext" /path/to/supply/ [email protected]:/path/to/vacation spot/
Within the supplied instance, rsync will exclude recordsdata with the desired extension (*.ext) in the course of the switch, whereas together with all different recordsdata and directories.
11. Embrace and Exclude Information with Rsync
To incorporate and exclude particular recordsdata or patterns throughout a rsync operation, you should use each the --include and --exclude choices with acceptable wildcard patterns.
These two choices enable us to embrace and exclude recordsdata by specifying parameters these choice helps us to specify these recordsdata or directories which you wish to embrace in your sync and exclude recordsdata and folders with which you don’t wish to be transferred.
Right here on this instance, the rsync command will embrace these recordsdata and directories solely which begins with ‘R’ and exclude all different recordsdata and directories.
# rsync -avze ssh --include 'R*' --exclude '*' [email protected]:/var/lib/rpm/ /root/rpm
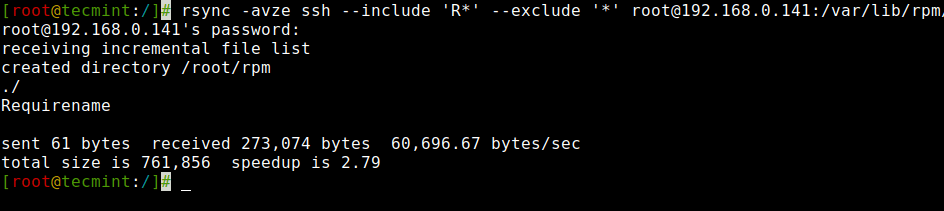
12. Use of –delete Possibility with Rsync
If a file or listing doesn’t exist on the supply, however already exists on the vacation spot, you would possibly wish to delete that current file/listing on the goal whereas syncing.
We are able to use the ‘--delete‘ choice to delete recordsdata that aren’t there within the supply listing.
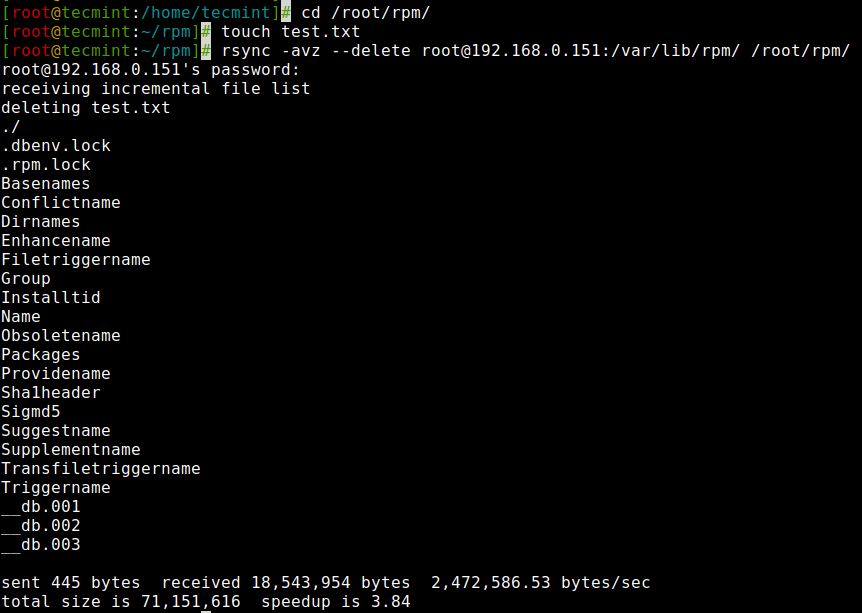
The supply and goal are in sync. Now create a brand new file take a look at.txt on the goal.
[[email protected]:~]# cd /root/rpm/ [[email protected]:~/rpm]# contact take a look at.txt [[email protected]:~/rpm]# rsync -avz --delete [email protected]:/var/lib/rpm/ /root/rpm/ [email protected]'s password: receiving incremental file listing deleting take a look at.txt ./ .dbenv.lock .rpm.lock Basenames Conflictname Dirnames Enhancename Filetriggername Group Installtid Identify Obsoletename Packages Providename Sha1header Sigmd5 Suggestname Supplementname Transfiletriggername Triggername __db.001 __db.002 __db.003 despatched 445 bytes obtained 18,543,954 bytes 2,472,586.53 bytes/sec whole measurement is 71,151,616 speedup is 3.84
Goal has the brand new file known as take a look at.txt when synchronizing with the supply with the ‘–delete‘ choice, it eliminated the file take a look at.txt.
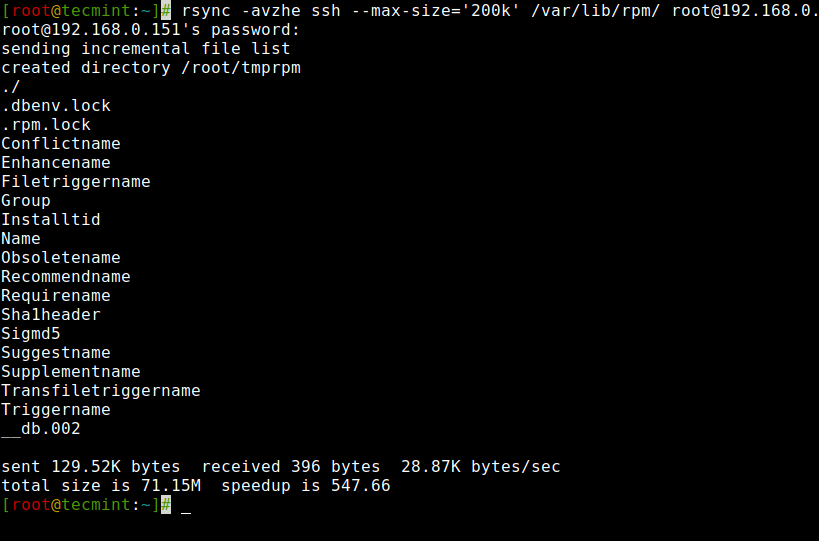
13. Set File Switch Restrict with Rsync
You possibly can specify the Max file measurement to be transferred or synced. You are able to do it with the “--max-size” choice. Right here on this instance, the Max file measurement is 200k, so this command will switch solely these recordsdata that are equal to or smaller than 200k.
# rsync -avzhe ssh --max-size="200k" /var/lib/rpm/ [email protected]:/root/tmprpm [email protected]'s password: sending incremental file listing created listing /root/tmprpm ./ .dbenv.lock .rpm.lock Conflictname Enhancename Filetriggername Group Installtid Identify Obsoletename Recommendname Requirename Sha1header Sigmd5 Suggestname Supplementname Transfiletriggername Triggername __db.002 despatched 129.52K bytes obtained 396 bytes 28.87K bytes/sec whole measurement is 71.15M speedup is 547.66
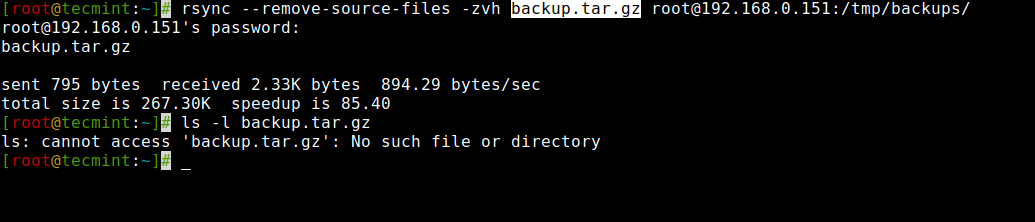
14. Mechanically Delete Supply Information After Switch
Now, suppose you’ve gotten the primary net server and a knowledge backup server, you created a each day backup and synced it together with your backup server, however now you don’t wish to hold that native copy of the backup in your net server.
So, will you watch for the switch to finish after which delete that native backup file manually? Of Course NO. This computerized deletion may be completed utilizing the ‘--remove-source-files‘ choice.
# rsync --remove-source-files -zvh backup.tar.gz [email protected]:/tmp/backups/ [email protected]'s password: backup.tar.gz despatched 795 bytes obtained 2.33K bytes 894.29 bytes/sec whole measurement is 267.30K speedup is 85.40 [[email protected]:~]# ls -l backup.tar.gz ls: can't entry 'backup.tar.gz': No such file or listing
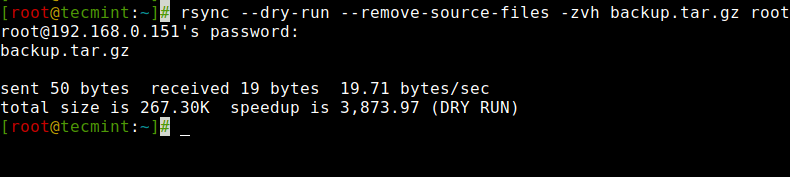
15. Do a Dry Run with Rsync
If you’re a beginner utilizing rsync and don’t know what precisely your command going to do. Rsync might actually mess up the issues in your vacation spot folder after which doing an undo generally is a tedious job.
Use of this selection won’t make any adjustments to the recordsdata and exhibits the output of the command, if the output exhibits precisely the identical as you wish to do then you possibly can take away the ‘--dry-run‘ choice out of your command and run on the terminal.
# rsync --dry-run --remove-source-files -zvh backup.tar.gz [email protected]:/tmp/backups/ [email protected]'s password: backup.tar.gz despatched 50 bytes obtained 19 bytes 19.71 bytes/sec whole measurement is 267.30K speedup is 3,873.97 (DRY RUN)
16. Rsync Set Bandwidth Restrict and Switch File
You possibly can set the bandwidth restrict whereas transferring knowledge from one machine to a different machine with the assistance of ‘--bwlimit‘ choice. This selection helps us to restrict I/O bandwidth.
# rsync --bwlimit=100 -avzhe ssh /var/lib/rpm/ [email protected]:/root/tmprpm/ [email protected]'s password: sending incremental file listing despatched 324 bytes obtained 12 bytes 61.09 bytes/sec whole measurement is 38.08M speedup is 113347.05
Additionally, by default rsync syncs modified blocks and bytes solely, in order for you explicitly wish to sync the entire file you then use the ‘-W‘ choice with it.
# rsync -zvhW backup.tar /tmp/backups/backup.tar backup.tar despatched 14.71M bytes obtained 31 bytes 3.27M bytes/sec whole measurement is 16.18M speedup is 1.10
Conclusion
That concludes our overview of rsync and its capabilities. For additional exploration of its intensive choices and functionalities, I encourage you to check with the great handbook pages (man pages) out there.